Credit: DU Xuemin
A research group led by Prof. DU Xuemin from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a “smart” contact lens that can show real-time changes in moisture and pressure by altering colors. The “smart” contact lens can potentially be used for point-of-care (POC) diagnosis of xerophthalmia and high intraocular pressure disease.
Early diagnosis is important for avoiding severe eye problems, such as exophthalmia – which causes relatively mild symptoms – or glaucoma – which may lead to loss of vision. Such diagnoses rely on facile and reliable monitoring of several features with significant pathologic relevance, such as the amount of tears and intraocular pressure.
However, current methods usually require complex procedures and instruments operated by professionals, causing difficulties for point-of-care (POC) ophthalmic health monitoring.
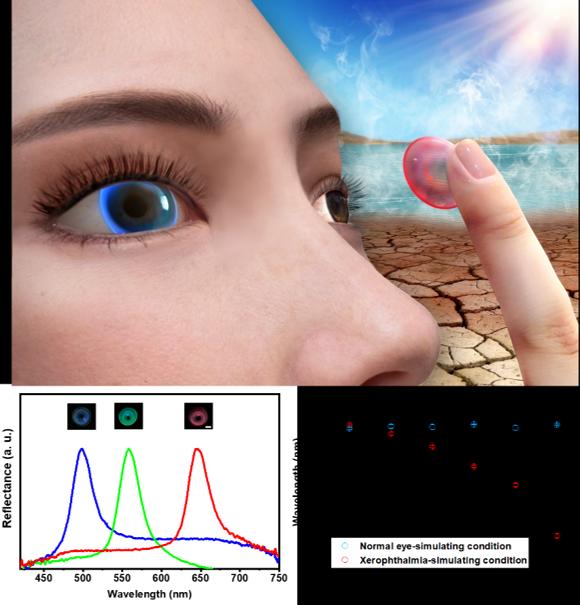
The “smart” contact lens features periodic nanostructures within the poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (pHEMA) hydrogel matrix, resulting in bright, tunable structural colors ranging from red to green to blue.
This structurally colored contact lens sensor is made solely from a biocompatible hydrogel, without the addition of any chemical pigments, thus exhibiting superior biosafety and comfort for wearable applications.
Importantly, the spacing of periodic nanostructures within the pHEMA hydrogel are sensitive to changes in moisture and pressure, leading to real-time color changes in the “smart” contact lens.
“Based on these features, the ‘smart’ contact lens was explored as a means for monitoring xerophthalmia and high intraocular pressure disease. In normal eye-simulation conditions, its color will not change over time; while its color changes from red to blue in the xerophthalmia-simulation condition in about 25 minutes,” said ZHAO Qilong, first author of the study.
Additionally, a linear decrease in the wavelength of the reflectance peak of the “smart” cosmetic contact lens is observed when human intraocular pressure changes in the pathological range.
“This study provides a novel and smart wearable device for timely and facile warning of the risks of xerophthalmia and high intraocular pressure disease. It will also inspire the design of a new generation of wearable devices with colorimetric sensing capabilities for real-time POC monitoring of various human body signs and diseases,” said Prof. DU.
###
The results were published in Journal of Materials Chemistry B.
Media Contact
ZHANG Xiaomin
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




