Osaka University-led study shows that semaphorin protein induces allergic reactions and causes formation of nasal polyps in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis
Credit: Osaka University
Osaka, Japan – Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis (ECRS) is a type of airway disease involving nasal inflammation. Many studies have attempted to understand the molecular-based pathogenesis of recurrent ECRS; none have provided a clear explanation, until now.
In a new study published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, a team led by researchers from Osaka University investigated the activity of semaphorin protein, a cell-surface molecule that participates in nervous system signaling and immune responses. They found that semaphorin protein contributes to allergic reactions and development of nasal polyps in patients with ECRS.
In ECRS, inflammation leads to development of nasal polyps containing eosinophils (a subset of white blood cells). Treatment options include sinus surgery and systemic glucocorticoids. However, the effectiveness of these treatments can be insufficient and multiple side effects can occur. Thus, targeted molecular therapies may provide novel treatment options for patients with ECRS without these drawbacks. Because semaphorin has been identified in inflamed airway tissues, it is an attractive candidate for use in such therapies.
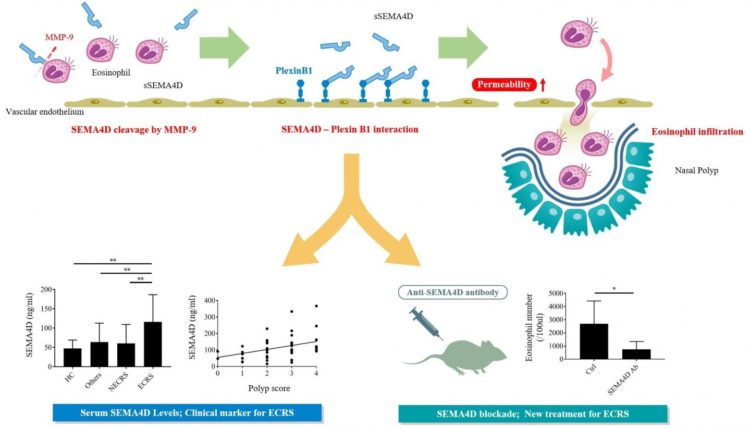
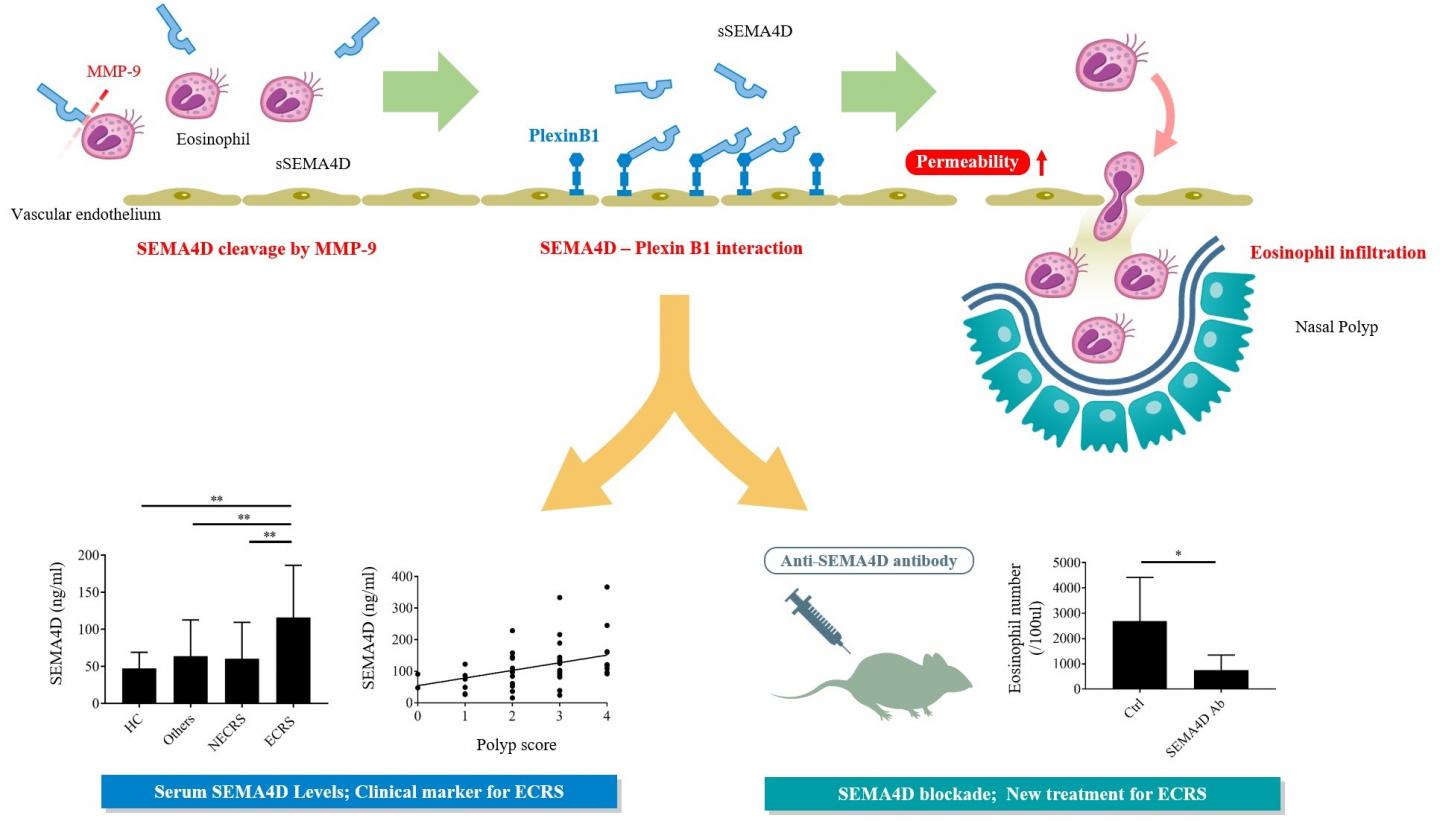
“In this study, we found that serum levels of semaphorin proteins were elevated in patients with ECRS, and that these levels were positively associated with multiple measures of disease severity,” says Masayuki Nishide, corresponding author on the study. “We suspected that semaphorin protein played an important role in the pathogenesis of ECRS.”
The Osaka University team found that activated eosinophils expressed high levels of semaphorin protein on the cell surface, which could be released into the surrounding environment through an enzymatic reaction. This soluble form of semaphorin protein could enable eosinophils to pass through endothelial cell lining, resulting in the onset of inflammation and formation of nasal polyps.
“Our analyses revealed that, in a mouse model of ECRS, mice without semaphorin protein had less nasal inflammation than normal mice, so we tested whether blocking semaphorin with an antibody could affect inflammation in normal mice with ECRS,” says Takeshi Tsuda, lead author on the study. “As expected, we found that treatment with an anti-semaphorin antibody substantially reduced nasal inflammation in mice with ECRS.”
Based on the results in the mouse model, the Osaka team concluded that anti-semaphorin antibody could provide a new treatment option for patients with ECRS. Additionally, the increased levels of semaphorin protein in patients with ECRS suggest that semaphorin protein can be used as a biomarker for ECRS in patients with nasal inflammation.
###
The article, “Pathological and therapeutic implications of eosinophil-derived semaphorin 4D in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis,” was published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology at DOI: https:/
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and now has expanded to one of Japan’s leading comprehensive universities. The University has now embarked on open research revolution from a position as Japan’s most innovative university and among the most innovative institutions in the world according to Reuters 2015 Top 100 Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017. The university’s ability to innovate from the stage of fundamental research through the creation of useful technology with economic impact stems from its broad disciplinary spectrum.
Website: https:/
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
81-661-055-886
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.