Credit: Image courtesy of Jigang Wang/Iowa State University
AMES, Iowa – Scientists are using light waves to accelerate supercurrents and access the unique properties of the quantum world, including forbidden light emissions that one day could be applied to high-speed, quantum computers, communications and other technologies.
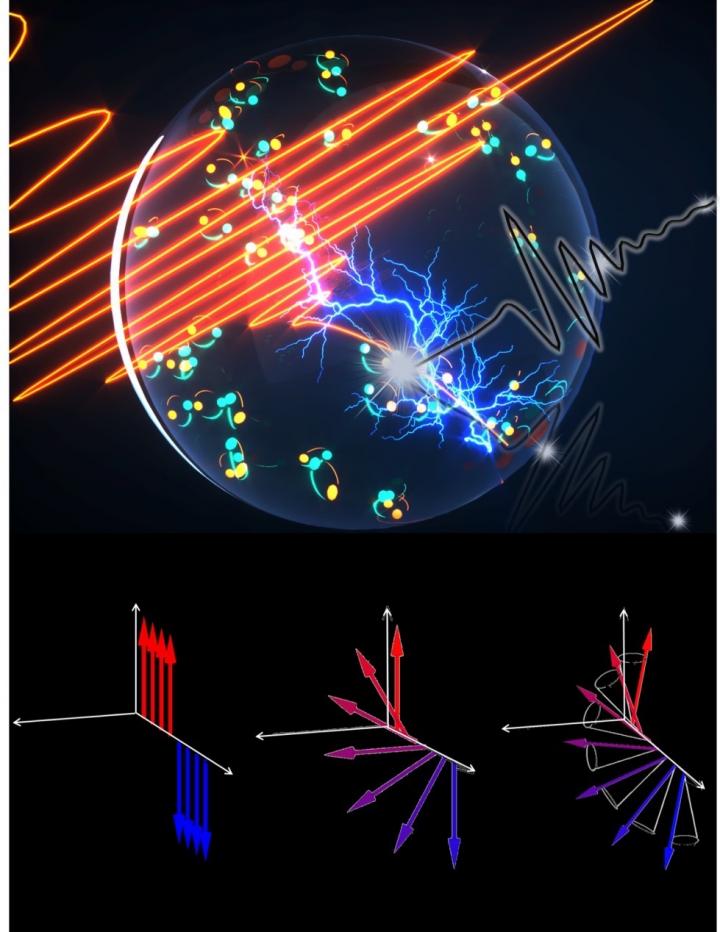
The scientists have seen unexpected things in supercurrents – electricity that moves through materials without resistance, usually at super cold temperatures – that break symmetry and are supposed to be forbidden by the conventional laws of physics, said Jigang Wang, a professor of physics and astronomy at Iowa State University, a senior scientist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Ames Laboratory and the leader of the project.
Wang’s lab has pioneered use of light pulses at terahertz frequencies- trillions of pulses per second – to accelerate electron pairs, known as Cooper pairs, within supercurrents. In this case, the researchers tracked light emitted by the accelerated electrons pairs. What they found were “second harmonic light emissions,” or light at twice the frequency of the incoming light used to accelerate electrons.
That, Wang said, is analogous to color shifting from the red spectrum to the deep blue.
“These second harmonic terahertz emissions are supposed to be forbidden in superconductors,” he said. “This is against the conventional wisdom.”
Wang and his collaborators – including Ilias Perakis, professor and chair of physics at the University of Alabama at Birmingham and Chang-beom Eom, the Raymond R. Holton Chair for Engineering and Theodore H. Geballe Professor at the University of Wisconsin-Madison – report their discovery in a research paper just published online by the scientific journal Physical Review Letters. (See sidebar for a list of the other co-authors.)
“The forbidden light gives us access to an exotic class of quantum phenomena – that’s the energy and particles at the small scale of atoms – called forbidden Anderson pseudo-spin precessions,” Perakis said.
(The phenomena are named after the late Philip W. Anderson, co-winner of the 1977 Nobel Prize in Physics who conducted theoretical studies of electron movements within disordered materials such as glass that lack a regular structure.)
Wang’s recent studies have been made possible by a tool called quantum terahertz spectroscopy that can visualize and steer electrons. It uses terahertz laser flashes as a control knob to accelerate supercurrents and access new and potentially useful quantum states of matter. The National Science Foundation has supported development of the instrument as well as the current study of forbidden light.
The scientists say access to this and other quantum phenomena could help drive major innovations:
- “Just like today’s gigahertz transistors and 5G wireless routers replaced megahertz vacuum tubes or thermionic valves over half a century ago, scientists are searching for a leap forward in design principles and novel devices in order to achieve quantum computing and communication capabilities,” said Perakis, with Alabama at Birmingham. “Finding ways to control, access and manipulate the special characteristics of the quantum world and connect them to real-world problems is a major scientific push these days. The National Science Foundation has included quantum studies in its ’10 Big Ideas’ for future research and development critical to our nation.”
- Wang said, “The determination and understanding of symmetry breaking in superconducting states is a new frontier in both fundamental quantum matter discovery and practical quantum information science. Second harmonic generation is a fundamental symmetry probe. This will be useful in the development of future quantum computing strategies and electronics with high speeds and low energy consumption.”
Before they can get there, though, researchers need to do more exploring of the quantum world. And this forbidden second harmonic light emission in superconductors, Wang said, represents “a fundamental discovery of quantum matter.”
###
Read the paper
“Terahertz Second-Harmonic Generation from Lightwave Acceleration of Symmetry-Breaking Nonlinear Supercurrents,” Physical Review Letters, Volume 124, Issue 20.
The research team
In addition to Wang, Perakis and Eom, the research team includes Iowa State’s Chirag Vaswani, Dinusha Herath Mudiyanselage, Xu Yang, Di Cheng, Chuankun Huang, Richard H. Kim, Zhaoyu Liu and Liang Luo; Alabama at Birmingham’s Martin Mootz; and Wisconsin-Madison’s Christopher Sundahl and Jong-Hoon Kang.
The terahertz spectroscopy study was performed at Iowa State. Model building and analysis were performed at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. Sample development and structural/transport measurements were performed at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Media Contact
Jigang Wang
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




