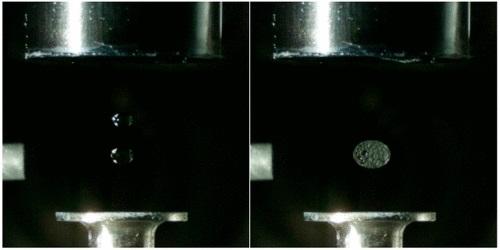
Credit: Analytical Chemistry 2020, DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c00929
Levitation has long been a staple of magic tricks and movies. But in the lab, it’s no trick. Scientists can levitate droplets of liquid, though mixing them and observing the reactions has been challenging. The pay-off, however, could be big as it would allow researchers to conduct contact-free experiments without containers or handling that might affect the outcome. Now, a team reporting in ACS’ Analytical Chemistry has developed a method to do just that.
Scientists have made devices to levitate small objects, but most methods require the object to have certain physical properties, such as electric charge or magnetism. In contrast, acoustic levitation, which uses sound waves to suspend an object in a gas, doesn’t rely on such properties. Yet existing devices for acoustic levitation and mixing of single particles or droplets are complex, and it is difficult to obtain measurements from them as a chemical reaction is happening. Stephen Brotton and Ralf Kaiser wanted to develop a versatile technique for the contactless control of two chemically distinct droplets, with a set of probes to follow the reaction as the droplets merge.
The team made an acoustic levitator and suspended two droplets in it, one above the other. Then, they made the upper droplet oscillate by varying the amplitude of the sound wave. The oscillating upper droplet merged with the lower droplet, and the resulting chemical reaction was monitored with infrared, Raman and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopies. The researchers tested the technique by combining different droplets. In one experiment, for example, they merged an ionic liquid with nitric acid, causing a tiny explosion. The new levitation method could help scientists study many different types of chemical reactions in areas such as material sciences, medicinal chemistry and planetary science, the researchers say.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the Office of Naval Research.
The abstract that accompanies this paper can be viewed here.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and its people. The Society is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a specialist in scientific information solutions (including SciFinder® and STN®), its CAS division powers global research, discovery and innovation. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




