Novel biometric tool, EarEcho, uses sound waves to identify the ear canal’s unique geometry
Credit: University at Buffalo
BUFFALO, N.Y. — Visit a public space. Chances are you’ll see people wearing earbuds or earphones.
The pervasiveness of this old-meets-new technology, especially on college campuses, intrigued University at Buffalo computer scientist Zhanpeng Jin.
“We have so many students walking around with speakers in their ears. It led me to wonder what else we could do with them,” says Jin, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering in the UB School of Engineering and Applied Sciences.
That curiosity has led to EarEcho, a biometric tool a research team led by Jin is developing that uses modified wireless earbuds to authenticate smartphone users via the unique geometry of their ear canal.
A prototype of the system, described in this month’s Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, a journal published quarterly by the Association for Computing Machinery, proved roughly 95% effective.
UB’s Technology Transfer office has filed a provisional patent application for the technology.
How EarEcho works
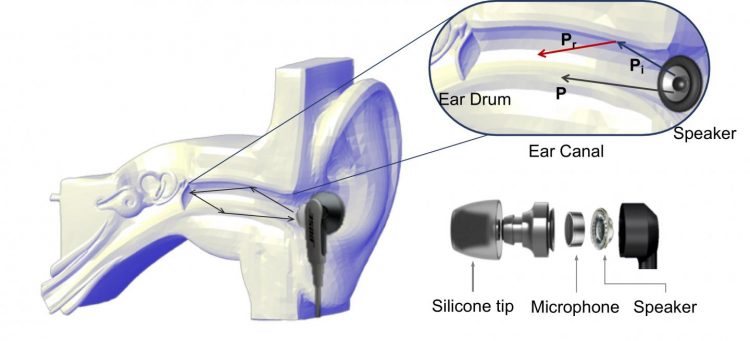
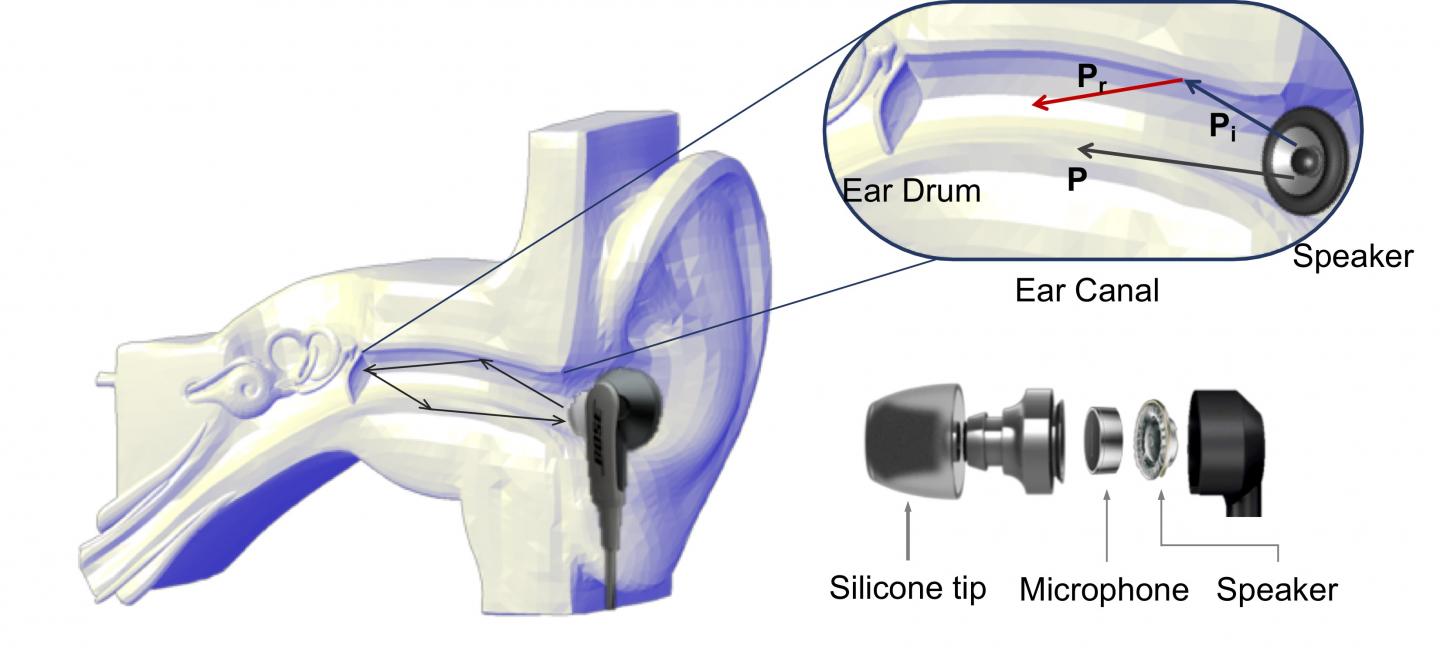
The team built the prototype with off-the-shelf products, including a pair of in-ear earphones and a tiny microphone. Researchers developed acoustic signal processing techniques to limit noise interference, and models to share information between EarEcho’s components.
When a sound is played into someone’s ear, the sound propagates through and is reflected and absorbed by the ear canal — all of which produce a unique signature that can be recorded by the microphone.
“It doesn’t matter what the sound is, everyone’s ears are different and we can show that in the audio recording,” says Jin. “This uniqueness can lead to a new way of confirming the identity of the user, equivalent to fingerprinting.”
The information gathered by the microphone is sent by the earbuds’ Bluetooth connection to the smartphone where it is analyzed.
To test the device, 20 subjects listened to audio samples that included a variety of speech, music and other content. The team conducted tests in different environmental settings (on the street, in a shopping mall, etc.) and with the subjects in different positions (sitting, standing, head tilted, etc.).
EarEcho proved roughly 95 percent effective when given 1 second to authenticate the subjects. The score improved to 97.5 percent when it continued to monitor the subject in 3 second windows.
How EarEcho can be used
Theoretically, users could rely on EarEcho to unlock their smartphones, thereby reducing the need for passcodes, fingerprints, facial recognition and other biometrics.
But Jin sees its greatest potential use in continuously monitoring a smartphone user. EarEcho, which works when users are listening to their earbuds, is a passive system, meaning users need not take any action, such as submitting a fingerprint or voice command, for it to work, he says.
Such a system, he argues, is ideal for situations where users are required to verify their identity such as making mobile payments. It also could eliminate the need to re-enter passcodes or fingerprints when a phone locks up after not being used.
“Think about that,” says Jin, “just by wearing the earphones, which many people already do, you wouldn’t have to do anything to unlock your phone.”
###
Additional co-authors of the study include Yang Gao and Wei Wang, both graduate students in Jin’s lab; Wei Sun, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Communicative Disorders and Sciences in the College of Arts and Sciences; and Vir V. Phoha, PhD, professor of electrical engineering and computer science at Syracuse University.
Media Contact
Cory Nealon
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.