Credit: University of Tokyo, NAOJ
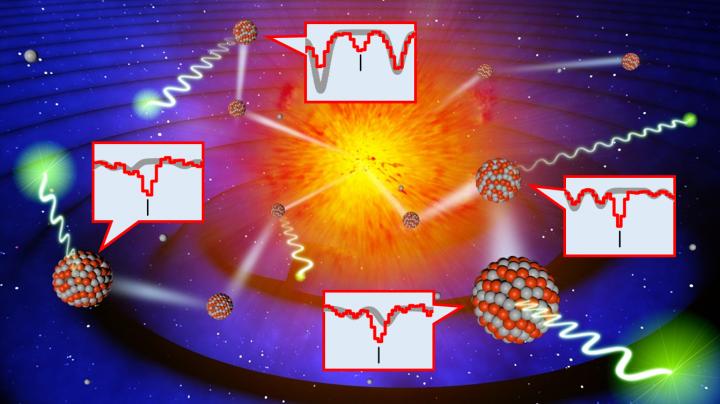
Astronomers have cataloged signs of 9 heavy metals in the infrared light from supergiant and giant stars. New observations based on this catalog will help researchers to understand how events like binary neutron star mergers have affected the chemical composition and evolution of our own Milky Way Galaxy and other galaxies.
Right after the Big Bang, the Universe contained only hydrogen and helium. Other elements were formed later through nuclear fusion in stars or violent events like supernovae or binary neutron star mergers. However, the details of the various processes and their relative contributions are still poorly understood. Better understanding of the chemical evolution of galaxies is important to understand how the rich element environment of planets like Earth came to be. In particular, metals heavier than nickel can be used to trace violent events such as binary neutron star mergers.
A research team including members from the University of Tokyo, Kyoto Sangyo University, and NAOJ used the WINERED near-infrared spectrograph on the 1.3 m Araki Telescope at Koyama Astronomical Observatory in Kyoto Japan to look for signs of heavy metals in 13 supergiant and giant stars. Large, bright supergiant and giant stars are easy to observe, even far away; and infrared light has the advantage that it can still be observed in regions where interstellar matter blocks visible light.
Every element present in a star produces a distinct “signature” in the star’s light by absorbing specific wavelengths of light. The team compared the spectrum, the detailed wavelength information, of each star to libraries containing dozens of theoretically predicted absorption lines and found that 23 lines produced by 9 elements ranging from zinc to dysprosium could actually be observed.
Based on these results, astronomers can now measure the levels of these heavy metals in other stars to map the chemical diversity and evolution of the Milky Way and other galaxies.
###
Media Contact
Dr. Hitoshi Yamaoka
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




