Credit: CASSACA
The Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST) is the largest telescope with the highest sensitivity in the world. Extragalactic neutral hydrogen detection is one of important scientific goals of FAST.
Recently, an international research team led by Dr. CHENG Cheng from Chinese Academy of Sciences South America Center for Astronomy (CASSACA) observed four extragalactic galaxies by using the FAST 19-beam receiver, and detected the neutral hydrogen line emission from three targets with only five minutes of exposure each. This is the first publication for FAST to detect extragalactic neutral hydrogen.
The research paper was published in Astronomy & Astrophysics Letter.
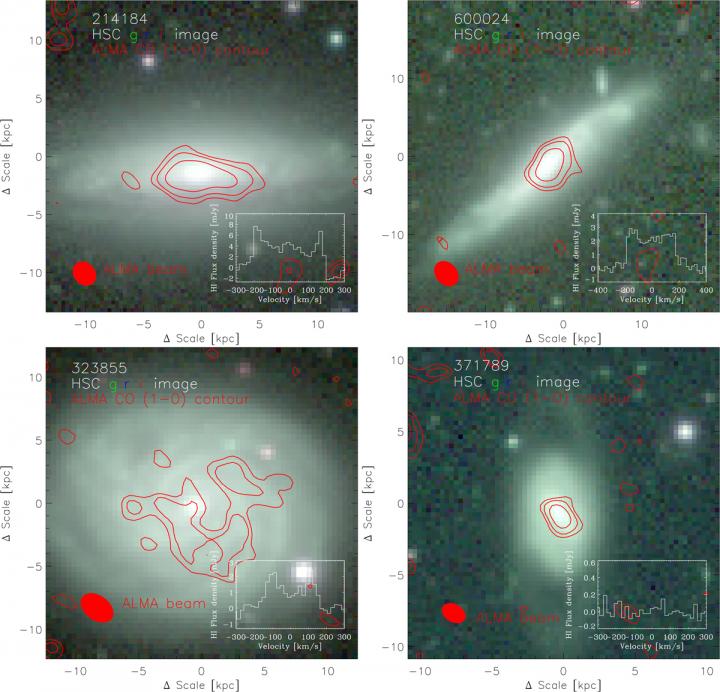
Neutral hydrogen gas is the most extended baryons in galaxies, while cold gas traced by CO is more concentrated to a galaxy center (red contour in Fig.1). “With dynamical measurements of neutral hydrogen and CO, we can estimate the mass distribution of galaxies at different radii,” said Dr. CHENG, first author of the study.
Dynamical masses of these four galaxies estimated from the newly observed neutral hydrogen line were 10 times higher than the observed baryon masses, indicating contribution of dark matter.
On the other hand, dynamical masses estimated using previous CO observations were equivalent to their observed baryon masses. Therefore, the new FAST observation illustrated its ability of studying dark matter in galaxies using the neutral hydrogen 21cm emission line.
The FAST observation of these galaxies was an important part of an international research project, the Valparaíso ALMA Line Emission Survey (VALES), led by Prof. Edo Ibar from Valparaiso University in Chile.
The VALES is a project of observing star forming galaxies using first-class international facilities such as Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), Herschel Space Observatory, Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA), Atacama Pathfinder Experiment telescope (APEX) and Very Large Telescope (VLT).
FAST, with the unpreceded sensitivity, provides a unique chance to observe the extra-galactic neutral hydrogen, and therefore has been added to the list of modern astronomical facilities used by this international collaboration.
###
Media Contact
XU Ang
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




