Credit: Department of Biochemistry,TMDU
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) discover a novel mechanism by which claudin-1 contributes to the progression of tongue squamous cell carcinoma
Tokyo, Japan – While it is known that most cancers try to grow and spread to the rest of the body, for many cancers it is unclear how they actually achieve taking over the host’s body. In a new study published in Cancer Science, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) revealed a novel mechanism by which tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC) exploits a protein whose task actually is to keep the tissue together.
A group of cells, also called tissue, is held together by a number of proteins that form a complex called tight junctions on the cell surface. Their function is to provide stability to the tissue as well as to prevent leakage of transported solutes and water by ensuring that molecules only pass through, and not between, the cells. One of the proteins that is part of tight junctions is claudin-1. Several studies have shown that claudin-1 plays an important role in several cancers, such as oral, gastric, liver and colon cancer.
“The amount of claudin-1 that a cancer makes has not been shown to correlate with how malignant that cancer is,” says corresponding author of the study Miki Hara-Yokoyama. “The goal of our study was to understand at the molecular level how claudin-1 is involved in cancer progression.”
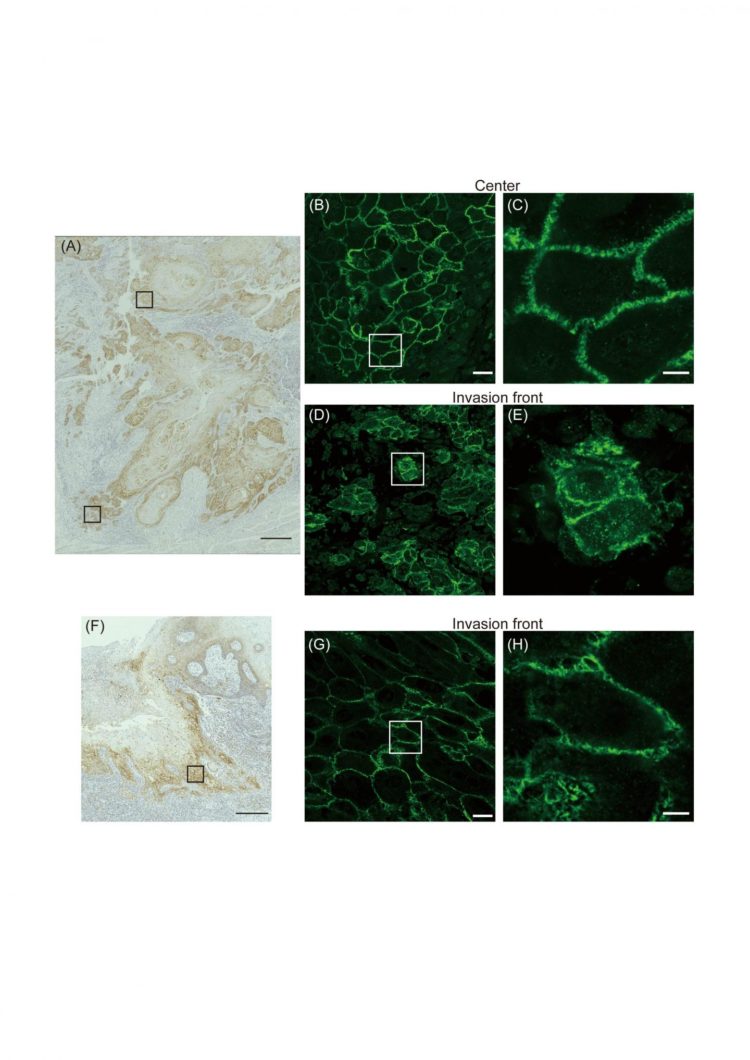
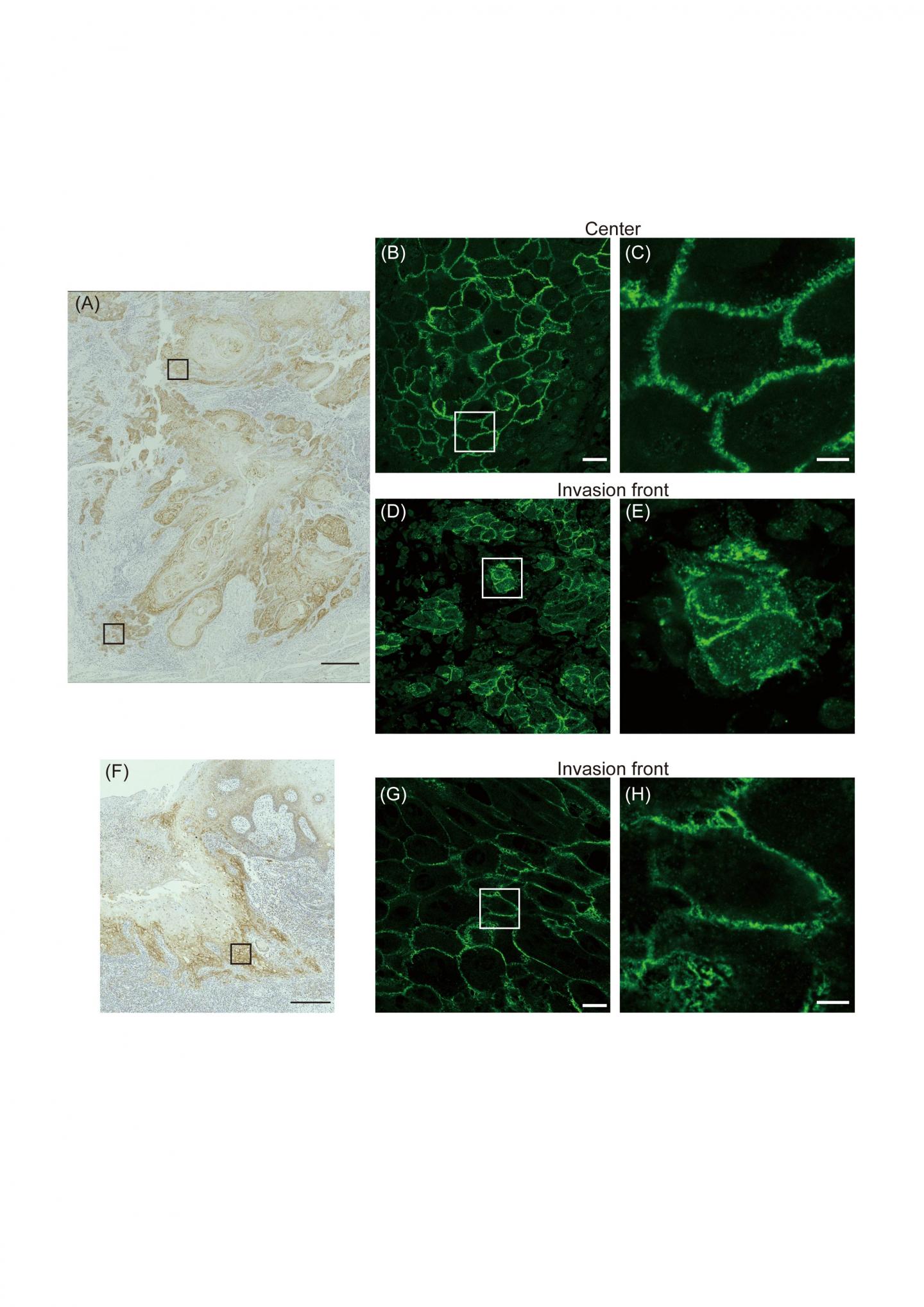
To achieve their goal, the researchers investigated specimens from patients with TSCC for the amount of claudin-1 produced by the cancer, as well as where in the cancer cell the protein is located. Given that claudin-1 is part of tight junctions, one might expect that they are naturally localized to the cell surface. It turns out it is not that simple.
“We know that localization is a key determinant of protein function. So we wanted to know if the localization of claudin-1 was connected to the progression of TSCC,” says lead author of the study Daisuke Yamamoto.
The researchers found that although the total amount of claudin-1 in TSCC cells and the invasiveness of the cancer were not associated, the amount of claudin-1 localized to the interior of the cell increased with the degree of cervical lymph node metastasis. They then isolated cells from TSCC and showed that when claudin-1 is locked within the cells or when the cells are entirely depleted of claudin-1, the cancer cells become more migratory.
“These are striking results that show how cancer cells break free from a tissue and increase their motility to invade lymph nodes and other organs of the body,” says Hara-Yokoyama. “Invasive cancers that are capable of spreading and disabling vital organ functions are often very difficult to contain. Our findings could offer a novel therapy to prevent cancers from progressing and metastasizing.”
###
The article, “Intracellular claudin-1 at the invasive front of tongue squamous cell carcinoma is associated with lymph node metastasis,” was published in Cancer Science at DOI: 10.1111/cas.14249
Media Contact
Miki YOKOYAMA
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.