Credit: John Sibbick
The first complete dinosaur skeleton ever identified has finally been studied in detail and found its place in the dinosaur family tree, completing a project that began more than a century and a half ago.
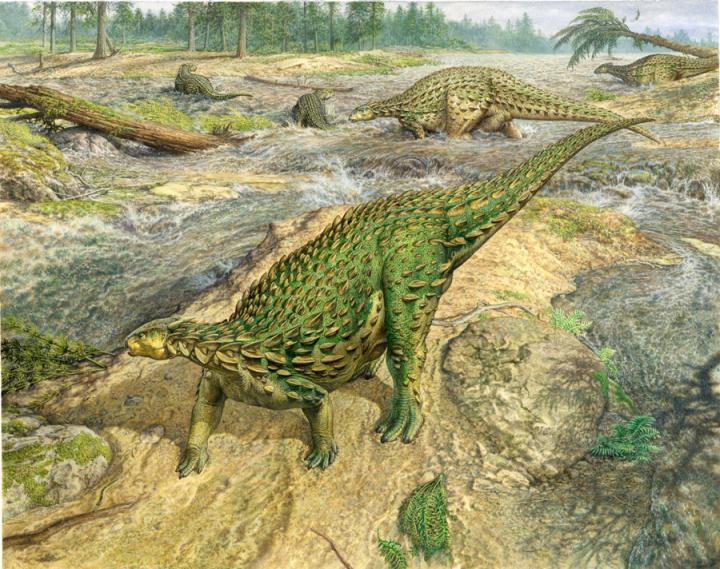
The skeleton of this dinosaur, called Scelidosaurus, was collected more than 160 years ago on west Dorset’s Jurassic Coast. The rocks in which it was fossilised are around 193 million years old, close to the dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs.
This remarkable specimen – the first complete dinosaur skeleton ever recovered – was sent to Richard Owen at the British Museum, the man who invented the word dinosaur.
So, what did Owen do with this find? He published two short papers on its anatomy, but many details were left unrecorded. Owen did not reconstruct the animal as it might have appeared in life and made no attempt to understand its relationship to other known dinosaurs of the time. In short, he ‘re-buried’ it in the literature of the time, and so it has remained ever since: known, yet obscure and misunderstood.
Over the past three years, Dr David Norman from Cambridge’s Department of Earth Sciences has been working to finish the work which Owen started, preparing a detailed description and biological analysis of the skeleton of Scelidosaurus, the original of which is stored at the Natural History Museum in London, with other specimens at Bristol City Museum and the Sedgwick Museum, Cambridge.
The results of Norman’s work, published as four separate studies in the Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society of London, not only reconstruct what Scelidosaurus looked like in life, but reveal that it was an early ancestor of ankylosaurs, the armour-plated ‘tanks’ of the Late Cretaceous Period.
For more than a century, dinosaurs were primarily classified according to the shape of their hip bones: they were either saurischians (‘lizard-hipped’) or ornithischians (‘bird-hipped’).
However, in 2017, Norman and his former PhD students Matthew Baron and Paul Barrett argued that these dinosaur family groupings needed to be rearranged, re-defined and re-named. In a study published in Nature, the researchers suggested that bird-hipped dinosaurs and lizard-hipped dinosaurs such as Tyrannosaurus evolved from a common ancestor, potentially overturning more than a century of theory about the evolutionary history of dinosaurs.
Another fact that emerged from their work on dinosaur relationships was that the earliest known ornithischians first appeared in the Early Jurassic Period. “Scelidosaurus is just such a dinosaur and represents a species that appeared at, or close to, the evolutionary ‘birth’ of the Ornithischia,” said Norman, who is a Fellow of Christ’s College, Cambridge. “Given that context, what was actually known of Scelidosaurus? The answer is remarkably little!”
Norman has now completed a study of all known material attributable to Scelidosaurus and his research has revealed many firsts.
“Nobody knew that the skull had horns on its back edge,” said Norman. “It had several bones that have never been recognised in any other dinosaur. It’s also clear from the rough texturing of the skull bones that it was, in life, covered by hardened horny scutes, a little bit like the scutes on the surface of the skulls of living turtles. In fact, its entire body was protected by skin that anchored an array of stud-like bony spikes and plates.”
Now that its anatomy is understood, it is possible to examine where Scelidosaurus sits in the dinosaur family tree. It had been regarded for many decades as an early member of the group that included the stegosaurs, including Stegosaurus with its huge bony plates along its spine and a spiky tail, and ankylosaurs, the armour-plated ‘tanks’ of the dinosaur era, but that was based on a poor understanding of the anatomy of Scelidosaurus. Now it seems that Scelidosaurus is an ancestor of the ankylosaurs alone.
“It is unfortunate that such an important dinosaur, discovered at such a critical time in the early study of dinosaurs, was never properly described,” said Norman. “It has now – at last! – been described in detail and provides many new and unexpected insights concerning the biology of early dinosaurs and their underlying relationships. It seems a shame that the work was not done earlier but, as they say, better late than never.”
###
Media Contact
Sarah Collins
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




