Credit: DING Shiping
Supported single-atom catalysts (SACs) have emerged as a new frontier in heterogeneous catalysis and have attracted broad interest for their demonstrated good catalytic performance due to high atomic efficiency and relatively homogeneous active sites.
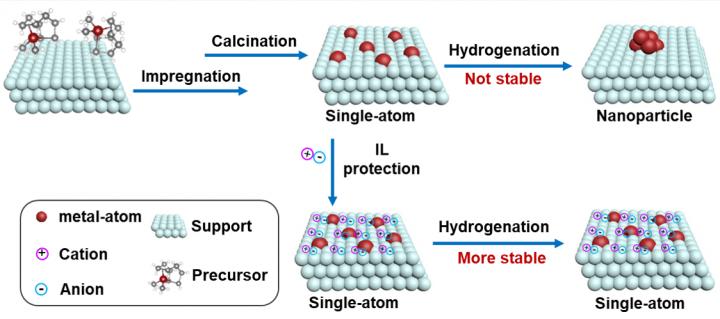
Strategies have been developed to fabricate various SACs. However, how to effectively stabilize these SACs remains challenging as singly dispersed isolated atoms tend to aggregate into thermodynamically more stable nanoparticles (NPs).
Scientists at the National University of Singapore, Kyoto University, Hokkaido University and the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a strategy to stabilize isolated metal atoms on various oxide supports by using ionic liquids (ILs) as an electronic stabilizer. Their findings were published in Chem on November 4.
The scientists investigated the effect of common ILs on stabilizing single-atom Pt1 and Pd1 on several supports. The ILs-stabilized SAC (ILSSAC) 0.2Pt/HAP (hydroxyapatite) was first selected as an example to systematically characterize the dispersion state of Pt before and after the hydrogenation reaction, and to quantify the electrostatic stabilization effect of ILs on single-atom Pt using density functional theory (DFT) calculations.
Afterwards, the strategy was extended to Pt1 catalysts dispersed on various supports and single-atom Pd1 catalysts loaded on HAP to prove the general applicability of the strategy.
“The results showed that the introduction of ionic liquids as a stabilizer not only effectively stabilizes single-atom Pt1 and Pd1 on HAP and other oxide supports, but also improves their catalytic performance,” said QIAO Botao, a researcher from DICP.
Considering that the physicochemical properties of ILs can be easily finetuned by the rational control of cations and anions, ILs stabilization is a simple strategy for enhancing the stability of a broad range of single-atom catalysts already reported in the literature or under development in various labs.
###
Media Contact
WANG Yongjin
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




