Credit: UC San Diego Health Sciences
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurological condition that affects motor neurons — the nerve cells that control breathing and muscles. Under a microscope, researchers have noticed that the motor neurons of patients with ALS contain excessive aggregation of a protein called TDP-43. Since TDP-43 proteins stuck in these aggregates can’t perform their normal function, the scientists believe this build-up contributes to motor neuron degeneration, the hallmark of ALS.
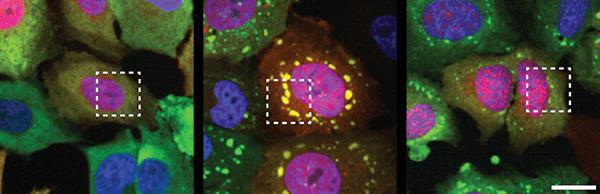
In a study publishing July 1, 2019 in Neuron, UC San Diego School of Medicine researchers discovered that prolonged cellular stress, such as exposure to toxins, triggers TDP-43 clumping in the cytoplasm of human motor neurons grown in a laboratory dish. Even after the stress is relieved, TDP-43 clumping persists in ALS motor neurons, but not in healthy neurons.
The team then screened and identified chemical compounds (potential precursors to therapeutic drugs) that prevent this stress-induced, persistent TDP-43 accumulation. These compounds also increased the survival time of neurons with TDP-43 proteins containing an ALS-associated mutation.
“These compounds could provide a starting point for new ALS therapeutics,” said senior author Gene Yeo, PhD, professor at UC San Diego School of Medicine and faculty member in the Sanford Consortium for Regenerative Medicine.
Yeo and team, including first author Mark Fang, PhD, who was a graduate student in Yeo’s lab at the time, generated motor neurons from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) that had been converted from human skin cells. To mimic cellular aspects of ALS, they exposed these laboratory motor neurons to toxins such as puromycin, which stressed the cells and led to TDP-43 clumps.
Normally, TDP-43 proteins help process molecules called messenger RNA, which serve as the genetic blueprints for making proteins. But when they clump outside the nucleus, TDP-43 proteins can’t perform their normal duty, and that can have a profound effect on many cellular functions.
The researchers tested thousands of chemical compounds for their effects on RNA-protein aggregation. They were surprised to find compounds that not only reduced the overall amount of clumping by up to 75 percent, but also varied clump size and number per cell.
Some of the compounds tested were molecules with extended planar aromatic moieties — arms that allow them to insert themselves in nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA. TDP-43 must bind RNA in order to join ALS-associated clumps. Thus, according to Yeo, it makes sense that a compound that interacts with RNA would prevent TDP-43 from clumping.
“While these findings still need to be tested in model organisms and there is more work to do before a potential therapy could one day be tested in patients,” Fang said, “these compounds already expand our toolbox for unraveling the relationship between RNA-protein aggregations and neurological disease.”
ALS, also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, affects more than 20,000 Americans. Currently, there are no effective treatments for ALS, largely due to poor understanding of how the disease initiates and progresses at the molecular level. The disease is invariably fatal.
###
Co-authors include: Sebastian Markmiller, Anthony Q. Vu, UC San Diego; Ashkan Javaherian, Nicholas A. Castello, Ashmita Baral, Michelle Chan, Jeremy W. Linsley, Gladstone Institutes; William E. Dowdle, Joseph W. Lewcock, Denali Therapeutics Inc.; Philippe Jolivet, Institut de Recherches Cliniques de Montréal; Paul J. Bushway, Mark M. Mercola, Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute; Drew Linsley, Brown University; Steven Finkbeiner, Gladstone Institute and University of California San Francisco; and Eric Lecuyer, Institut de Recherches Cliniques de Montréal, Université de Montréal and McGill University.
Disclosure: Gene Yeo is co-founder, member of the Board of Directors and scientific advisory board, equity holder and paid consultant for Locana and Eclipse BioInnovations. Yeo is also a visiting faculty at the National University of Singapore. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the University of California San Diego in accordance with its conflict of interest policies.
Media Contact
Heather Buschman, Ph.D.
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




