Metals from implants can accumulate in bone tissue
Credit: Naujok/Charité
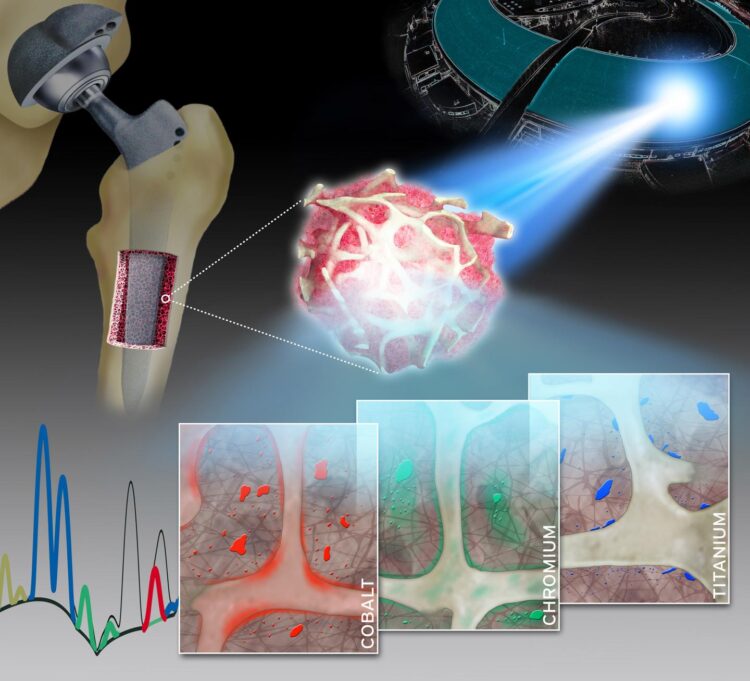
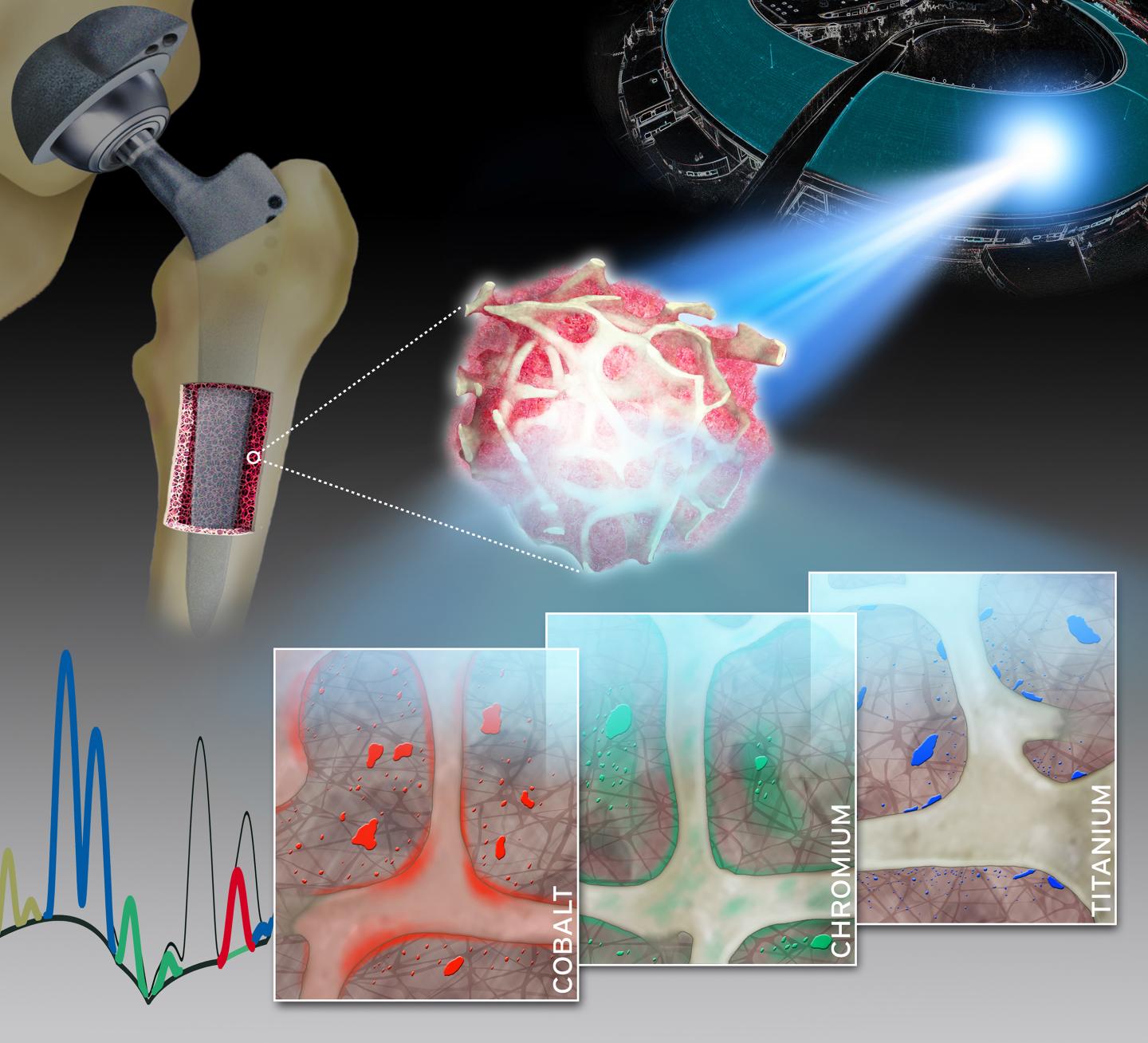
Using highly complex analytical techniques, a group of researchers from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin were able to observe in detail how different metals are released from joint implants and accumulate in the surrounding bone tissue. Findings showed a steady release of metals from various implant components. In contrast to previous assumptions, this was not related to the degree of mechanical stress involved. The researchers’ findings, which have been published in Advanced Science*, will help to optimize the materials used in implants and enhance their safety.
Modern joint implants restore pain-free mobility of patients with chronic degenerative joint disease, thereby drastically enhancing their quality of life. To ensure long-term mechanical stability, artificial joints are made from materials containing a range of different metal alloys. A crucial factor in determining an implant’s long-term effectiveness, however, is its integration into the surrounding bone tissue. Previous studies on implant stability show that friction between the articulating surfaces (bearing surfaces) can result in the formation of metal debris. This wear debris can lead to osteolysis – the destruction of bone around the implant – which can result in premature loosening of the implant. The possibility of a steady release of metal from other parts of the prosthesis had not previously received much attention.
A group of researchers led by Dr. Sven Geißler of Charité’s Julius Wolff Institute for Biomechanics and Musculoskeletal Regeneration and BIH Center for Regenerative Therapies has now studied the spatial distribution and local toxicokinetics of metallic wear and corrosion products within the surrounding bone tissue. For their detailed analysis, the researchers used a unique synchrotron-based X-ray fluorescence imaging setup. “Our work has enabled us to show, for the first time, that both particulate and dissolved metals released from arthroplasty implants are present in the surrounding bone and bone marrow at supraphysiological levels,” says Dr. Geißler. “Therefore, the collagen-rich layer which encapsulates the implant after surgery does not separate these metals from human tissue to the extent previously assumed.”
The researchers collected minute bone and bone marrow samples from 14 patients undergoing either a hip or knee arthroplasty procedure. The researchers then determined the qualitative and quantitative composition of the samples using a technique known a X-ray fluorescence. This technique provides unique insights into the concentration, distribution, location and accumulation of metallic degradation products like cobalt, chromium or titanium in adjacent bone and bone marrow. The extremely bright and intensively focused X-ray beam required was achieved by the synchrotron radiation source at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF). The ESRF, which is located in Grenoble, France, is the only particle accelerator in the world to offer a spatial resolution of up to 30 nanometers. Summing up the researchers’ achievements, the study’s first author, Dr. Janosch Schoon, says: “Our work therefore addresses an issue of enormous clinical relevance with a highly complex experimental setup.”
“Our study has made a major contribution to the improvement of the risk-benefit evaluation of medical devices. It has shown that these evaluations should not only comprise biocompatibility testing of raw materials; rather, biocompatibility testing should also extend to wear and corrosion products. The data from this study will therefore prove instrumental in keeping implant safety at the highest possible level,” explains Dr. Geißler. Based on their findings, the researchers plan to conduct additional studies which will investigate the biological consequences of metal release on bones and bone marrow. At the same time, the researchers will develop new approaches which will facilitate the reliable preclinical testing of implant materials using both human cells and engineered tissues.
###
*Schoon J et al. Metal-specific biomaterial accumulation in human peri-implant bone and bone marrow. Adv Sci (2020), DOI: 10.1002/advs.202000412
Media Contact
Dr. Sven Geißler
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.