Credit: ©Science China Press
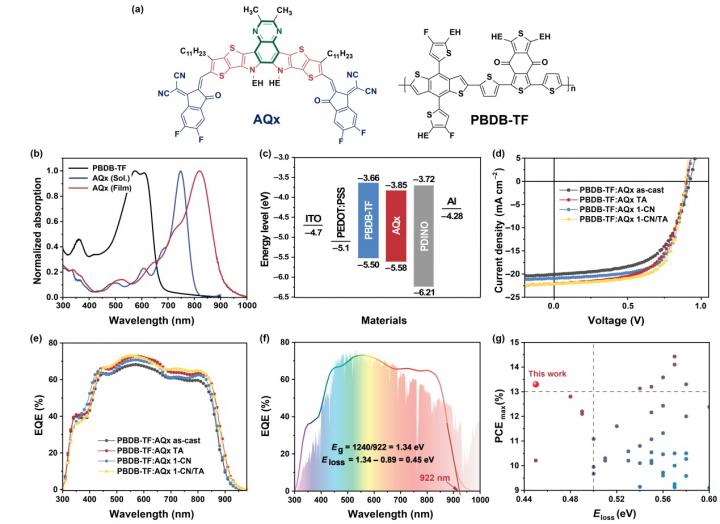
Organic photovoltaics (OPVs) have attracted much attention because of the advantages in low-cost and large-area fabrication and the great potentials in achieving flexible and semi-transparent devices. However, compared with inorganic and perovskite solar cells, OPVs show relatively low photoelectric conversion efficiencies, which is admittedly attributed to intrinsically low dielectric constants of organic materials resulting in large energy losses (Eloss = Eg-qVoc, where Eg is the optical bandgap of the photoactive layer, Voc is the open-circuit voltage of photovoltaic devices and q is elementary charge.). For the traditional bulk-heterojunction OPVs applying fullerene derivatives as the electron acceptors, the Elosss are always higher than 0.6 eV, which limits the power conversion efficiencies (PCEs) less than 12%. With the rapid development of fused-ring electron acceptors especially with an acceptor (A)-donor (D)-acceptor (A) arrangement, PCEs of OPV devices quickly surpassed 12% and even reached 16% in a very short period, in quite a few of which the Elosss are less than 0.6 eV.
Although it is common for inorganic or perovskite solar cells, high-performance OPVs with the Elosss less than 0.5 eV are quite rare up to date, which means that the Eloss is still the key factor that limits the photovoltaic efficiency of the OPV technique. Recently, a research team led by Prof. Xiaozhang Zhu from Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has designed and synthesized an electron acceptor AQx by fusing the quinoxaline moiety with the quinoid-resonance effect to the D-A system. The optical bandgap of AQx is estimated to be 1.35 eV according to the absorption onset in thin film, 918 nm. Cyclic voltammetry was performed to evaluate the frontier orbital energy levels of AQx: the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) energy levels of AQx are -5.58 and -3.85 eV, respectively. By matching with a middle-bandgap polymer donor PBDB-TF, as-cast devices exhibit the PCEmax of up to 10.99% and the optimized AQx-based device shows a much improved short-circuit current (Jsc) from 20.06 to 22.18 mA cm-2 and fill factor (FF) from 59.34% to 67.14% with a comparable Voc of 0.893 V, delivering the highest PCEmax of 13.31%. They measured the corresponding current density-voltage (J-V) and the external quantum efficiency (EQE) curves. The AQx-based device shows a broad and high EQE response in the 300-900 nm region, which is consistent with the absorption spectra of the corresponding photoactive components and matches well with the photon flux spectrum of solar radiation. The calculated Jscs based on the integration of the EQE spectra at different conditions are in good agreement with those obtained from the J-V curves with minor errors of 2~3%. They calculated the Elosss of AQx-based devices according to the equation: Eloss = Eg – qVoc, in which Eg is determined based on the EQE spectra. All the Elosss of the blend films processed at different conditions are well below 0.47 eV and reach 0.45 eV for the most optimized device, the smallest value for the binary OPVs with PCEs over 13% reported so far.
###
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFA0204700), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB12010200), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21572234, 21661132006, 91833304, 21805289)
See the article: Wenrui Liu, Jianyun Zhang, Shengjie Xu, Xiaozhang Zhu. Efficient organic solar cells achieved at a low energy loss. Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(16)1144-1147
https:/
Media Contact
Xiaozhang Zhu
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




