Credit: Kanazawa University
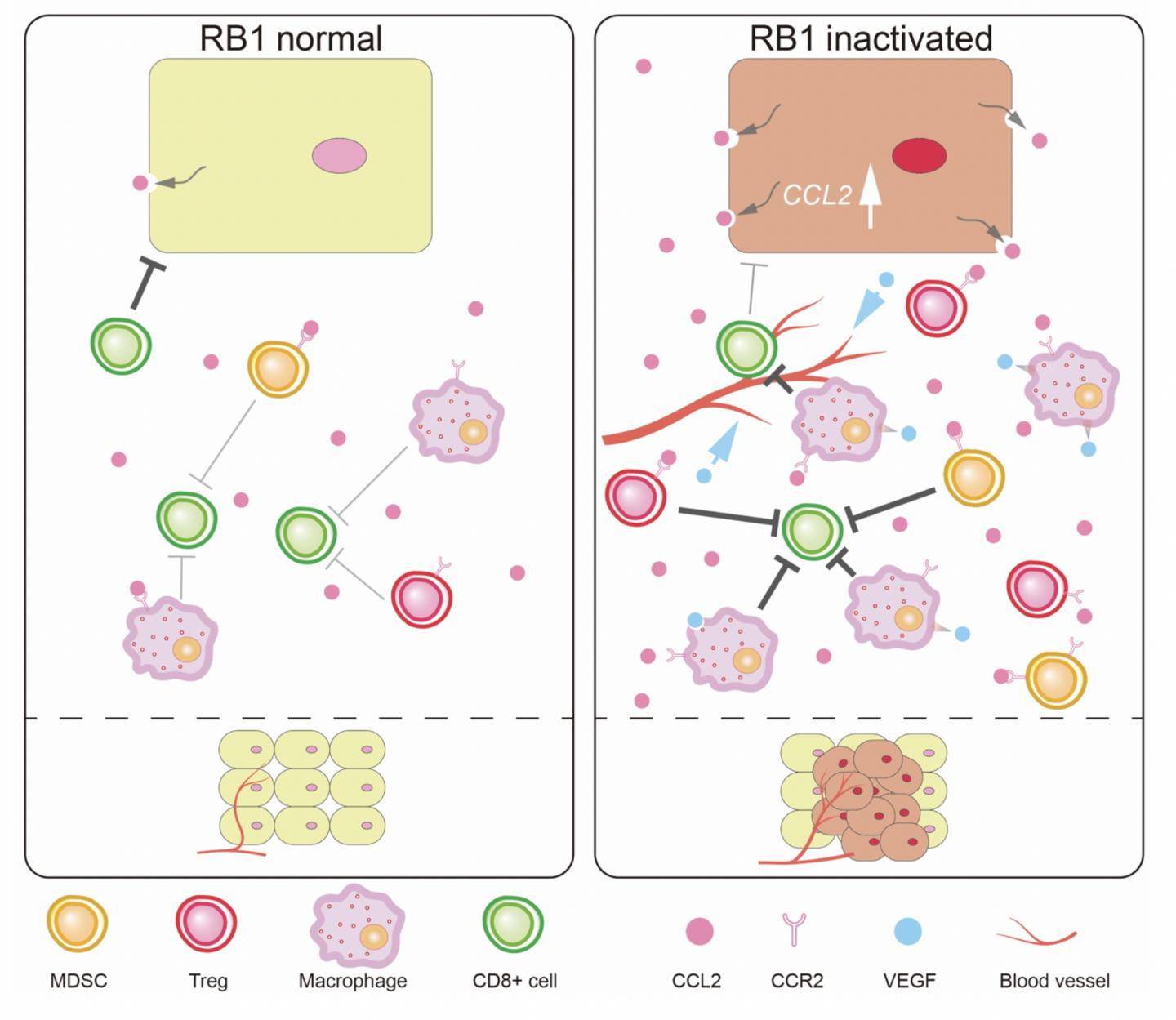
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a mix of fluids, immune cells and blood vessels which envelops the tumors. Interactions between tumor cells and the TME determine the progression and fate of tumors. Therefore, understanding the composition and functions of the TME is thus very important for keeping cancer in check. Although several genetic mutations can result in the incidence of cancer, not much is known about their effects on the TME. A research team led by Chiaki Takahashi at Kanazawa University has recently reported the role of one such cancer gene, RB, in this regard.
Retinoblastoma (RB) is a tumor-suppressing gene, mutations in which promote the growth of tumors. Therefore, the team first inactivated RB in mice with sarcoma, a type of cancer, and observed the ensuing effects on tumor growth. The tumors in these mice were indeed enlarged. Further analysis of their TME revealed the presence of new blood vessels which usually nourish cancer cells. Newly recruited immunosuppressive cells, which overpower the body’s natural defense system, were also found in the TME. Inactivation of RB thus made the TME conducive for cancer progression.
The researchers then dug deeper to investigate molecular changes in the TME. The secretion of Ccl2, a molecule that attracts immunosuppressive cells, was found to be greatly increased. Alterations in the TME, however, were not seen in mice without the Ccl2 gene, suggesting its increase as the primary culprit for the RB-mediated TME changes. To establish the relevance of these findings to human cancer, breast cancer cell lines were used. As expected, enhanced secretion of Ccl2 was also observed in the breast tumor cells with inactivated RB. In previous reports, the research team has disclosed imbalances in certain mitochondrial metabolites in RB-associated cancer. Mitochondrial superoxide (MS) is one such metabolite. To build on those findings, they examined whether altered Ccl2 secretion was related to MS imbalance in RB-associated cancer. When breast cancer cells were treated with antioxidants, which prevent the accumulation of MS, Ccl2 secretion was greatly decreased. The two were thus closely linked.
This study elucidated detailed mechanisms by which mutations in the RB gene induce changes in the TME and promote tumor growth. A deeper understanding of this dynamic will help devise tumor-suppressing strategies in cancer patients with RB mutations. Preventing mitochondrial imbalances or directly targeting Ccl2 in the TME of such patients warrant further investigation as therapeutic approaches.
###
Media Contact
Tomoya Sato
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




