Credit: Kiyonobu Nagaya, Department of Physics, Kyoto University
Researchers at Japan's Tohoku University are investigating novel ways by which electrons are knocked out of matter. Their research could have implications for radiation therapy.
Exposing a small cluster of neon atoms to a very short and intense burst of extreme ultraviolet light initiates a novel mechanism that produces a large number of electrons and ions.
A team of researchers led by physical chemist Kiyoshi Ueda of Tohoku University used a free electron laser (FEL) at Japan's SPring-8 Compact SASE Source test accelerator to investigate how electrons are 'knocked out' of neon atom clusters. Intense extreme ultraviolet FEL pulses were directed at the clusters and the resultant energy distribution of electrons knocked out of the clusters was measured using a 'velocity map imaging spectrometer'.
Electrons inside a material absorb energy when the material is exposed to light. Normally, this energy is used to 'knock electrons out' of the material. This can only happen, however, if the energy of the light particle, or 'photon', absorbed by the electron is higher than the amount of energy needed by the material, or its 'work function', to eject the electron. In 1921, Albert Einstein won a Nobel Prize for describing this 'photoelectric effect'.
The team tested what would happen when they set the photon energy of the FEL light below the work function of clusters of neon atoms. Instead of being knocked out, when an electron tightly bound to a neon atom absorbs the lower energy photon, it becomes loosely bound, causing the atom to become 'excited'. Since the FEL pulse is so intense, many electrons become loosely bound in the clusters at the same time; meaning many atoms become excited. Electrons are then knocked out of the clusters even though the photon energy is below their work function.
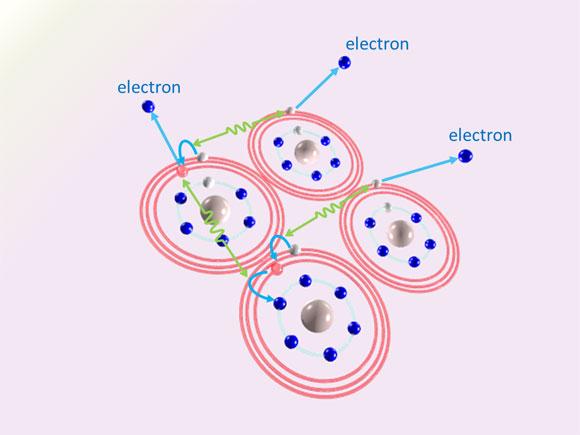
The team discovered that loosely bound electrons are knocked out of the clusters in a novel 'cascading' process.
The process begins when an atom with a loosely bound electron interacts with a nearby atom that also has a loosely bound electron. The first transfers energy to its neighbour, which 'knocks down' its own loosely bound electron hovering in a 'high-energy' orbit into a 'low-energy' orbit closer to the atom's core. At the same time, the energy transferred to the neighbouring atom knocks a loosely bound electron out of it. The first atom, which is now 'less excited', then interacts with another neighbouring excited atom, also giving it energy and thus 'de-exciting' itself even further while knocking an electron out of another neighbour. This cascading process occurs in many pairs of excited atoms, resulting in the emission of a large number of low-energy electrons.
"The cascades of knocking electrons out and down produce more electrons and more ions, damaging the sample more. I am convinced these cascades might play a crucial role in future radiation therapy," says Lorenz Cederbaum of Germany's Heidelberg University, one of the study's co-authors.
The release of low-energy electrons exposed to intense light can damage DNA. This concept is used in cancer radiation therapy. The findings could have implications for the use of radiation therapy in the future.
The researchers published their findings in the journal Nature Communications.
###
Media Contact
Kiyoshi Ueda
[email protected]
81-222-175-481
@TohokuUniPR
http://www.tohoku.ac.jp/en/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag