Administering a smaller, less toxic dose of DOX, along with intravenous perfluocarbon, shows tumor regression, reduces recurrence, and is less invasive than common treatments
Credit: Jonah S. Harmon
WASHINGTON, September 8, 2020 — Hepatocellular carcinoma is a particularly stubborn form of cancer with few treatments and a high mortality rate. It is usually treated by blocking the flow of blood to the tumor to induce cancer cell death. The common treatment, transarterial chemoembolization, is invasive and too imprecise to be a local drug delivery method.
Aiming to increase the precision, researchers at Tulane University created a combination treatment that involves vaporizing tiny droplets of perfluorocarbon, a common organic material composed of carbon and fluorine that is used in pharmaceuticals, anesthetics, and industrial fluids. The method of gas embolization, published in APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, is relatively new, and it is the authors’ specialty.
“By changing the treatment parameters in this paper, we were able to achieve tumor regression, and by combining our method with chemotherapy, we were able to reduce regrowth following treatment,” author Joseph Bull said. “Gas embolization has never been used in patients. Demonstrating that it can induce tumor regression is really new. We’re very excited about the work in this paper.”
Their study tested gas embolization alone and in combination with two common cancer drugs, doxorubicin (DOX) and tirapazamine. Gas embolization stops blood flow to the tumor, and it was highly effective used in combination with DOX.
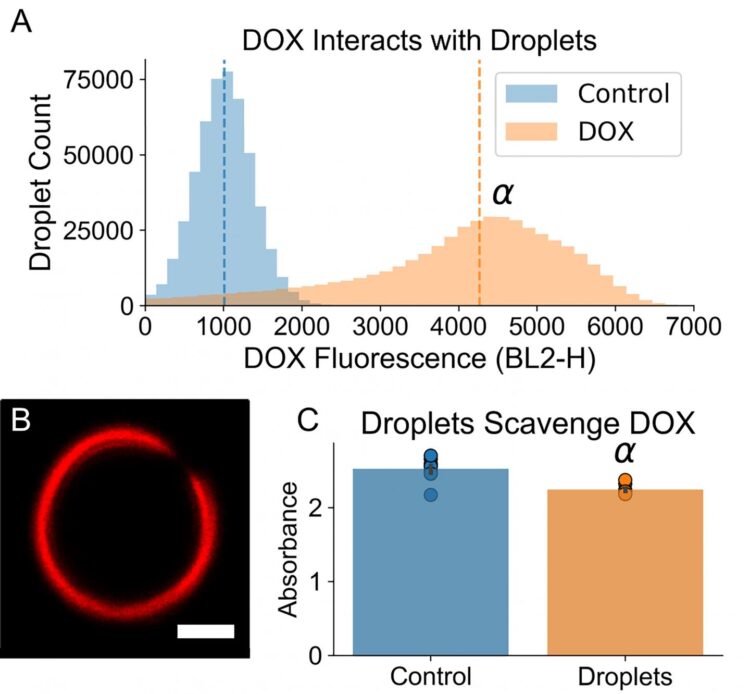
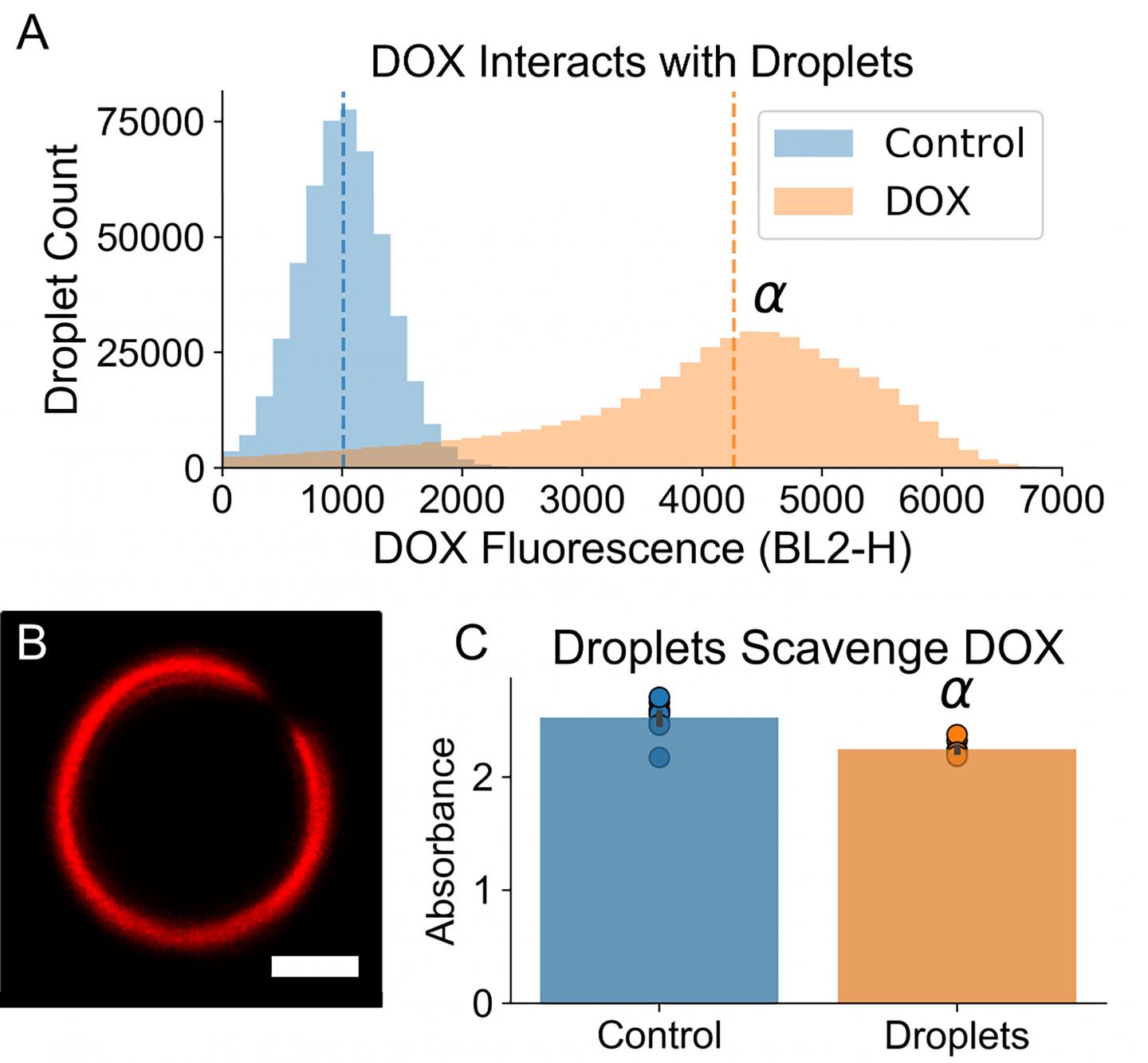
In the gas embolization method, perfluorocarbon liquid is administered intravenously, and it interacts with DOX that has been administered in the body. DOX binds to the surface of the droplets of liquid, which are small enough to travel through capillaries and do not cause blood vessel blockage until they are vaporized, so treatment can be applied at the specific site of the tumor.
To turn these tiny liquid droplets into microbubbles and cut off the blood flow to the tumor, ultrasound is applied from outside the body. The fluid mechanical interface of the droplet focuses the ultrasound in a cavitationlike event, in which gas bubbles inside the liquid droplet grow due to a drop in pressure, until the droplet turns completely into microbubbles.
The drug DOX binds to the shell of the droplet, and the medicine becomes available to diffuse into the tumor, while the microbubbles cut off blood supply to the tumor.
The combination of gas embolization and DOX was so effective that, on average, tumors shrank to 2.9% of their initial size, while using DOX alone slowed tumor growth but still allowed them to grow to 300% of their initial size.
###
The article, “Combined gas embolization and chemotherapy can result in complete tumor regression in a murine hepatocellular carcinoma model,” is authored by Jonah S. Harmon, Foad Kabinejadian, and Joseph L. Bull. The article appears in APL Bioengineering on Sept. 8, 2020 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0005329) and be accessed at https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Bioengineering is an open access journal publishing significant discoveries specific to the understanding and advancement of physics and engineering of biological systems. See http://aip.
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.