Results could lead to new medications, diets that improve health
Credit: Cristal Hill and Christopher Morrison
BATON ROUGE, Louisiana – A new federally funded study could reveal the nervous system cells and circuits in our brains that influence our metabolism and health in response to dietary changes.
“Changing what we eat can profoundly affect our health for better or worse,” said Christopher Morrison, Ph.D., Professor and Director, Neurosignaling Laboratory, Pennington Biomedical Research Center. “We hope that by understanding how we sense and respond to altered nutrient intake, we can make better nutritional recommendations and identify new metabolic and/or neural pathways that regulate our metabolism.”
Morrison is the primary investigator on a $1.5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. The new study will look at how a hormone called Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21) tells the brain how many calories our bodies should burn, limits fat storage, and keeps blood sugar levels steady.
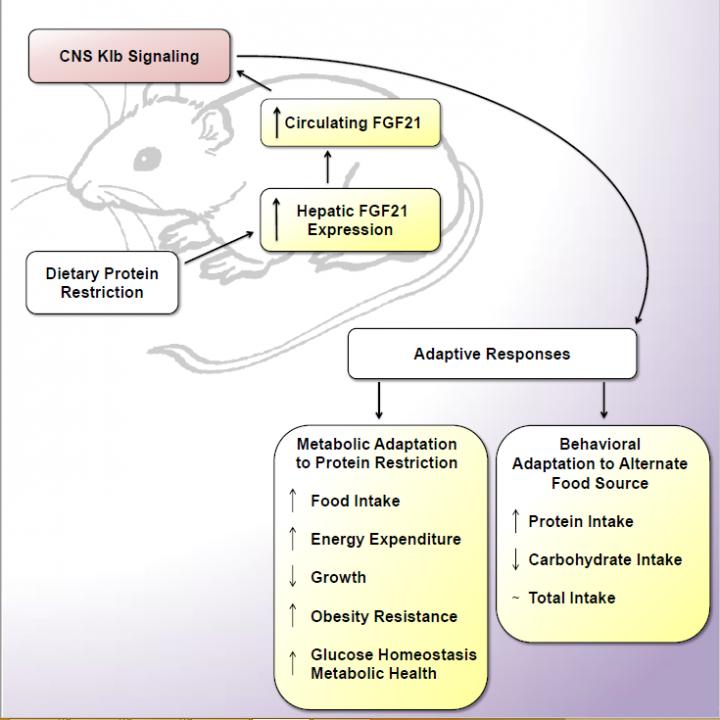
Over the last several years, Dr. Morrison and the scientists in his lab have focused on the effects of limiting protein intake on metabolism and health. Scientists in the lab recently discovered that FGF21 is an essential signal for mice to detect and respond to low-protein diets.
“FGF21 is the only known hormone that acts as a protein signal. Our work suggests that FGF21 acts as an emergency flare, telling a mouse’s brain that the animal is not eating enough protein,” Dr. Morrison said. “In response, the brain triggers a number of metabolic changes, including altering food intake, increasing metabolic rate, lowering body fat, and lowering lipids and glucose.”
At present, science has almost no understanding of the brain regions that sense changes in FGF21. Morrison and his lab will identify where and how FGF21 acts in the brain.
“I am excited about the possibility that we might discover completely new neural circuits that directly control our health,” Morrison said. “Each new discovery provides us with a deeper understanding of how the brain controls metabolism in response to dietary change, and this knowledge provides the opportunity to develop new drugs, diets, or behaviors that can improve our health.”
This research is supported by the National Institutes of Health via the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases under award number DK121370-01A1. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
How the Liver Tells the Brain What to Eat
FGF21 is an endocrine signal that links the liver and brain.
When the liver detects low levels of protein, it activates cells that produce FGF21 and release the hormone into the bloodstream. FGF21 is then carried to target cells (neurons) in the brain. Those cells hit the alarm button when they see FGF21, signaling that protein intake is too low.
The brain reacts by sending out a complex set of directions that, among other things, stop the mouse from growing, alter food intake, and perhaps most importantly for obesity researchers, increase the number of calories burned and limit the amount of fat the mouse stores.
###
About the Pennington Biomedical Research Center
The Pennington Biomedical Research Center is at the forefront of medical discovery as it relates to understanding the triggers of obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer and dementia. The Center conducts basic, clinical, and population research, and is affiliated with Louisiana State University. The research enterprise at Pennington Biomedical includes over 450 employees within a network of 40 clinics and research laboratories, and 13 highly specialized core service facilities. Its scientists and physician/scientists are supported by research trainees, lab technicians, nurses, dietitians, and other support personnel. Pennington Biomedical is located in state-of-the-art research facilities on a 222-acre campus in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. For more information, see http://www.
Media Contact
Ted Griggs
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




