Credit: Bryan Smith, Michigan State University
Michigan State University and Stanford University scientists have invented a nanoparticle that eats away – from the inside out – portions of plaques that cause heart attacks.
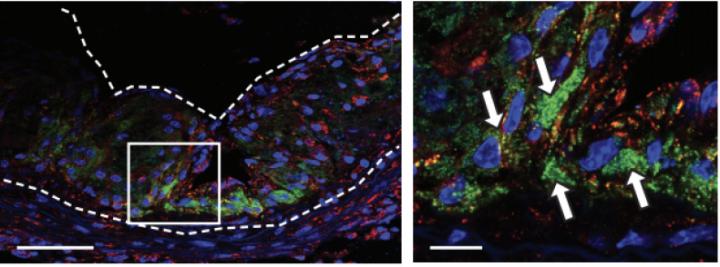
Bryan Smith, associate professor of biomedical engineering at MSU, and a team of scientists created a “Trojan Horse” nanoparticle that can be directed to eat debris, reducing and stabilizing plaque. The discovery could be a potential treatment for atherosclerosis, a leading cause of death in the United States.
The results, published in the current issue of Nature Nanotechnology, showcases the nanoparticle that homes in on atherosclerotic plaque due to its high selectivity to a particular immune cell type – monocytes and macrophages. Once inside the macrophages in those plaques, it delivers a drug agent that stimulates the cell to engulf and eat cellular debris. Basically, it removes the diseased/dead cells in the plaque core. By reinvigorating the macrophages, plaque size is reduced and stabilized.
Smith said that future clinical trials on the nanoparticle are expected to reduce the risk of most types of heart attacks, with minimal side effects due to the unprecedented selectivity of the nanodrug.
Smith’s studies focus on intercepting the signaling of the receptors in the macrophages and sending a message via small molecules using nano-immunotherapeutic platforms. Previous studies have acted on the surface of the cells, but this new approach works intracellularly and has been effective in stimulating macrophages.
“We found we could stimulate the macrophages to selectively eat dead and dying cells – these inflammatory cells are precursor cells to atherosclerosis – that are part of the cause of heart attacks,” Smith said. “We could deliver a small molecule inside the macrophages to tell them to begin eating again.”
This approach also has applications beyond atherosclerosis, he added.
“We were able to marry a groundbreaking finding in atherosclerosis by our collaborators with the state-of-the-art selectivity and delivery capabilities of our advanced nanomaterial platform. We demonstrated the nanomaterials were able to selectively seek out and deliver a message to the very cells needed,” Smith said. “It gives a particular energy to our future work, which will include clinical translation of these nanomaterials using large animal models and human tissue tests. We believe it is better than previous methods.”
Smith has filed a provisional patent and will begin marketing it later this year.
Note for media: Please include a link to the original paper in online coverage: https:/
###
Media Contact
Layne Cameron
[email protected]
517-353-8819
Original Source
https:/




