Credit: Robert R. Alfano & Yury Budansky
Hailed as a pioneer by Photonics Media for his previous discoveries of supercontinuum and Cr tunable lasers, City College of New York Distinguished Professor of Science and Engineering Robert R. Alfano and his research team are claiming another breakthrough with a new super class of photons dubbed “Majorana photons.” They could lead to enhanced information on quantum-level transition and imaging of the brain and its working.
Alfano’s group based its research on the fact that photons, while possessing salient properties of polarization, wavelength, coherence and spatial modes, take on several forms. “Photons are amazing and are all not the same,” Alfano states.
Their focus “was to use a ‘special super form’ of photons, which process the entanglement twists of both polarizations and the wavefront to probe and would propagate deeper in brain tissues, microtubules and neuron cells, giving more fundamental information of the brain than the conventional photon forms.”
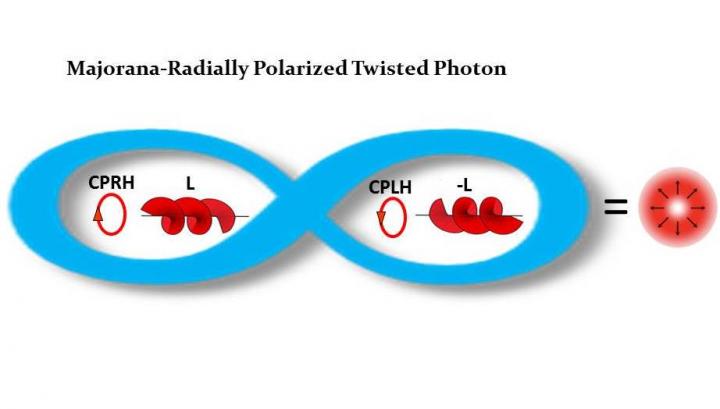
These unique photons can travel with different wavefronts. They also have a vortex where the wavefront twists and polarization is non- homogenous in the wave beam diameter. These beams are called Cylindrical Vector Vortex Beams (CVVB).
Among these CVVB photons, the Alfano team identified a new “super special” class called classical entangled photon beams. These photons are mixed having both different types of circular polarization and + L and – L orbital angular momentum, locally. In addition, they are entangled with their own anti photon. Two stand out Radial and Azmuthal optical beams.
Alfano named them “Majorana Photons,” after Ettore Majorana, an Italian theoretical physicist and protégé of Enrico Fermi, who worked on neutrino masses.
“The ‘super special photon” will play an important role in understanding the fundamental and quantum processes in materials, deeper penetration and to advance applications in photo detection sensing, information, communication and future computers,” said Alfano, a prolific inventor whose research has led to advancements in ultrafast laser science and nonlinear optical imaging, since 1970.
###
This research was partly funded by a five-year $1.5 million grant from the United States Army Research Office (ARO) to investigate quantum effects in brain, microtubules, and neuron cells.
Alfano’s collaborators in ARO grant included Travis Craddock (Nova Southeastern University); Lingyan Shi (University of California San Diego) and Enrique Galvez (Colgate University), Daniel Nolan (Corning), and Sandra Mamani, an electrical engineering PhD student at CCNY.
Media Contact
Jay Mwamba
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




