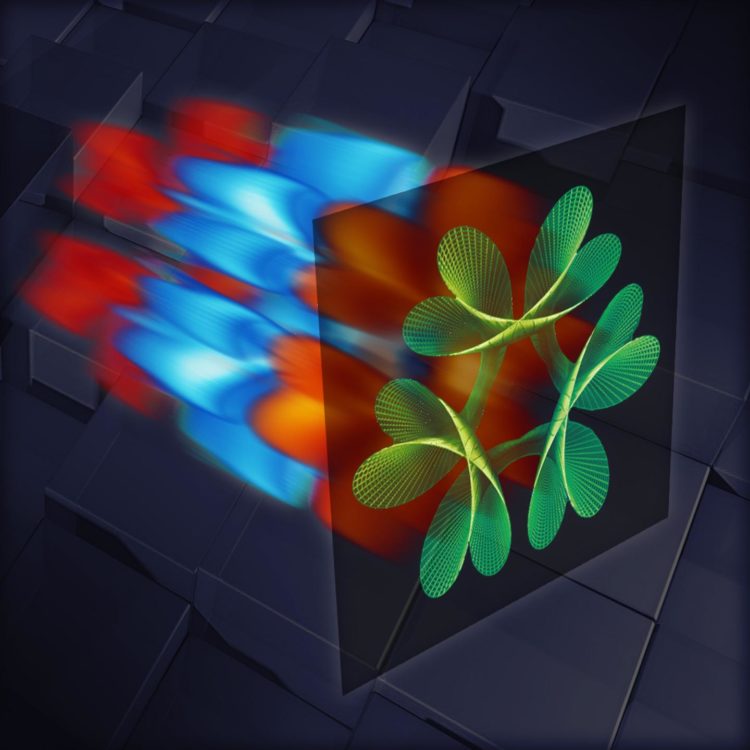
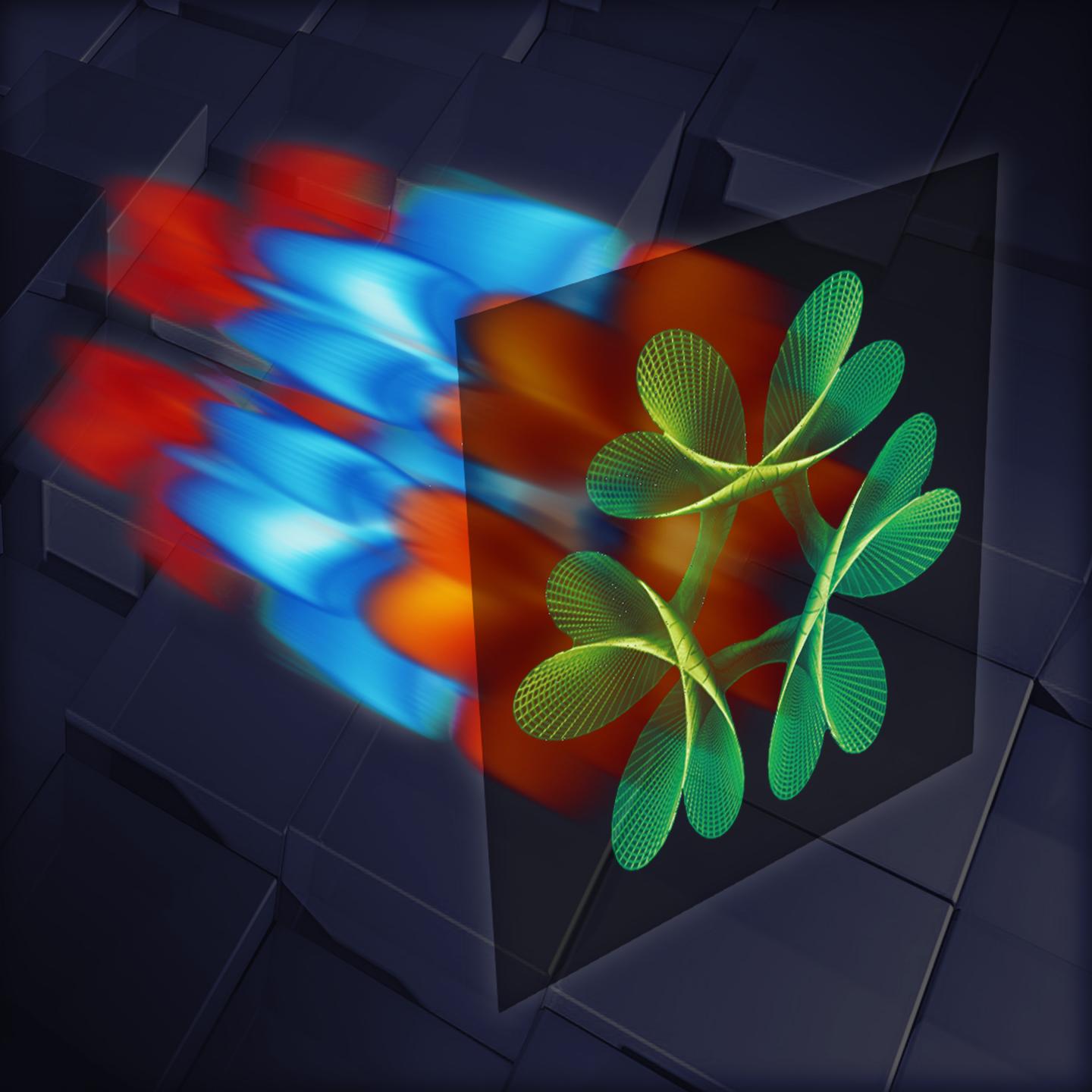
Terahertz camera uses laser light patterns to ‘see inside’ objects — Terahertz imaging can reveal tiny hidden features of living things
Credit: University of Sussex
A team of physicists at the University of Sussex has successfully developed the first nonlinear camera capable of capturing high-resolution images of the interior of solid objects using terahertz (THz) radiation.
Led by Professor Marco Peccianti of the Emergent Photonics (EPic) Lab, Luana Olivieri, Dr Juan S. Totero Gongora and a team of research students built a new type of THz camera capable of detecting THz electromagnetic waves with unprecedented accuracy.
Images produced using THz radiation are called ‘hyperspectral’ because the image consists of pixels, each one containing the electromagnetic signature of the object in that point.
Lying between microwaves and infrared in the electromagnetic spectrum, THz radiation easily penetrates materials like paper, clothes and plastic in the same way X-rays do, but without being harmful. It is safe to use with even the most delicate biological samples. THz imaging makes it possible to ‘see’ the molecular composition of objects and distinguish between different materials – such as sugar and cocaine, for example.
Explaining the significance of their achievement, Prof Peccianti said: “The core challenge in THz cameras is not about collecting an image, but it is about preserving the objects spectral fingerprint that can be easily corrupted by your technique. This is where the importance of our achievement lies. The fingerprint of all the details of the image is preserved in such a way that we can investigate the nature of the object in full detail. “
Until now, cameras capable of capturing a hyperspectral image preserving all the fine details revealed by THz radiation had not been considered possible.
The EPic Lab team used a single-pixel camera to image sample objects with patterns of THz light. The prototype they built can detect how the object alters different patterns of THz light. By combining this information with the shape of each original pattern, the camera reveals the image of an object as well as its chemical composition.
Sources of THz radiation are very faint and hyperspectral imaging had, until now, limited fidelity. To overcome this, The Sussex team shone a standard laser onto a unique non-linear material capable of converting visible light to THz. The prototype camera creates THz electromagnetic waves very close to the sample, similar to how a microscope works. As THz waves can travel right through an object without affecting it, the resulting images reveal the shape and composition of objects in three dimensions.
Dr Totero Gongora said: “This is a major step forward because we have demonstrated that all the possibilities explored in our previous theoretical research are not only feasible, but our camera works even better than we expected. While building our device, we discovered several ways to optimise the imaging process and now the technology is stable and works well. The next phase of our research will be in speeding up the image reconstruction process and taking us closer to applying THz cameras to real-world applications; like airport security, intelligent car sensors, quality control in manufacturing and even scanners to detect health problems like skin cancer.”
###
Note to editors: Hyperspectral terahertz microscopy via nonlinear ghost-imaging is published in the OSA Optica Journal, https:/
Media Contact
Margaret Ousby
[email protected]
01-273-873-685
Original Source
https:/