Transfer RNA recognition mechanism of eukaryotic tRNA methyltransferase Trm7-Trm734 complex and functions of its subunits
Credit: Ehime University
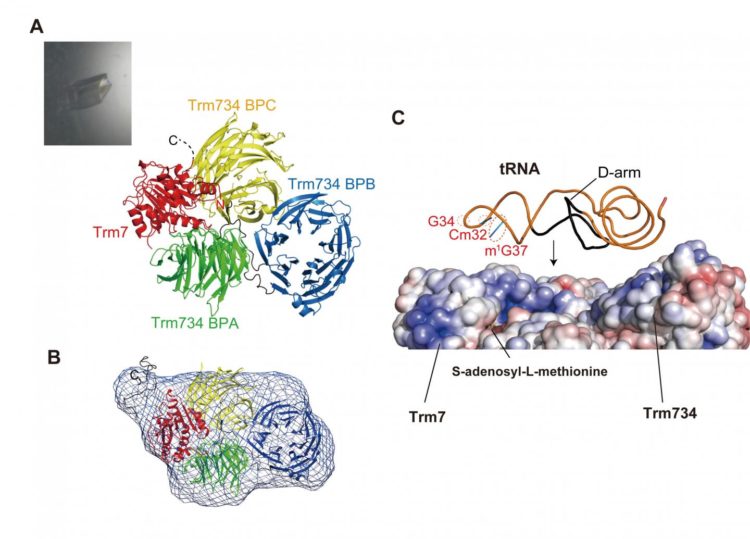
Genetic information on DNA is transcribed onto messenger RNA and then is decoded by transfer RNA (tRNA) during protein synthesis. The methylation of ribose of the first position of anticodon (position 34 in tRNA) is commonly observed in tRNAs from three domains of life. This methylation reinforces the codon-anticodon interaction and prevents errors during protein synthesis. We knew that eukaryote, a protein complex between Trm7 and Trm734 (Trm7-Trm734), is the responsible tRNA methyltransferase for this methylation. However, important questions remained. For example, why does Trm7-Trm734 act only on specific tRNA?, and why is Trm734 required for the methylation at position 34 in tRNA? To address these issues, a group at Ehime University (Akira Hirata, Keisuke Okada, Kazunori Yoshii, Hiroyuki Shiraishi and Hiroyuki Hori) working with a group at KEK (Shinya Saijo, Kento Yonezawa and Nobutaka Shimizu) solved the crystal structure of Trm7-Trm734 and measured a small angle X-ray scattering. Based on these structural studies, they performed biochemical studies. Their findings are as follows: Trm7-Trm734 preferentially methylates tRNA transcript variants possessing two of three factors (Cm32, m1G37 and pyrirmidine34). Therefore, tRNAPhe, tRNATrp and tRNALeu are specifically methylated by Trm7-Trm734. Trm7 possesses a Rossmann-fold catalytic domain, while Trm734 consists of three WD40 ?-propeller domains (termed BPA, BPB and BPC). BPA and BPC form a unique V-shaped cleft, which docks with Trm7. Small angle X-ray scattering reveals that Trm7-Trm734 exists as a hetero-dimer in solution and Trm734 is required for the positioning of tRNA for methylation.
It has long been a mystery as to why Trm7-Trm734 acts only on specific tRNAs. The study explains the tRNA recognition mechanism of Trm7-Trm734 and clarifies the roles of the subunits. In humans, the defect of methylation at the first position of anticodon in tRNA causes nosyndromic X-linked intellectual disability. Therefore, this study contributes to the understanding of genetic defects and developments in genetic diagnosis and gene therapy.
###
The synchrotron radiation experiments were performed at the BL26B1, BL38B1 and BL45XU in the SPring-8 with the approval of the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) (Proposal No. 2013B1272, 2014A1246, 2014B1063, 2015B2047 and 2016A2547), and at the BL-10C in the Photon Factory with the support of the Platform for Drug Discovery, Informatics, and Structural Life Science (PDIS) from Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED). This research was partially supported by the Platform Project for Supporting Drug Discovery and Life Science Research [Basis for Supporting Innovative Drug Discovery and Life Science Research (BINDS)] from AMED under Grant Number JP19am0101071 (support number 0997). Furthermore, the authors thank the Division of Material Science and Applied Protein Research of the Advanced Research Support Center, Ehime University for the Typhoon FLA 7000 system.
Media Contact
Public Relations Division
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.