Nature just published the research on unprecedented “Self-assembled poly-catenanes”
Credit: Politecnico di Torino
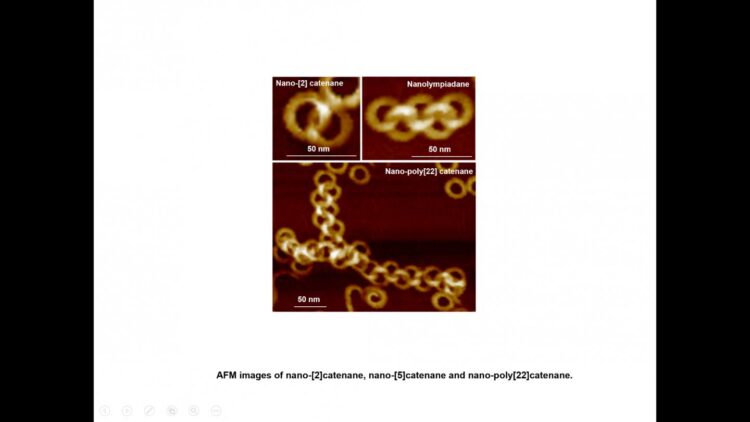
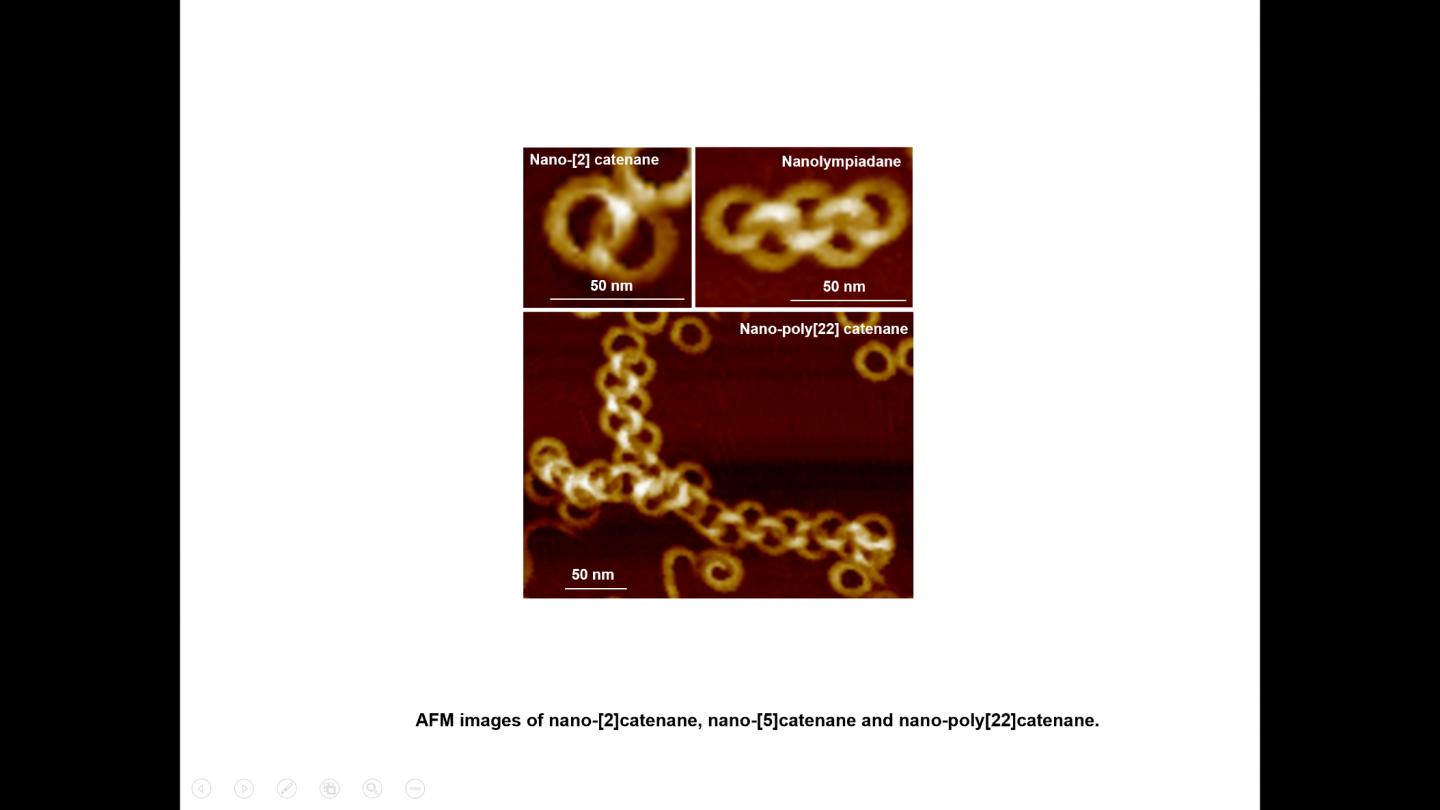
The “nanolimpiad”, as the complex structure of self-assembled links has been named, looks like the five Olympic Rings and may become the source of new polymeric materials with innovative properties.
A collaboration of research groups from Japan (Chiba University), Italy (Politecnico di Torino), Switzerland (SUPSI) and the UK (Keele University, the Diamond Light Source &the ISIS Pulsed Neutron and Muon Source) has succeeded in developing and studying supramolecular poly-catenanes: hierarchical structures composed of mechanically interlocked self-assembled rings, made solely from one elementary molecular ingredient.
In 2016, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry (for the contribution to the synthesis of molecular machines) was awarded to Ben Feringa, Fraser Stoddart and Jean-Pierre Sauvage, the latter having managed to connect two ring-shaped molecules into what is called a “catenane”. Unlike ordinary polymers, consisting of monomers united via covalent chemical bonds, catenanes are composed by interconnected units mechanically interlocked like rings in a chain. This allows the links to move relatively to each other, imparting to these materials unique properties in terms of absorption, conversion and dissipation of energy, super-elasticity, etc.
The synthesis and characterisation of such structures are notoriously difficult, particularly when the fundamental rings themselves are not held together by strong covalent bonds.
This research work, led by Shiki Yagai (Chiba University), has been just published on the prestigious journal Nature.
It is the first report on the creation of nano-poly[n]catenanes via molecular self-assembly, without the use of models or other supporting materials. By altering the self-assembly conditions, this group of scientists has been able to create intricate structures, including a nano-[5]catenane with interlocked rings in a linear arrangement, which has been named “nanolympiadane” in homage to the [5]catenane system “olympiadane” first reported by Fraser Stoddart and colleagues in 1994, so called for the similarity with the well-known symbol of the Olympic games.
The scientists were able to probe these impressive structures composed of nano-rings using atomic force microscopy, X-ray and neutron scattering.
Each component ring (nano-toroid, ~30 nm of diameter) comprises around 600 identical small molecules (monomers). These monomers first spontaneously assemble into 6-membered flat “rosettes”, which then collectively stack on each other to form a ring. The consortium designed methods to purify the rings, removing any material that hadn’t assembled as desired, and found that the addition of such rings to the hot monomer solution facilitates the formation of new assemblies on the surface of the rings, a process known as secondary nucleation. Based on this finding, they applied the sequential addition of monomers, and were able to create poly[n]catenanes with up to 22 rings.
Multiscale molecular simulations carried out by the research group of Giovanni M. Pavan, full professor at the Politecnico, were instrumental for understanding the formation of the poly-catenanes. This computational work was supported by the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program, by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) and by the CSCS Swiss National Supercomputing Centre (CSCS) and the CINECA, which provided the needed computational resources.
The simulations allowed to model the secondary nucleation taking place on the rings surface, and, together with small-angle scattering experiments, to characterize this process.
The molecular simulations showed that the prime cause triggering the nucleation and growth of new rings onto pre-existing ones is the limited solubility in the solvent, which causes the monomers and the rosettes to stick onto the surface of pre-formed toroids.
A stepwise addition of monomers allowed the authors to greatly improving the extent of interlocking of the rings, generating unprecedentedly long poly-catenanes.
The size of these interlocked structures will allow for in-depth study of the unique physical properties that a structure made up of miniscule interlocked chain links may have, and to explore their potential for creating new types of molecular machines and active materials.
###
Media Contact
Elena Foglia Franke
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.