The research carried out by the Politecnico di Torino shows that space flight ages astronauts’ heart
Credit: Politecnico di Torino
Human spaceflight has been fascinating man for centuries, representing the intangible need to explore the unknown, challenge new frontiers, advance technology and push scientific boundaries further. A key aspect of long-term human spaceflight is the physiological response and the consequent microgravity (0G) adaptation, which has all the features of accelerated aging involving almost every body system: muscle atrophy and bone loss, onset of balance and coordination problems, loss of functional capacity of the cardiovascular system.
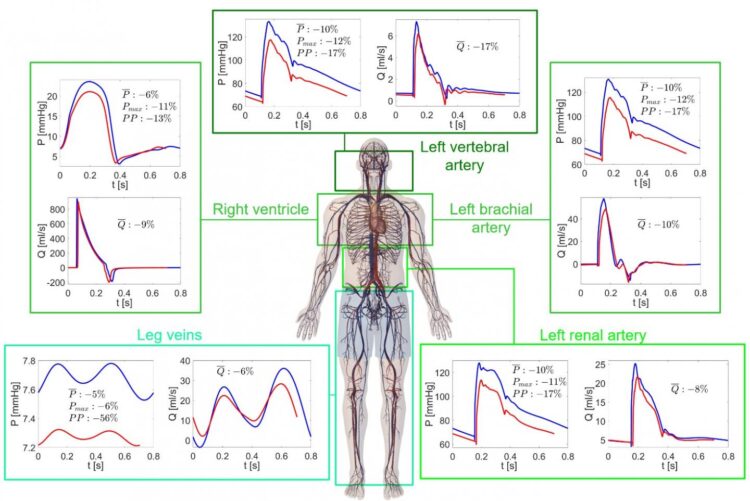
A research published in recent days in npj Microgravity – a prestigious journal of the Nature group “Cardiovascular deconditioning during long-term spaceflight through multiscale modeling”) – and conducted by Caterina Gallo, Luca Ridolfi and Stefania Scarsoglio shows that human spaceflight reduces exercise tolerance and ages astronauts’ heart.
The study is based on a mathematical model which allowed to investigate some spaceflight mechanisms inducing cardiovascular deconditioning, that is the adaptation of the cardiovascular system to a less demanding environment.
Understanding 0G configuration is crucial to ensure the full health and well-being of astronauts in view of the now imminent missions to the Moon and Mars. Moreover, since spaceflight deconditioning has features similar to accelerated aging, gravitational physiology may lead to useful insights to delay or prevent the modern lifestyle medical disorders related with living longer.
The proposed study compared the cardiovascular response in microgravity (0G) conditions with what happens on Earth: several hemodynamic parameters – such as cardiac work, oxygen consumption and contractility indexes, as well as arterial pressure – were reduced. Exercise tolerance of a spaceflight traveler was found to be comparable to an untrained person with a sedentary lifestyle. At the capillary-venous level significant waveform alterations were observed which can modify the regular perfusion and average nutrient supply at the cellular level.
“Present findings” professor Scarsoglio observes “are useful to design future long-term spaceflights, individuate optimal countermeasures and understand the state of health of astronauts when prompt physical capacity at the time of restoration of partial gravity (e.g., Moon/Mars landing) is required”.
###
Media Contact
Relazioni Media
[email protected]