Researchers with the joint US-Mexico-European HAWC Observatory have identified a host of galactic sources of super-high-energy gamma rays
Credit: Los Alamos National Laboratory
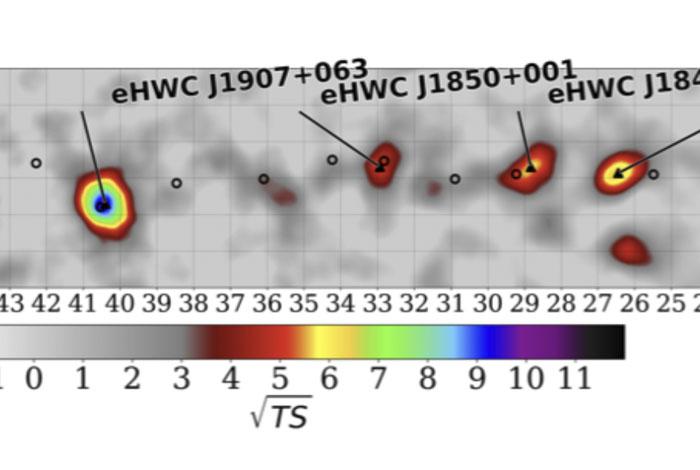
Nine sources of extremely high-energy gamma rays comprise a new catalog compiled by researchers with the High-Altitude Water Cherenkov (HAWC) Gamma-Ray Observatory. All produce gamma rays with energies over 56 trillion electron volts (TeV) and three emit gamma rays extending to 100 TeV and beyond, making these the highest-energy sources ever observed in our galaxy. The catalog helps to explain where the particles originate and how they are accelerated to such extremes.
“The Earth is constantly being bombarded with charged particles called cosmic rays, but because they are charged, they bend in magnetic fields and don’t point back to their sources. We rely on gamma rays, which are produced close to the sources of the cosmic rays, to narrow down their origins,” said Kelly Malone, an astrophysicist in the Neutron Science and Technology group at Los Alamos National Laboratory and a member of the HAWC scientific collaboration. “There are still many unanswered questions about cosmic-ray origins and acceleration. High energy gamma rays are produced near cosmic-ray sites and can be used to probe cosmic-ray acceleration. However, there is some ambiguity in using gamma rays to study this, as high-energy gamma rays can also be produced via other mechanisms, such as lower-energy photons scattering off of electrons, which commonly occurs near pulsars.”
For an affiliated video about the research, see Newly Discovered Gamma Ray Sources Have the Highest Energy Ever Recorded
The newly cataloged astrophysical gamma-ray sources have energies about 10 times higher than can be produced using experimental particle colliders on Earth. While higher-energy astrophysical particles have been previously detected, this is the first time specific galactic sources have been pinpointed. All of the sources have extremely energetic pulsars (highly magnetized rotating neutron stars) nearby. The number of sources detected may indicate that ultra-high-energy emission is a generic feature of powerful particle winds coming from pulsars embedded in interstellar gas clouds known as nebulae, and that more detections will be forthcoming.
The HAWC Gamma-Ray Observatory consists of an array of water-filled tanks sitting high on the slopes of the Sierra Negra volcano in Puebla, Mexico, where the atmosphere is thin and offers better conditions for observing gamma rays. When these gamma rays strike molecules in the atmosphere they produce showers of energetic particles. Although nothing can travel faster than the speed of light in a vacuum, light moves more slowly through water. As a result, some particles in cosmic ray showers travel faster than light in the water inside the HAWC detector tanks. The faster-than-light particles, in turn, produce characteristic flashes of light called Cherenkov radiation. By recording the Cherenkov flashes in the HAWC water tanks, researchers can reconstruct the sources of the particle showers to learn about the particles that caused them in the first place.
The HAWC collaborators plan to continue searching for the sources of high-energy cosmic rays. By combining their data with measurements from other types of observatories such as neutrino, x-ray, radio and optical telescopes, they hope to disentangle the astrophysical mechanisms that produce the cosmic rays that continuously rain down on our planet.
###
Video Clip: Newly Discovered Gamma Ray Sources Have the Highest Energy Ever Recorded
Publication: Multiple Galactic Sources with Emission Above 56 TeV Detected by HAWC, Physical Review Letters
Funding: Los Alamos LDRD, DOE-HEP
About Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory, a multidisciplinary research institution engaged in strategic science on behalf of national security, is operated by Triad, a public service oriented, national security science organization equally owned by its three founding members: Battelle Memorial Institute (Battelle), the Texas A&M University System (TAMUS), and the Regents of the University of California (UC) for the Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration.
Los Alamos enhances national security by ensuring the safety and reliability of the U.S. nuclear stockpile, developing technologies to reduce threats from weapons of mass destruction, and solving problems related to energy, environment, infrastructure, health, and global security concerns.
Media Contact
James Riordon
[email protected]
505-667-3272
Original Source
https:/




