Credit: © Serge Morand/Biological Conservation
Research has shown a global increase in the emergence of infectious diseases and epidemics, an accelerated loss of biodiversity and a marked increase in the breeding of domesticated animals. This subject was brought back to the fore by the COVID-19 outbreak and a new study in parasite ecology is providing some initial answers to the ongoing question of whether these events are connected. Its goal was to trace the global patterns of biodiversity and infectious diseases both spatially and temporally.
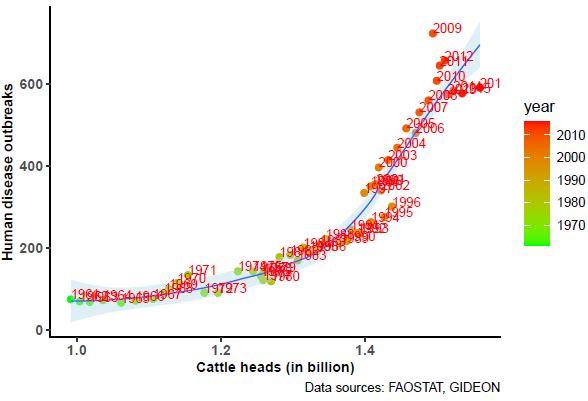
To achieve this, the researcher cross referenced various open databases* on human and animal health, livestock expansion and biodiversity loss. An initial analysis showed that the number of epidemics identified in humans in each country increased in correlation with local biodiversity loss (16,994 epidemics caused by 254 infectious diseases between 1960-2019). The emergence of epidemics is a worrying sign for the future of species conservation as it could well signal biodiversity’s march towards extinction. The relation between the number of endangered species and the number of epidemics first increases, then peaks, before finally declining. However, the risk of an epidemic does not decrease with the disappearance of a species, but on the contrary, is further relayed by the growing number of head of cattle. Data from 2006-2019 confirms this second result placing it at the heart of a potential health risk. Livestock expansion worldwide directly affects wildlife as well as the incidence of epidemics in humans and in domesticated animals.
The study brings up the question of the place of farmed animals and their increase across the world, which varies according to factors such as human demographics and diet. In order to lower the health risk and protect biodiversity we need to take into account the cultural value of animals to reflect on the place of both wild and domesticated species. Future studies will examine the role played by livestock in pandemics by looking at, on the one hand, the cultivation of vegetable protein needed for feed, which contributes to reduce the space for wild animals, and on the other, on the role of livestock as an epidemiological bridge between wildlife and humans facilitating the transmission of pathogens.
###
Note
1- The Global Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology Online Network (GIDEON) was used for data on human epidemics, the World Organisation for Animal Health was used for data on animal epidemics, the Food and Agricultural Organisation of the United Nations was used for data on livestock production, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature was used for data on biodiversity and endangered species.
Media Contact
Francois Maginiot
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




