Credit: IDIBELL
Researchers from the Cognition and Cerebral Plasticity group of the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute and the University of Barcelona (IDIBELL-UB), in collaboration with researchers from the University of McGill (Montreal), have published a new study in which brain mechanisms associated to the lack of sensitivity to music are explained. The study, published by PNAS journal, gives clues about the importance of music at an evolutionary level based on the connection between the auditory and emotional areas of the brain.
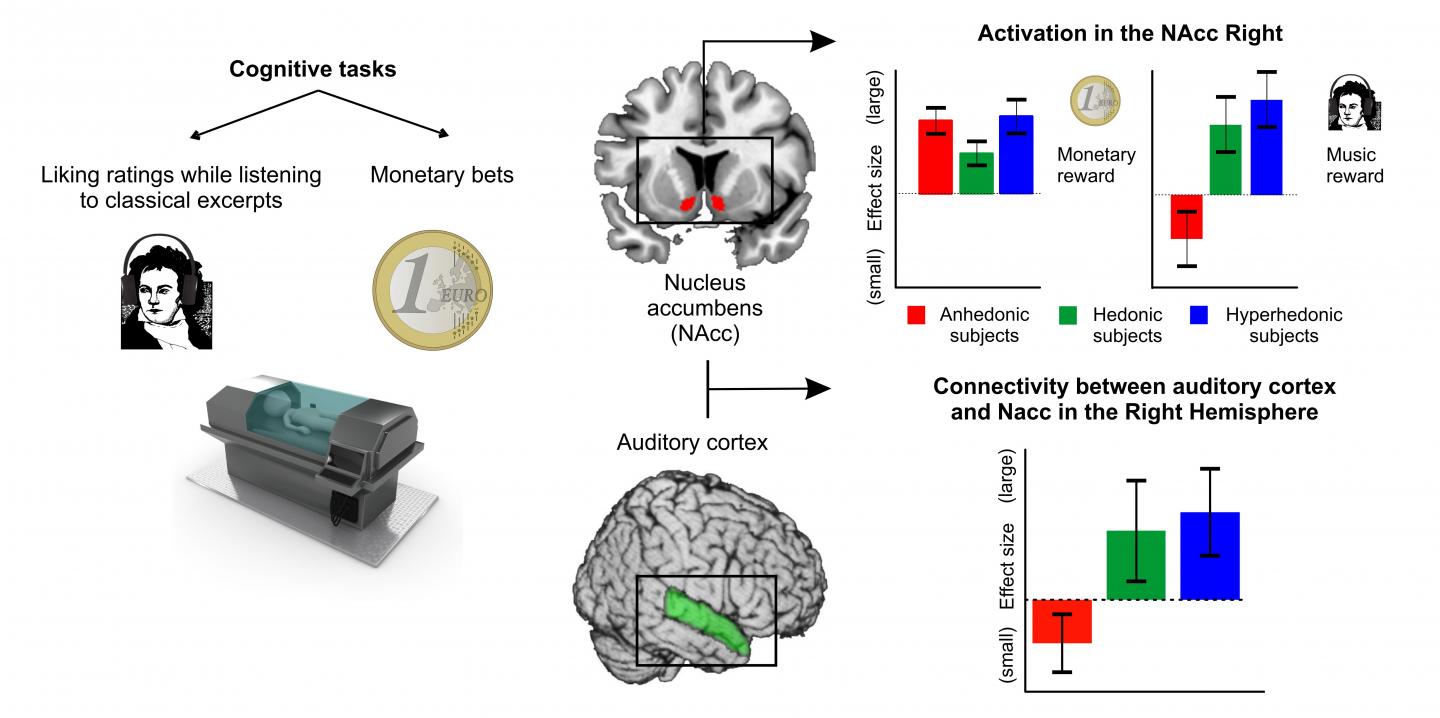
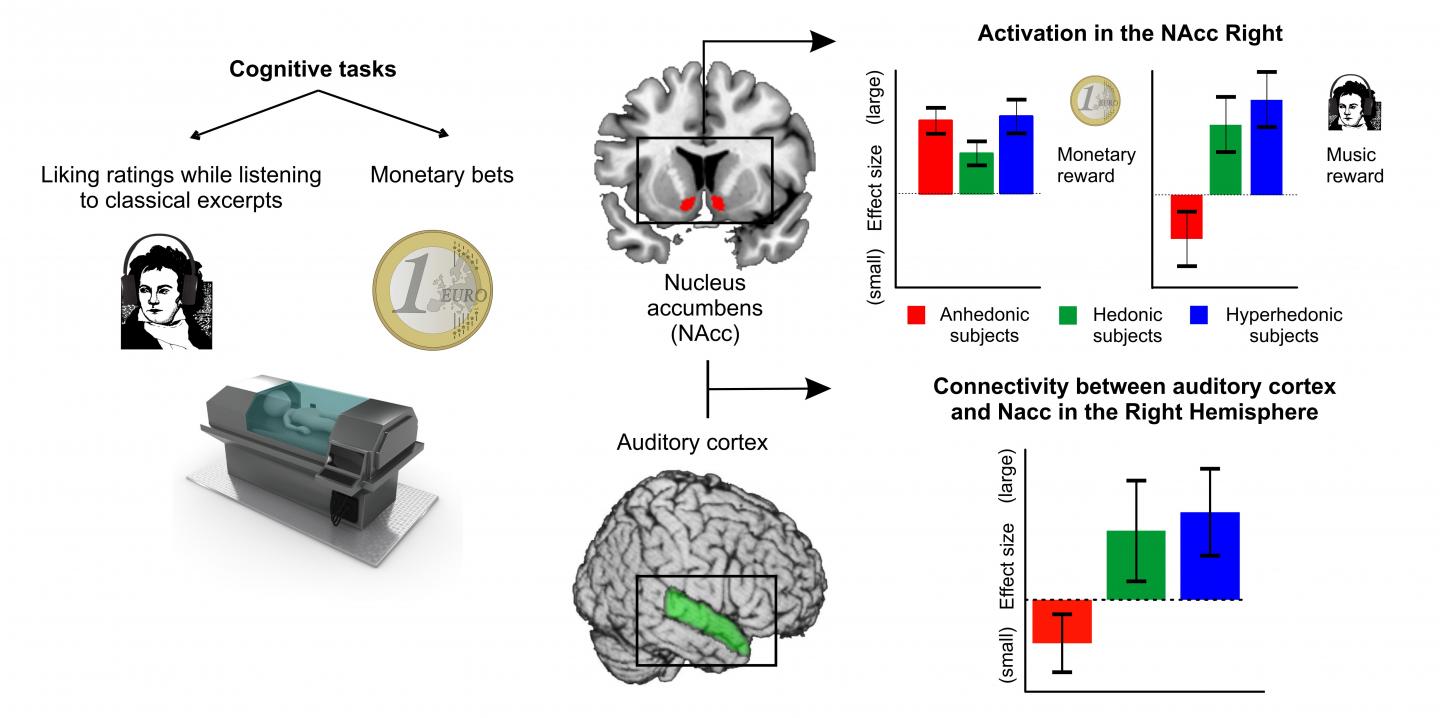
Although listening to music is considered a rewarding activity on a universal scale, about 3-5% of the healthy population does not experience pleasurable feelings in response to any type of music. This condition is known by the specific name of musical anhedonia. "Anhedonic people do not have problems correctly perceiving and processing the information contained in a melody (such as intervals or rhythms) and present a normal pleasure response to other pleasant stimuli (such as money), but do not enjoy musical stimuli", explains Noelia Martínez-Molina, researcher at the IDIBELL-UB group and lead author of the study. Although the existence of this phenomenon has been known for some years, it was not known why or how it was produced.
In their work, researchers analyzed 45 healthy volunteers using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Participants were divided into three groups according to the score obtained in a questionnaire developed by the same research group, the Barcelona Music Reward Questionnaire (BMRQ, available online at http://www.brainvitge.org/bmrq.php). During the fMRI session, participants had to listen to snippets of classic genre songs and provide pleasure values on a scale from 1 to 4 in real time. To control the brain response to other types of rewards, participants also had to play a monetary wagering task in which they could win or lose real money.
The results showed that the decrease of pleasant response to music shown by participants with musical anhedonia is related to a reduction in the activity of the nucleus accumbens, a key subcortical structure of the reward system. However, the activity of this structure is maintained when other reinforcers, such the money gained in the task of betting, are in place.
"It is interesting to consider the evolutionary importance of the connection between the auditory areas, cortical, and the more primitive system of emotional evaluation, subcortical", says the researcher. This connection is very clear in hedonic musical people – those who enjoy music – but diminishes in anhedonics. "The link between areas ensures that music is experienced as very rewarding, while stressing its importance at an evolutionary level, even when it does not seem obvious what the biological gain of this cultural production is."
###
Media Contact
Gemma Fornons
[email protected]
34-638-685-074
@idibell_en
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag