Credit: Image courtesy Collin Kaufman
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Miniature biological robots are making greater strides than ever, thanks to the spinal cord directing their steps.
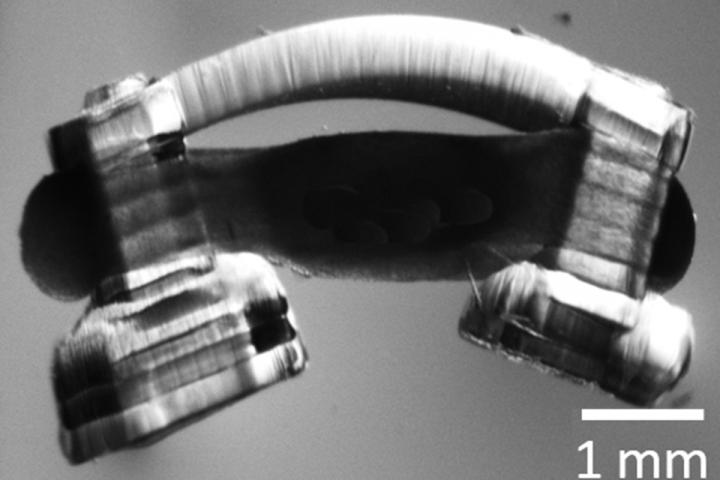
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign researchers developed the tiny walking “spinobots,” powered by rat muscle and spinal cord tissue on a soft, 3D-printed hydrogel skeleton. While previous generations of biological robots, or bio-bots, could move forward by simple muscle contraction, the integration of the spinal cord gives them a more natural walking rhythm, said study leader Martha Gillette, a professor of cell and developmental biology.
“These are the beginnings of a direction toward interactive biological devices that could have applications for neurocomputing and for restorative medicine,” Gillette said.
The researchers published their findings in the journal APL Bioengineering.
To make the spinobots, the researchers first printed the tiny skeleton: two posts for legs and a flexible “backbone,” only a few millimeters across. Then, they seeded it with muscle cells, which grew into muscle tissue. Finally, they integrated a segment of lumbar spinal cord from a rat.
“We specifically selected the lumbar spinal cord because previous work has demonstrated that it houses the circuits that control left-right alternation for lower limbs during walking,” said graduate student Collin Kaufman, the first author of the paper. “From an engineering perspective, neurons are necessary to drive ever more complex, coordinated muscle movements. The most challenging obstacle for innervation was that nobody had ever cultured an intact rodent spinal cord before.”
The researchers had to devise a method not only to extract the intact spinal cord and then culture it, but also to integrate it onto the bio-bot and culture the muscle and nerve tissue together – and do it in a way that the neurons form junctions with the muscle.
The researchers saw spontaneous muscle contractions in the spinobots, signaling that the desired neuro-muscular junctions had formed and the two cell types were communicating. To verify that the spinal cord was functioning as it should to promote walking, the researchers added glutamate, a neurotransmitter that prompts nerves to signal muscle to contract.
The glutamate caused the muscle to contract and the legs to move in a natural walking rhythm. When the glutamate was rinsed away, the spinobots stopped walking.
Next, the researchers plan to further refine the spinobots’ movement, making their gaits more natural. The researchers hope this small-scale spinal cord integration is a first step toward creating in vitro models of the peripheral nervous system, which is difficult to study in live patients or animal models.
“The development of an in vitro peripheral nervous system – spinal cord, outgrowths and innervated muscle – could allow researchers to study neurodegenerative diseases such as ALS in real time with greater ease of access to all the impacted components,” Kaufman said. “There are also a variety of ways that this technology could be used as a surgical training tool, from acting as a practice dummy made of real biological tissue to actually helping perform the surgery itself. These applications are, for now, in the fairly distant future, but the inclusion of an intact spinal cord circuit is an important step forward.”
###
The National Science Foundation supported this work through the Emergent Behaviors of Integrated Cellular Systems science and technology center. Gillette also directs the neuroscience program at the U. of I. and is affiliated with the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, the Carle Illinois College of Medicine, the Holonyak Micro and Nanotechnology Lab and the departments of bioengineering and molecular and integrative physiology.
Editor’s notes: To reach Martha Gillette, call 217-244-1355; email [email protected]. To reach Collin Kaufman, email [email protected].
The paper “Emergence of functional neuromuscular junctions in an engineered, multicellular spinal cord-muscle bioactuator” is available online. DOI: 10.1063/1.5121440
Media Contact
Liz Ahlberg Touchstone
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




