Discovery that radiation creates breaks that allow in foreign DNA must be confirmed in animal studies
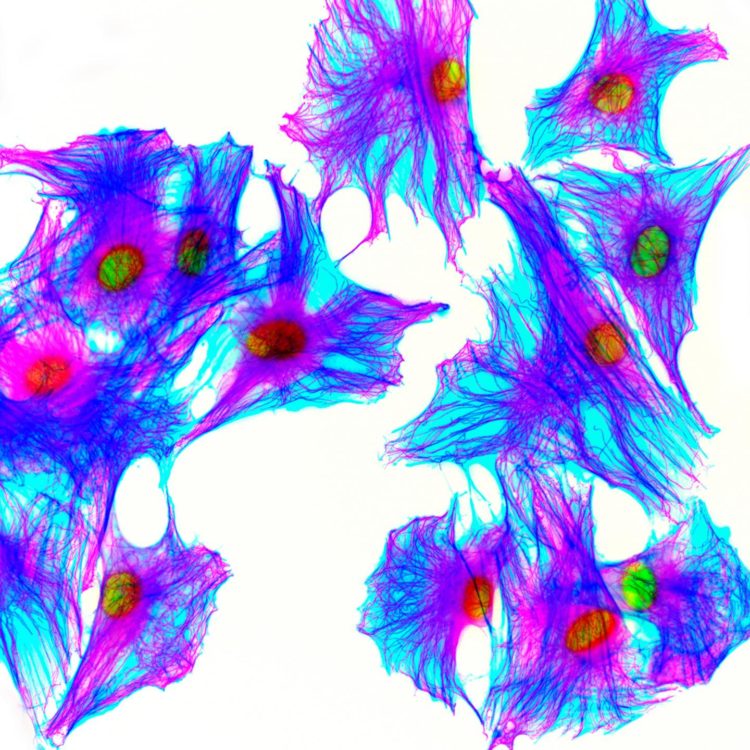
Credit: Kevin Mackenzie, University of Aberdeen, Wellcome Collection
Common medical imaging procedures use low doses of radiation that are believed to be safe. A new study, however, finds that in human cell cultures, these doses create breaks that allow extra bits of DNA to integrate into the chromosome. Roland Kanaar and Alex Zelensky of Erasmus University Medical Center and Oncode Institute and colleagues report these new findings in a study published 16th January in PLOS Genetics.
Scientists have long known that exposing cells to high doses of ionizing radiation generates mutations by creating double-strand breaks that let in external segments of DNA. These extraneous fragments of DNA can occur in the nucleus, left over from natural processes, such as genomic DNA repair and viral infections. In the new study, researchers investigated whether low doses of ionizing radiation have damaging side effects by irradiating human and mouse cells grown in the lab. When they counted the cells that had taken up foreign DNA, they found that low doses of radiation, in the upper range of common diagnostic procedures, create mutations through inserted DNA even more efficiently than the much larger doses studied previously.
While the new results in cell cultures are potentially concerning, the study’s authors stress that translating radiation’s effects on lab-grown cell cultures to effects in the body is premature. Future experiments using animal models will be necessary to determine the full effects of low-dose radiation, and whether its use in medical imaging has an impact on patient health. If the same phenomenon does occur inside the body, then doctors may need to take into account levels of extraneous DNA, such those resulting from a long-term viral infection, when assessing a patient’s risk from a procedure that requires radiation.
“Most molecular radiobiological research is focused on high doses of ionizing radiation relevant to cancer treatment, while effects of physiologically relevant doses of radiation on the cell are notoriously difficult to study at the molecular level,” said author Roland Kanaar. “Our discovery that mutagenic insertion of foreign DNA into cell’s genome is remarkably responsive to doses encountered during diagnostic, rather than therapeutic, procedures provides a new simple and sensitive tool to study their consequences and revealed surprising molecular genetic details of how cells cope with natural amounts of DNA damage.”
###
Peer-reviewed; Experimental Study; Cells
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Genetics:
http://journals.
Citation: Zelensky AN, Schoonakker M, Brandsma I, Tijsterman M, van Gent DC, Essers J, et al. (2020) Low dose ionizing radiation strongly stimulates insertional mutagenesis in a γH2AX dependent manner. PLoS Genet 16(1): e1008550. https:/
Funding: RK was funded by Gravitation program CancerGenomiCs.nl from the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO, nwo.nl) RK funded by Oncode Institute (oncode.nl), which is partly financed by the Dutch Cancer Society (kwf.nl). DvG, JE were funded by European Atomic Energy Community’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2011) under grant agreement n° 249689. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Media Contact
Roland Kanaar
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.