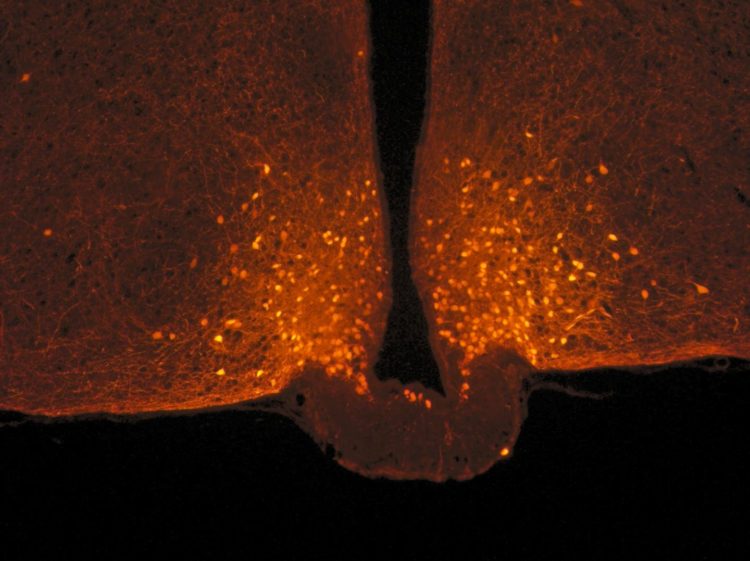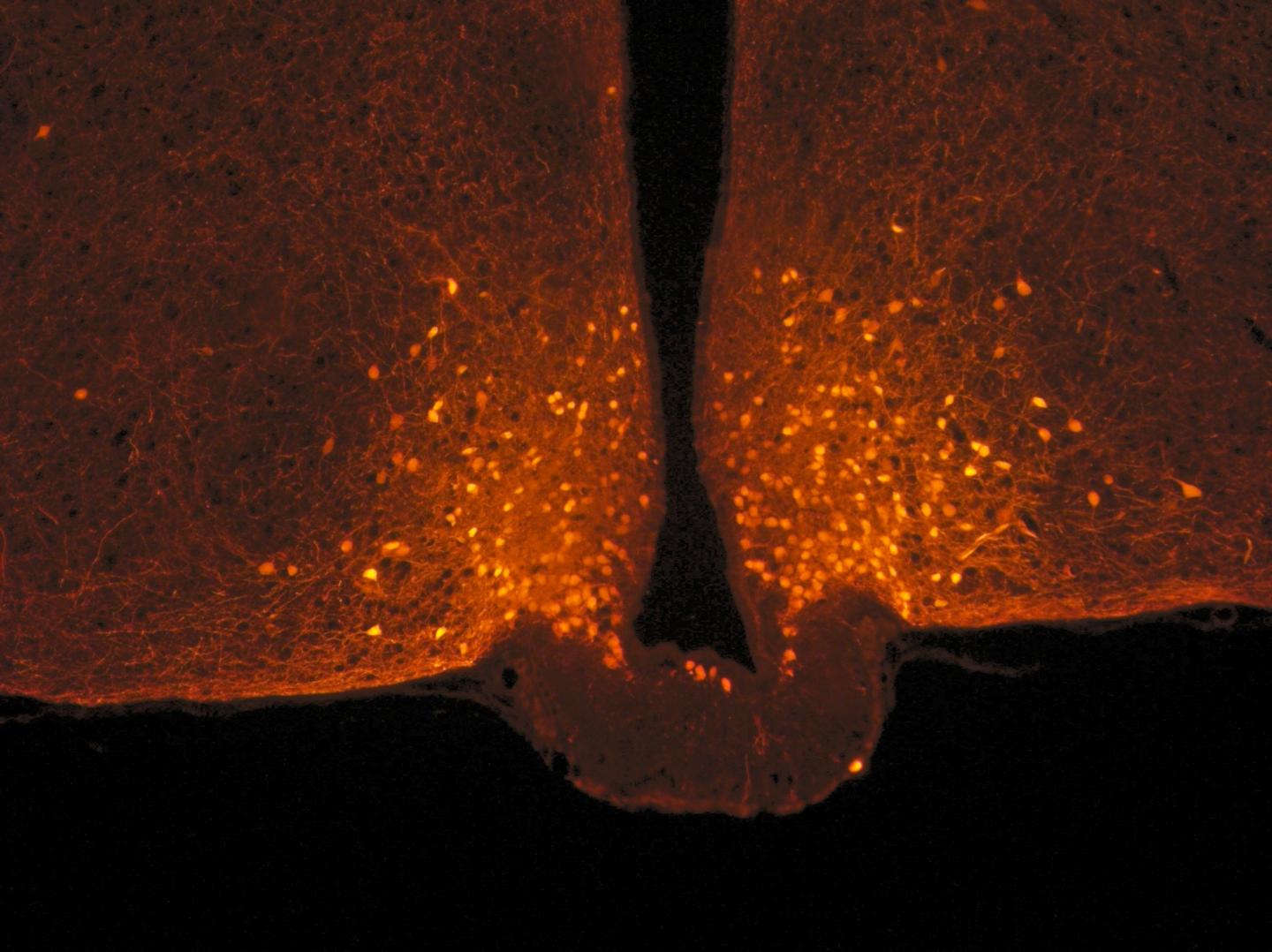
Credit: Danaé Nuzzaci / CNRS / CSGA
You just finished a good meal and are feeling full? Researchers from the CNRS, Inrae, University of Burgundy, Université de Paris, Inserm, and University of Luxembourg (1) have just revealed the mechanisms in our brains that lead to this state. They involve a series of reactions triggered by a rise in blood glucose levels. This study, which was conducted on mice, is published in Cell Reports on 3 March 2020.
The neuronal circuits in our brain governing feelings of hunger and satiety can modify their connections, thereby adjusting feeding behaviour to living conditions and maintaining a balance between food intake and calorie expenditure. Scientists suspect that this plasticity could be altered for obese subjects.
In a new study conducted on mice, a team led by Alexandre Benani, a CNRS researcher at the Centre for Taste and Feeding Behavior (CNRS/Inrae/University of Burgundy/AgroSup Dijon), has shown that these circuits are activated on the time scale of a meal, subsequently regulating feeding behaviour. However, this activation does not occur through a change in the circuit’s “connections.”
Scientists focused on POMC neurons in the hypothalamus, located at the base of the brain, which are known for limiting food intake. They are connected to a large number of neurons from other parts of the brain, with the connections of this circuit being malleable: they can be made and unmade very quickly based on hormonal fluctuations. Researchers observed that this neuronal circuit is not modified after a balanced meal, but that other nerve cells associated with POMC neurons, known as astrocytes, actually change form.
Astrocytes are star-shaped nerve cells that were first studied for their supporting role with respect to neurons. Under usual conditions, they sheathe POMC neurons and act somewhat like brake pads by limiting their activity. After a meal, blood glucose levels (glycaemia) temporarily increase, with astrocytes detecting this signal and retracting in less than one hour: once this “brake” is released, POMC neurons are activated, ultimately promoting the feeling of satiety.
Surprisingly, a meal that is high in fats does not lead to this remodelling. Does this mean that lipids are less effective in satisfying hunger? The scientists are trying to determine whether they trigger satiety through another circuit. It also remains to be seen whether sweeteners have the same effects, or whether they lure the brain by providing an addictive sensation of sweetness without satisfying hunger.
###
Notes
(1) The study was led by the Centre for Taste and Feeding Behavior (CNRS/Inrae/University of Burgundy/Agrosup Dijon), in close collaboration with colleagues from the Institute of Molecular and Cellular Pharmacology (CNRS/Université Côte d’Azur), Institute for Functional Genomics (CNRS/Inserm/ University of Montpellier), and University of Luxembourg / Luxembourg Center of Neuropathology, along with contributions from l’Unité de biologie fonctionnelle et adaptative (CNRS/Université de Paris) and Institute of Psychiatry and Neuroscience of Paris (Inserm/Université de Paris).
Media Contact
Veronique Etienne
[email protected]
33-144-965-137
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.