Credit: Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,TMDU
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) develop an artificial intelligence system that effectively evaluates endoscopic mucosal findings from patients with ulcerative colitis without the need for biopsy collection
Tokyo, Japan – Assessments of patients with ulcerative colitis (UC), which is a type of inflammatory bowel disease, are usually conducted via endoscopy and histology. But now, researchers from Japan have developed a system that may be more accurate than existing methods and may reduce the need for these patients to undergo invasive medical procedures.
In a study published this February in Gastroenterology, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have revealed a newly developed artificial intelligence (AI) system that can evaluate endoscopic findings of UC with an accuracy equivalent to that of expert endoscopists.
Accurate evaluations are critical in providing optimal care for patients with UC. Previous studies have indicated that both endoscopic remission, evaluated via assessment of endoscopic procedure, and histological remission, as indicated by the degree of microscopic inflammation, can predict patient outcomes, and are thus frequently used as treatment goals. However, intra- and inter-observer variations occur in both endoscopic and histological analyses, and histological analysis frequently requires the collection of tissue via biopsies, which are invasive and costly.
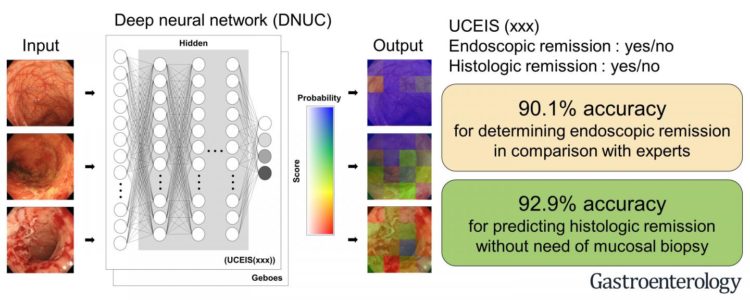
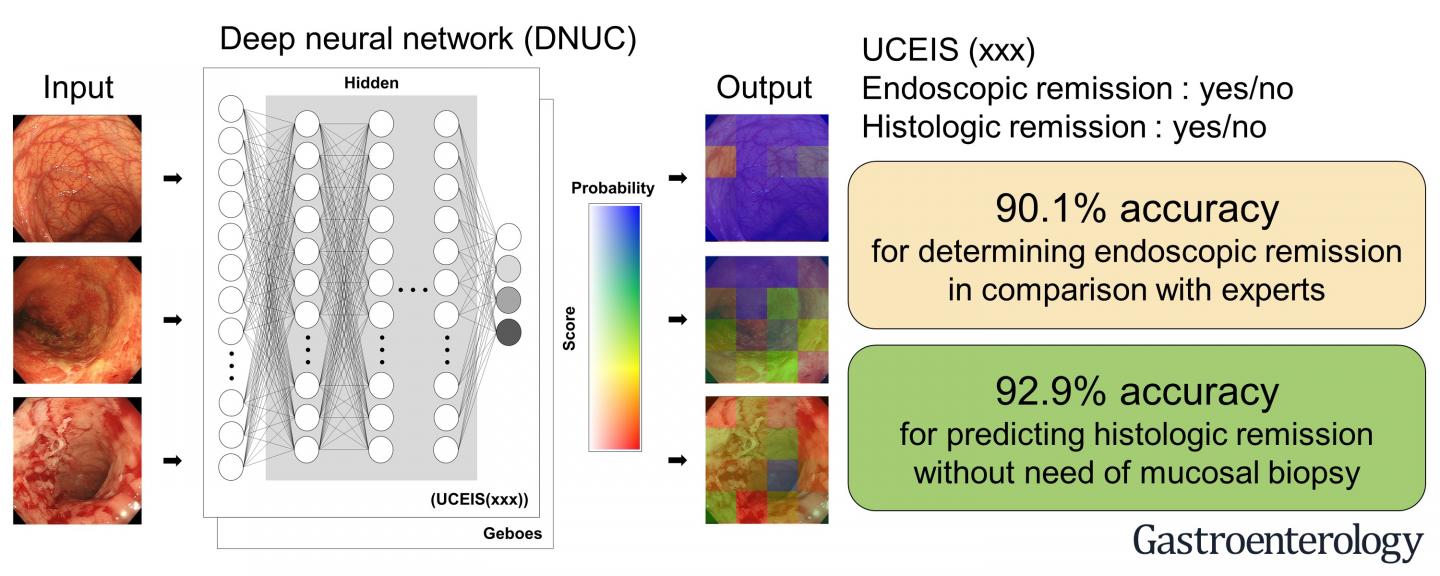
“The interpretation of endoscopic images is subjective and based on the experience of individual endoscopists, thereby making the standardization of evaluation and real-time characterization challenging,” says lead author of the study Kento Takenaka. “To address this, we sought to develop a deep neural network (DNN) system for consistent, objective, and real-time analysis of endoscopic images from patients with UC (DNUC).”
To do this, the researchers developed a system with DNNs to evaluate endoscopic images from patients with UC. DNNs are a type of AI machine-learning method that is based on the construction of artificial neural networks.
“We constructed the DNUC algorithm, using 40,758 images of colonoscopies and 6885 biopsy results from 2012 patients with UC,” says senior author Mamoru Watanabe. “This comprised the training set for machine-learning, which enabled the algorithm to learn to accurately evaluate and classify the data”.
The researchers then validated the accuracy of the DNUC algorithm using 4187 endoscopic images and 4104 biopsy specimens from 875 patients with UC.
“We found that the DNUC achieved a level of accuracy that was equivalent to that of expert endoscopists,” says Takenaka. “Thus, our system was able to predict histologic remission from UC using endoscopic images only, as opposed to both histological and endoscopic data. This represents an important development given the costs and risks associated with biopsies.”
The DNUC may be able to identify UC patients who are in remission without requiring them to undergo biopsy collection and analysis. This could save time and money for medical institutions, and limit exposure to invasive medical procedures for individuals with UC.
###
The article, “Development and Validation of a Deep Neural Network for Accurate
Evaluation of Endoscopic Images From Patients with Ulcerative Colitis”, was published in Gastroenterology at DOI:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.012
Media Contact
Mamoru WATANABE,Kento TAKENAKA
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.