Credit: Department of Molecular Oncology,TMDU
Tokyo, Japan – Biliary tract cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the bile ducts, which transport bile from the liver to the duodenum. While generally rare, these cancers are relatively common in Asian populations. Patients with one form of this cancer, called intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC), have very poor outcomes and rarely survive beyond five years after their diagnosis. In a new study, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have uncovered a protein that may eventually help doctors predict which patients with ICC will have the worst outcomes – and that may someday lead to more effective treatments for ICC.
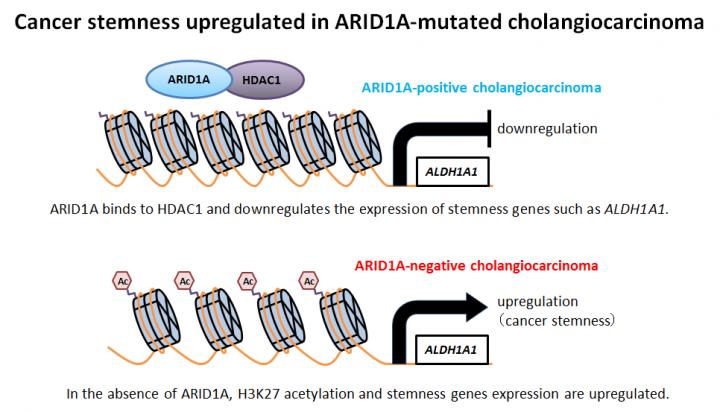
Recent studies have found that ICC tumors tend to have genetic mutations leading to the loss of a protein called ARID1A (AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 1A). However, the exact role of the protein in ICC was unknown.
“ARID1A is known to take part in complexes that control gene expression,” says Jun Yoshino, lead author of the study. “This hinted that loss of ARID1A could play a role in ICC by causing certain genes to turn on or off. However, it wasn’t clear which genes might be affected or how their expression might impact the ICC disease course.”
To answer this question, the researchers looked at ICC cell lines – cells that are grown in dishes and commonly used as a model for ICC tumors. Using the genome editing technique CRISPR/Cas9, the researchers deleted the gene coding for ARID1A, resulting in “knock-out” cells that mimic patients who have ARID1A-negative ICC tumors. The team discovered that when they removed ARID1A, the cells became especially malignant.
“We found that ARID1A suppresses a stemness gene ALDH1A1 implicated in other cancers. Removing ARID1A causes the gene to become highly overactive in ICC cells,” explains Dr Yoshino. “We found that when this cancer stemness gene is overactive, it causes the cells to act much more aggressively. For example, the cells can migrate and invade neighboring groups of cells, a behavior that is very common in highly-active cancers.”
The aggressive behavior of the cells suggested that ARID1A-negative ICC might represent a distinct form of the cancer, perhaps with a distinct prognosis. To confirm this suspicion, the team measured levels of ARID1A in tissue samples from patients with ICC, and then followed their medical history to see how well the patients eventually fared. They found that patients who were ARID1A-negative indeed had much poorer outcomes: five years after their diagnosis, less than 20% of ARID1A-negative patients had survived, compared with over 50% of ARID1A-positive patients.
“ARID1A-negative patients are more likely to have high levels of a tumorigenic gene, which in turn enhances the malignancy of their cancer,” says Shinji Tanaka, corresponding author of the study. “This has important medical implications for patients with ICC. For one, it may be possible to use ARID1A as a biomarker to help physicians predict the prognosis of their patients. What’s more, further research into how ARID1A functions could someday lead to more sophisticated treatment methods for this form of the disease.”
###
The article, “Loss of ARID1A induces a stemness gene ALDH1A1 expression with histone acetylation in the malignant subtype of cholangiocarcinoma” was published in Carcinogenesis at DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgz179.
Media Contact
Shinji TANAKA
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




