Credit: Dr Olof Johansson
Tiny, laser-activated magnets could enable cloud computing systems to process data up to 100 times faster than current technologies, a study suggests.
Chemists have studied a new magnetic material that could boost the storage capacity and processing speed of hard drives used in cloud-based servers.
This could enable people using cloud data systems to load large files in seconds instead of minutes, researchers say.
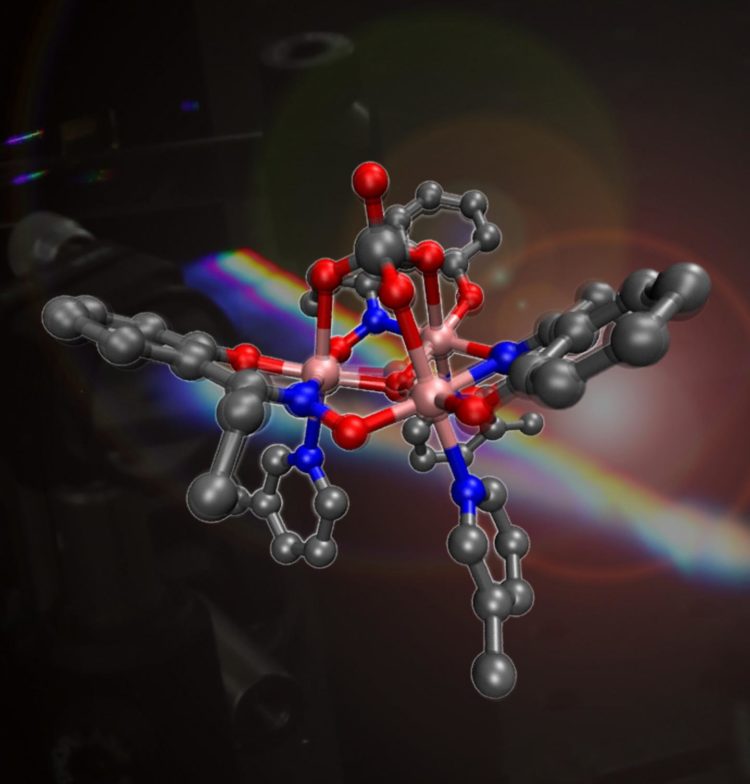
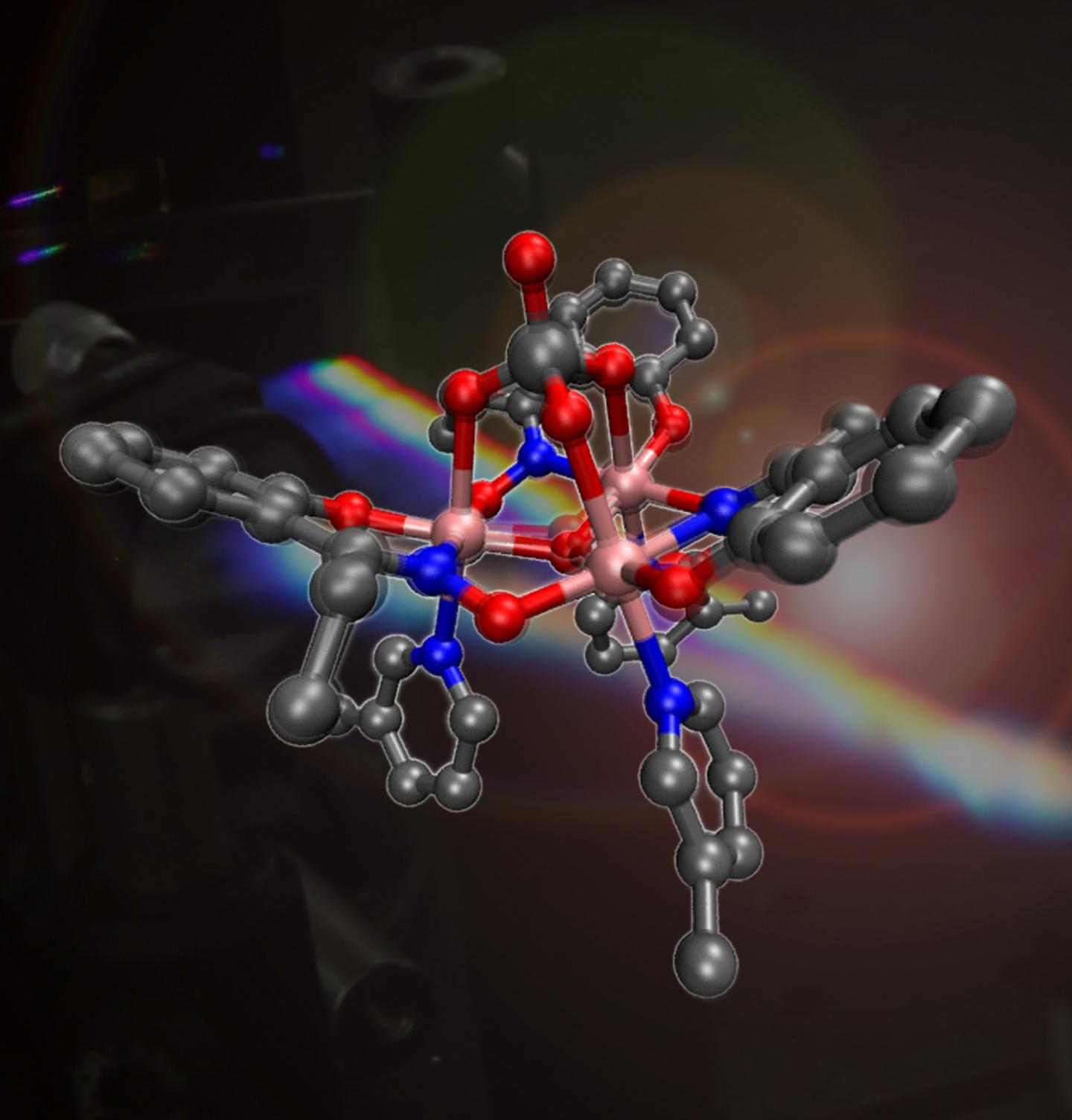
A team led by scientists from the University of Edinburgh created the material – known as a single-molecule magnet – in the lab.
They discovered that a chemical bond that gives the compound its magnetic properties can be controlled by shining rapid pulses from a laser on it. The compound is composed mainly of the element manganese, which is named after the Latin word magnes, which means magnet.
Their findings suggest that data could be stored and accessed on the magnets using laser pulses lasting one millionth of a billionth of a second. They estimate this could enable hard drives fitted with the magnets to process data up to 100 times faster than current technologies.
The development could also improve the energy efficiency of cloud computing systems, the team says, which collectively emit as much carbon as the aviation industry.
Existing hard drives store data using a magnetic field generated by passing an electric current through a wire, which generates a lot of heat, researchers say. Replacing this with a laser-activated mechanism would be more energy efficient as it does not produce heat.
The study, published in the journal Nature Chemistry, also involved researchers from Newcastle University. It was funded by the Royal Society of Edinburgh, the Carnegie Trust and the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council.
Dr Olof Johansson, of the University of Edinburgh’s School of Chemistry, who led the study, said: “There is an ever-increasing need to develop new ways of improving data storage devices. Our findings could increase the capacity and energy efficiency of hard drives used in cloud-based storage servers, which require tremendous amounts of power to operate and keep cool. This work could help scientists develop the next generation of data storage devices.”
###
Media Contact
Corin Campbell
[email protected]
44-131-650-6382