Credit: GAO Ji et al.
A collaborative research team from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and China Geological Survey (CGS) have succeeded in obtaining a high-resolution 3D resistivity model of approximately 20 km depth beneath the Weishan volcano in the Wudalianchi volcanic field (WVF) for the first time. The study, published in Geology, revealed the image of potential magma chambers and the estimated melt fractions.
WVF in the northeast of China, comprised of 14 volcanoes that have erupted about 300 years ago, is one of the largest active volcanic areas. Volcanic activities are hazard to human life and have severe environmental consequences, thus it is important to characterize the magmatic system beneath the volcanoes to understand the nature of the eruption.
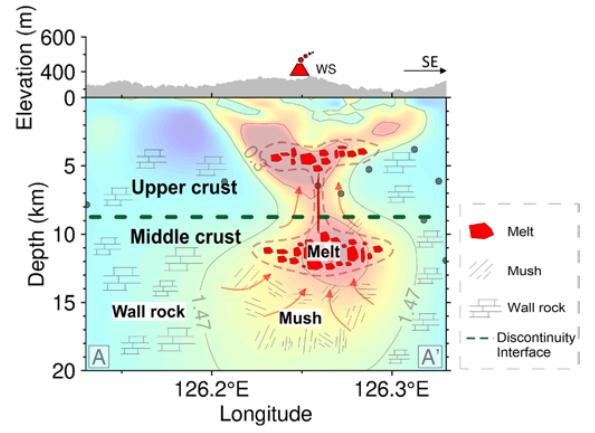
In conjunction with the Center for Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, CGS, Prof. ZHANG Jianghai’s group from School of Earth and Space Sciences, USTC, utilized magnetotelluric (MT) methods to image magma reservoirs beneath Weishan volcano and obtained its high-resolution spatial resistivity distribution up to 20 km deep. Their findings showed the existence of vertically distributed low-resistivity anomalies that are narrowest in the middle. This was further interpreted as magma reservoirs existing both in the upper crust and the middle crust, which are linked by very thin vertical channels for magma upwelling.
Meanwhile, they cooperated with Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics of CAS, combining both the velocity model from ambient noise tomography (ANT) and the resistivity model from MT imaging to estimate that the melt fractions of the magma reservoirs in the upper crust and the middle crust are reliably to be >~15%. This phenomenon demonstrated that there should be an even deeper source for recharging the magma chambers to keep the melt fraction increasing, and indicated that the volcano is still active.
Considering the significant melt fractions and the active earthquakes and tremors occurred around the magma reservoirs several years ago, the Weishan volcano is likely in an active stage with magma recharging. Although the melt fraction does not reach the eruption threshold (~40%), it is necessary to increase monitoring capabilities to better forecasting its potential future eruptions.
Overall, this study has revealed that the volcanoes in northeast China may be in an active stage. This poses a grave threat to man and environment, thus proper monitoring is required to forecast its hazardous implications.
###
Media Contact
Jane FAN Qiong
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




