Extirpations of 5 megafauna taxa from much of China over the past 2 millennia were found to be closely linked to filtering effects driven by cultural evolution rather than climate change
Credit: Shuqing Teng
Cultural evolution has been the dominant driver of range contractions in megafauna taxa across China since the beginning of Common Era, with little or no direct importance of climate. A research team led by Aarhus University along with collaborators from Nanjing University analyzed maps of megafauna distribution dynamics and societal development based on Chinese archival records alongside data on climate across China from 2 to 1953 CE.
Human activities are now playing a dominant role in driving changes in Earth’s biodiversity and are responsible for the incipient sixth mass extinction, but the historical processes leading to this situation are poorly understood, often without emphasis on cultural evolution as a potential key process underlying anthropogenic impacts. A team of researchers from Aarhus University and Nanjing University has now shown that cultural evolution overshadowed climate change in driving historical broad-scale biodiversity dynamics.
By mining the deep Chinese administrative records in relation to culturally important wild megafauna species as well as sociocultural development, the researchers identified the millennia-long spread of agricultural land and agricultural intensification, as well as the specific expansion of the Han culture, as the main cause of the extirpation of five megafauna species from much of China, with little or no direct importance of climate.
Cultural evolution, not climate change, as the main driver
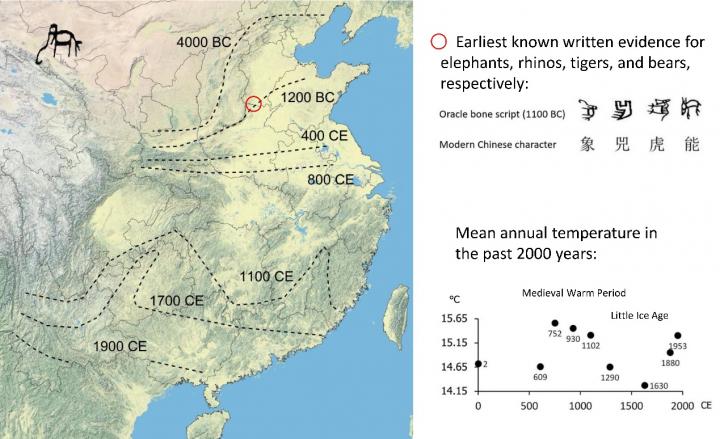
“China’s well-preserved written records for more than 2000 years provide a unique opportunity to reconstruct long-term dynamics of culture-nature interactions across large geographical extents,” says senior author Professor Jens-Christian Svenning, director of Center for Biodiversity Dynamics in Changing World (BIOCHANGE), Aarhus University. The five studied megafauna taxa include Asiatic elephant (Elephas maximus), Asian rhinoceroses (Rhinoceros sondaicus, R. unicornis and Dicerorhinus sumatrensis), tiger (Panthera tigris), Asiatic black bear (Ursus thibetanus), and brown bear (Ursus arctos), all of which were widely distributed across the study area and have played an important role in ancient China’s cultural activities.
“Ancient China used to host a highly biodiverse assemblage of large mammals even in its nowadays densely populated areas such as the North China Plain and the Middle-Lower Yangtze Plain. Our research shows that the relatively recent loss of this rich megafauna in large part can be attributed to the southward expansion of intensified agricultural practices with the Han culture, which originated in North China,” explains postdoc Shuqing Teng from Aarhus University and Nanjing University, the first author of the study.
Regional extirpation of these taxa from the study area were consistent with the sociocultural dynamics described above, but inconsistent with climate change. There were at least two conspicuous cooling-warming cycles during the last two thousand years, including the Medieval Warm Period and the Little Ice Age, with fluctuations of mean annual temperature around 1 to 1.5 °C, but neither had a conspicuous effect on the megafauna range dynamics.
Importance of cultural filtering
The study provides clear evidence that cultural evolution historically has overshadowed past climate change in shaping broad-scale megafauna patterns, in contrast to the common belief that human societies were unimportant in driving biodiversity dynamics at such large spatiotemporal scales until recent time frames such as the Industrial Revolution or the Great Acceleration of the 20th century.
This finding highlights the importance of culture’s role in filtering current ecological assemblages from historical species pools. Perspectives through the lens of cultural filtering should also stimulate thoughts on what is natural – notably helping to overcome the Shifting Baseline Syndrome, the tendency to accept an already degraded state as natural due to lacking recognition of earlier declines – and which natural world we aim to conserve or restore.
Furthermore, modification of cultural filters will be key to respond to the challenges of the Anthropocene biodiversity crisis, as it is fundamentally culturally driven, as shown by this study of historical China, and how to achieve this is an important research challenge.
###
Media Contact
Jens-Christian Svenning
[email protected]
45-28-99-23-04
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




