Credit: Courtesy photo
The U.S. Army partnered with the University of Pittsburg Medical Center to create a biocontainment unit that could help healthcare workers caring for COVID-19 patients.
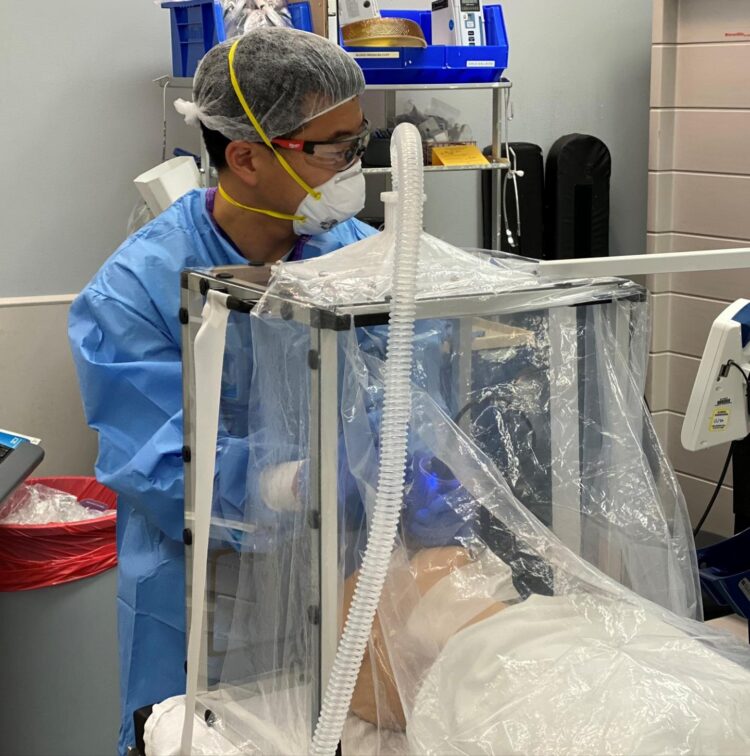
Researchers from the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command’s Army Research Laboratory and UPMC created an individual biocontainment unit that uses negative pressure to suction the air from around a patient and filter out viral particles. This prevents environmental contamination and limits exposure to SARS-CoV-2.
“Outside of the current pandemic, the IBU could be rapidly deployed to isolate patients with any respiratory illness.” said study co-author Dr. David Turer, a plastic surgeon who recently completed his residency at UPMC. “It’s easy to see this technology used to contain influenza, MERS, or tuberculosis, particularly in places lacking advanced hospital infrastructure.”
The device and the results of safety testing are described in a study published today in the Annals of Emergency Medicine. This research was first reported by the Army in April during an effort to identify solutions to help combat the spread of COVID-19.
At that time, initial approaches to minimize viral spread involved the use of plexiglass barriers, such as intubation boxes, to limit healthcare worker exposure when inserting a breathing tube down a patient’s throat. While these barriers may mitigate exposure to larger droplets, the research team hypothesized that they do little to stop the spread of smaller aerosolized viral particles.
Army researcher and study co-author, Dr. Cameron Good and Turer, along with a team of colleagues, developed prototype IBUs and tested them by performing simulated medical procedures. Using validated techniques adopted from the medical research laboratory community, they tested the IBU and a plexiglass intubation box for their ability to contain virus-sized particles from a simulated COVID-19 patient.
“Greater than 99.99% of the virus-sized aerosols were trapped by the IBU and prevented from escaping into the room,” Good said. “When we tested the passive intubation box, we observed more than three times the aerosol concentration outside the box–where the healthcare provider is located–than inside the box. It is not safe to use these intubation boxes without actively filtering the air.”
The Food and Drug Administration recently revoked an emergency use authorization for passive plexiglass intubation barriers and mandated the use of negative pressure systems, such as the IBU, to prevent viral spread.
The team is actively developing a portable vacuum and filter system that can run on a battery pack for use in austere environments where energy resources are limited, which is of particular interest for military and humanitarian applications.
“The ability to isolate COVID-19 patients at the bedside is key to stopping viral spread in medical facilities and onboard military ships and aircraft, particularly to limit transmission through close quarters or shared ventilation systems,” Good said.
The FDA is considering a recently submitted emergency use authorization. Once granted, hospitals and military units will be able to use IBUs immediately to protect healthcare workers caring for COVID-19 patients and to prepare for future surges.
“None of this would have been possible without the extremely dedicated clinicians and engineers who rapidly designed, built, tested and validated the equipment,” Good said. “I want to thank Dr. Robert Turer [David Turer’s brother] from Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nick Karlowsky from Filtech, Inc., Drs. Lucas Dvoracek, J. Peter Rubin and Jason Chang from UPMC, and Ben Schilling and Dr. Heng Ban from the University of Pittsburg. It truly takes a team.”
###
Media Contact
Joyce M. Conant
[email protected]