Credit: Oregon State University
CORVALLIS, Ore. — Natural disasters alone are not enough to motivate local communities to engage in climate change mitigation or adaptation, a new study from Oregon State University found.
Rather, policy change in response to extreme weather events appears to depend on a combination of factors, including fatalities, sustained media coverage, the unusualness of the event and the political makeup of the community.
Climate scientists predict that the frequency and severity of extreme weather events will only continue to increase in coming decades. OSU researchers wanted to understand how local communities are reacting.
“There’s obviously national and state-level climate change policy, but we’re really interested in what goes on at the local level to adapt to these changes,” said lead author Leanne Giordono, a post-doctoral researcher in OSU’s College of Public Health and Human Sciences. “Local communities are typically the first to respond to extreme events and disasters. How are they making themselves more resilient — for example, how are they adapting to more frequent flooding or intense heat?”
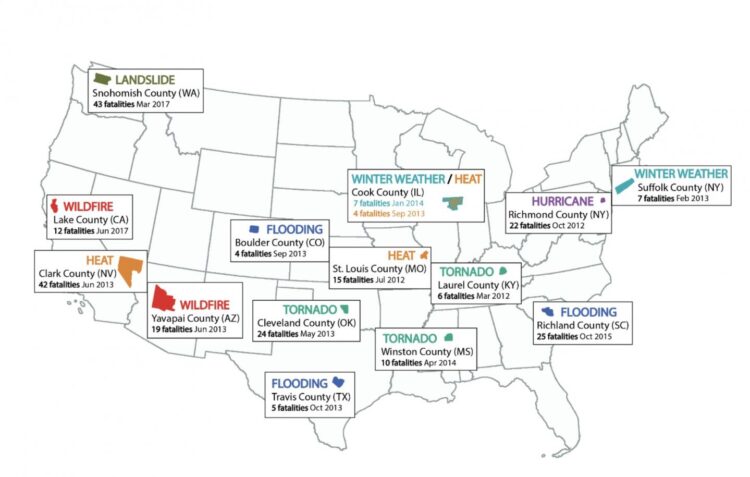
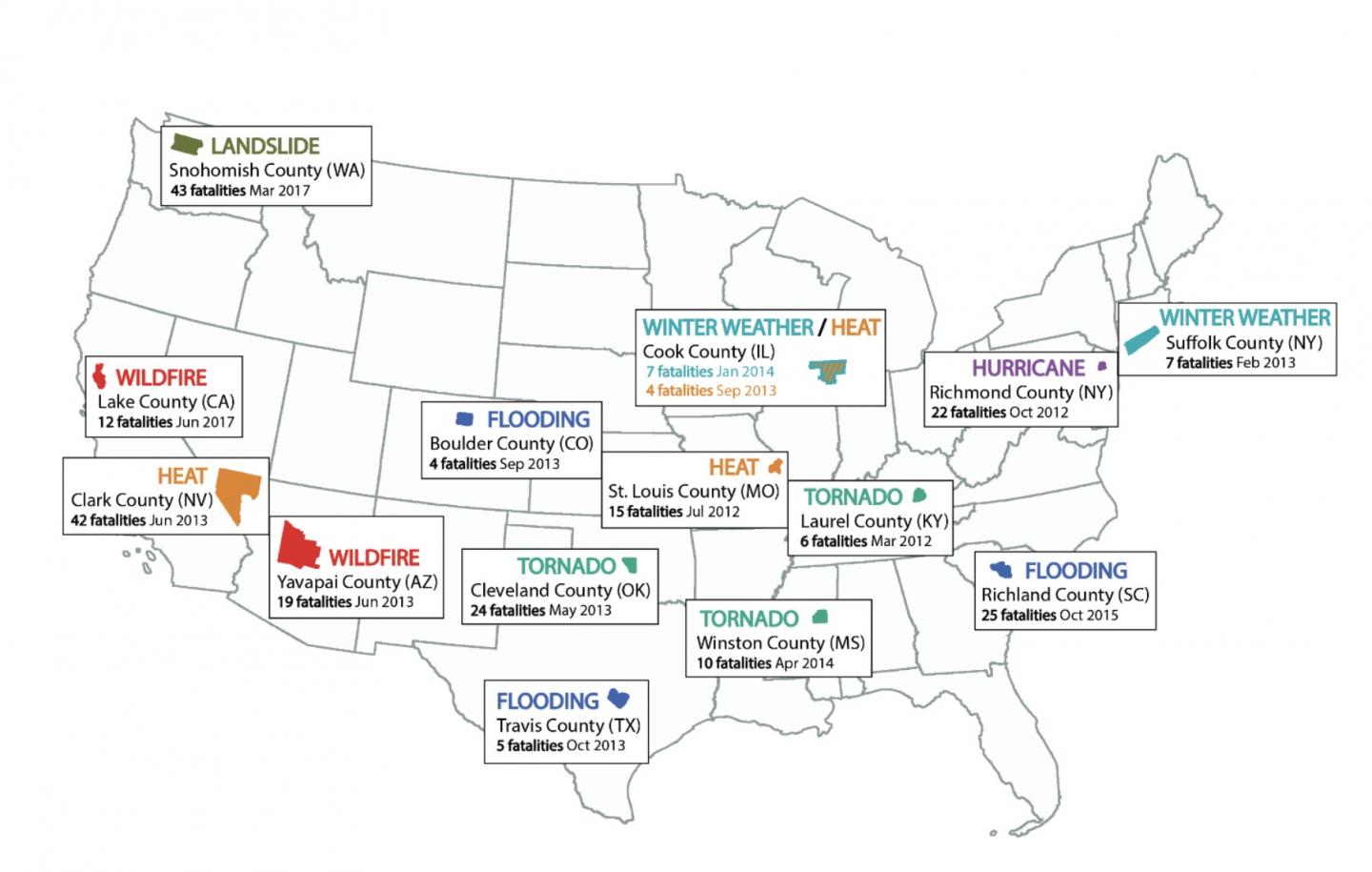
For the study, which was funded by the National Science Foundation, Giordono and co-authors Hilary Boudet of OSU’s College of Liberal Arts and Alexander Gard-Murray at Harvard University examined 15 extreme weather events that occurred around the U.S. between March 2012 and June 2017, and any subsequent local climate policy change.
These events included flooding, winter weather, extreme heat, tornadoes, wildfires and a landslide.
The study, published recently in the journal Policy Sciences, found there were two “recipes” for local policy change after an extreme weather event.
“For both recipes, experiencing a high-impact event — one with many deaths or a presidential disaster declaration — is a necessary condition for future-oriented policy adoption,” Giordono said.
In addition to a high death toll, the first recipe consisted of Democrat-leaning communities where there was focused media coverage of the weather event. These communities moved forward with adopting policies aimed at adapting in response to future climate change, such as building emergency preparedness and risk management capacity.
The second recipe consisted of Republican-leaning communities with past experiences of other uncommon weather events. In these locales, residents often didn’t engage directly in conversation about climate change but still worked on policies meant to prepare their communities for future disasters.
In both recipes, policy changes were fairly modest and reactive, such as building fire breaks, levees or community tornado shelters. Giordono referred to these as “instrumental” policy changes.
“As opposed to being driven by ideology or a shift in thought process, it’s more a means to an end,” she said. “‘We don’t want anyone else to die from tornadoes, so we build a shelter.’ It’s not typically a systemic response to global climate change.”
In their sample, the researchers didn’t find any evidence of mitigation-focused policy response, such as communities passing laws to limit carbon emissions or require a shift to solar power. And some communities did not make any policy changes at all in the wake of extreme weather.
The researchers suggest that in communities that are ideologically resistant to talking about climate change, it may be more effective to frame these policy conversations in other ways, such as people’s commitment to their community or the community’s long-term viability.
Without specifically examining communities that have not experienced extreme weather events, the researchers cannot speak to the status of their policy change, but Giordono said it is a question for future study.
“In some ways, it’s not surprising that you see communities that have these really devastating events responding to them,” Giordono said. “What about the vast majority of communities that don’t experience a high-impact event — is there a way to also spark interest in those communities?”
“We don’t want people to have to experience these types of disasters to make changes.”
###
Media Contact
Molly Rosbach
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.