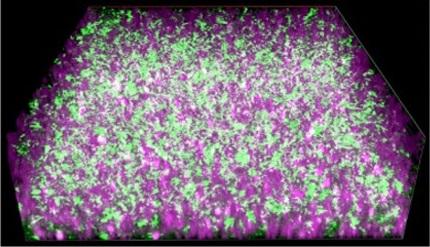
Credit: ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2020, DOI: 10.1021/acsami.9b22116
Someday, microbial cyborgs — bacteria combined with electronic devices — could be useful in fuel cells, biosensors and bioreactors. But first, scientists need to develop materials that not only nurture the microbes, but also efficiently and controllably harvest the electricity or other resources they make. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have developed one such material that enabled them to create a programmable “biohybrid” system that conducts electrons from electricity-producing (exoelectrogenic) bacteria.
Unlike other bacteria, exoelectrogens can move electrons across their outer membrane to the outside of their cell. Scientists have tried to harness this electricity by using various materials to conduct the electrons to an electrode. So far, however, conductive materials that support bacterial growth have been either inefficient, or not easily programmable to control the electrical current. Christof Niemeyer and colleagues wanted to develop a nanocomposite material that supports exoelectrogen growth while conducting electricity in a controlled way.
The researchers made a porous hydrogel composed of carbon nanotubes and silica nanoparticles, woven together by DNA strands. They added exoelectrogenic bacteria to this scaffold, along with liquid culture medium to supply the microbes with nutrients. The material efficiently conducted the electrons produced by the bacteria to an electrode. The bacteria grew well on the material, completely penetrating it. To cut off the electricity, the researchers added an enzyme that snipped DNA strands, causing the material to disassemble. The conductivity and other properties of the material could also be tailored by varying the size and sequence of the DNA fragments that hold the scaffold together, the researchers say.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the Helmholtz programme “BioInterfaces in Technology and Medicine,” the Chinese Scholarship Council and the Swedish Research Council.
The abstract that accompanies this paper can be viewed here.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and its people. The Society is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a specialist in scientific information solutions (including SciFinder® and STN®), its CAS division powers global research, discovery and innovation. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]




