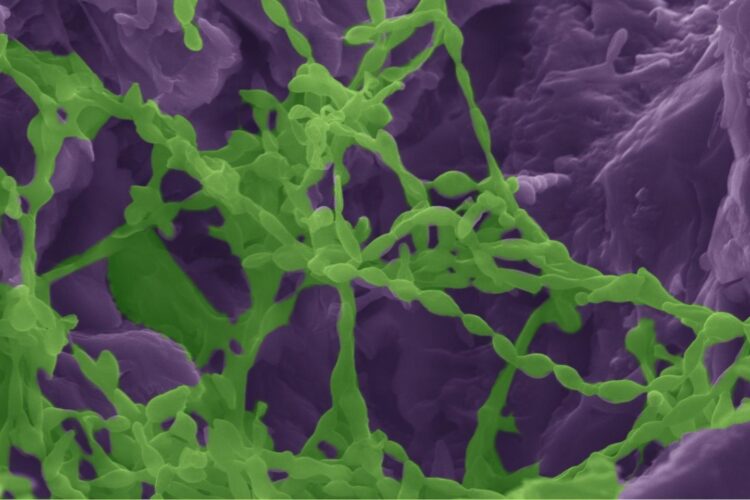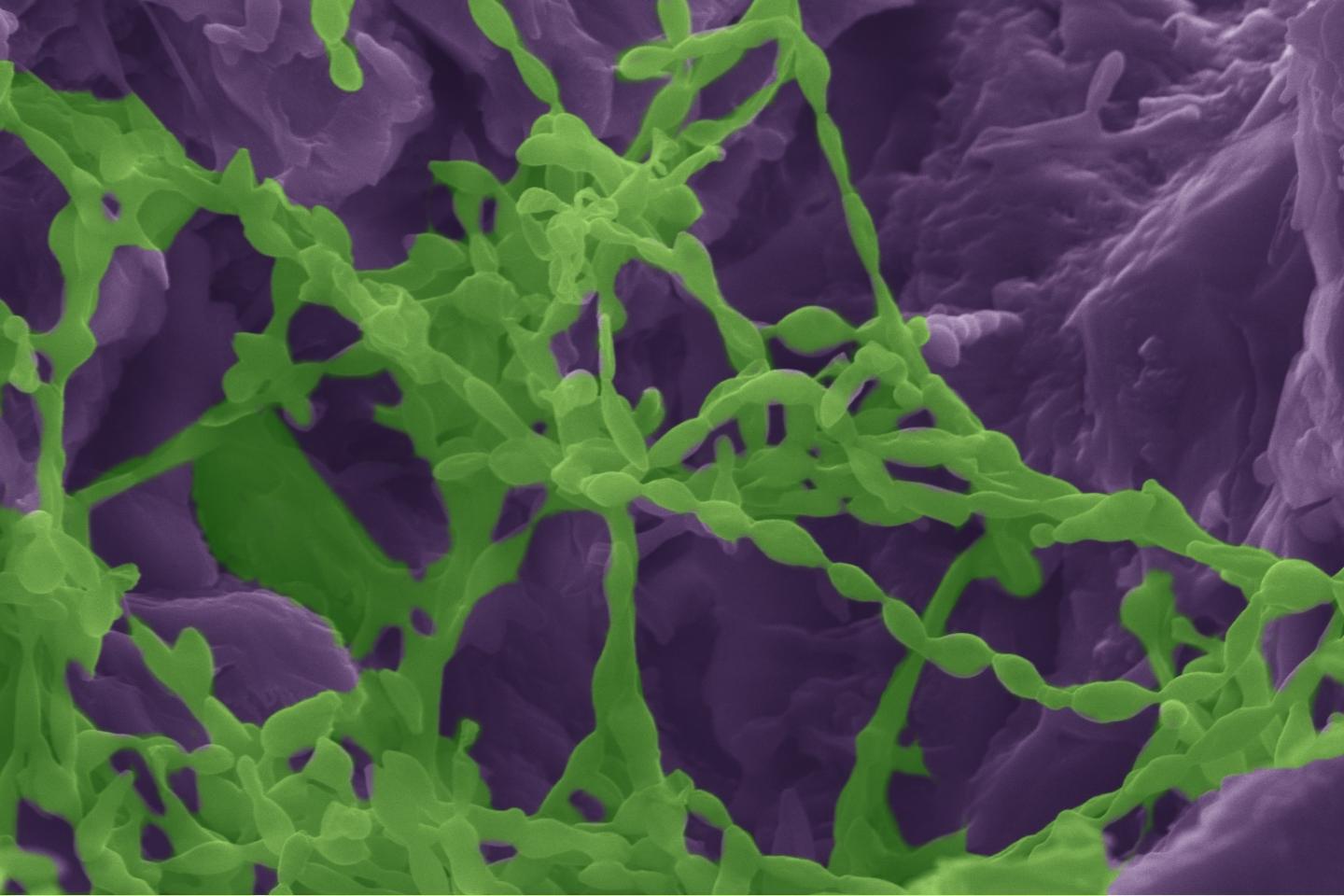
Credit: David Kisailus / UCI
By studying how the tiniest organisms in the Atacama Desert of Chile, one of the driest places on Earth, extract water from rocks, researchers at the Johns Hopkins University, University of California, Irvine, and U.C. Riverside revealed how, against all odds, life can exist in extreme environments.
A report of the findings published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences show how life can flourish in places without much water – including Mars, which has an environment similar to the Atacama – and how people living in arid regions may someday be able to procure hydration from available minerals.
“Scientists have suspected for a long time that microorganisms might be able to extract water from minerals, but this is the first demonstration of it,” says Jocelyne DiRuggiero, associate professor of biology at the Johns Hopkins University and the paper’s co-author.
“This is an amazing survival strategy for microorganisms living at the dry limit for life, and it provides constraints to guide our search for life elsewhere.”
The research team focused on Chroococcidiospsis, a species of cyanobacteria that is found in deserts around the world, and gypsum, a calcium sulfate-based mineral that contains water. The colonizing lifeforms exist beneath a thin layer of rock that gives them protection against the Atacama’s extreme temperature, battering winds and blistering sun.
DiRuggiero traveled to the remote desert to collect gypsum samples, which she brought back to her lab, cut into small pieces where the microorganisms could be found and sent to David Kisailus, professor of materials science & engineering at UCI, for materials analysis.
In one of the most striking findings of the study, the researchers learned that the microorganisms change the very nature of the rock they occupy. By extracting water, they cause a phase transformation of the material – from gypsum to anhydrite, a dehydrated mineral.
According to DiRuggiero, the study’s inspiration came when Wei Huang, a UCI post-doctoral scholar in materials science & engineering, spotted data showing an overlap in concentrations of anhydrite and cyanobacteria in the gypsum samples collected in the Atacama.
DiRuggiero’s team then allowed the organisms to colonize half-millimeter cubes of rocks, called coupons, under two different conditions: one in the presence of water, to mimic a high-humidity environment, and the other completely dry. In the presence of moisture, the gypsum did not transform to the anhydrite phase.
“They didn’t need water from the rock, they got it from their surroundings,” said Kisailus. “But when they were put under stressed conditions, the microbes had no alternative but to extract water from the gypsum, inducing this phase transformation in the material.”
Kisailus’ team used a combination of advanced microscopy and spectroscopy to examine the interactions between the biological and geological counterparts, finding that the organisms bore into the material like tiny miners by excreting a biofilm containing organic acids, Kisailus said.
Huang used a modified electron microscope equipped with a Raman spectrometer to discover that the organisms used the acid to penetrate the rock in specific crystallographic directions – only along certain planes where they could more easily access water existing between faces of calcium and sulfate ions.
“Does it mean there is life on Mars? We cannot say, but it gives us an idea of how crafty microorganisms can be,” says DiRuggiero.
The findings may also help researchers develop other practical applications for defense. “The Army has a strong interest in how microorganisms well-adapted to extreme environments can be exploited for novel applications such as material synthesis and power generation within these harsh fielded environments,” adds Robert Kokoska, program manager, Army Research Office, an element of U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command’s Army Research Office.
“This study provides valuable clues for uncovering the evolved “design strategies” used by these native desert-dwelling microbes to maintain their viability in the face of multiple environmental challenges.”
Funding for this project was provided by the Army Research Office and NASA.
###
Media Contact
Chanapa Tantibanchachai
[email protected]