Researchers develop a new microscopy system for creating maps of cells, using chemical reactions to encode spatial information
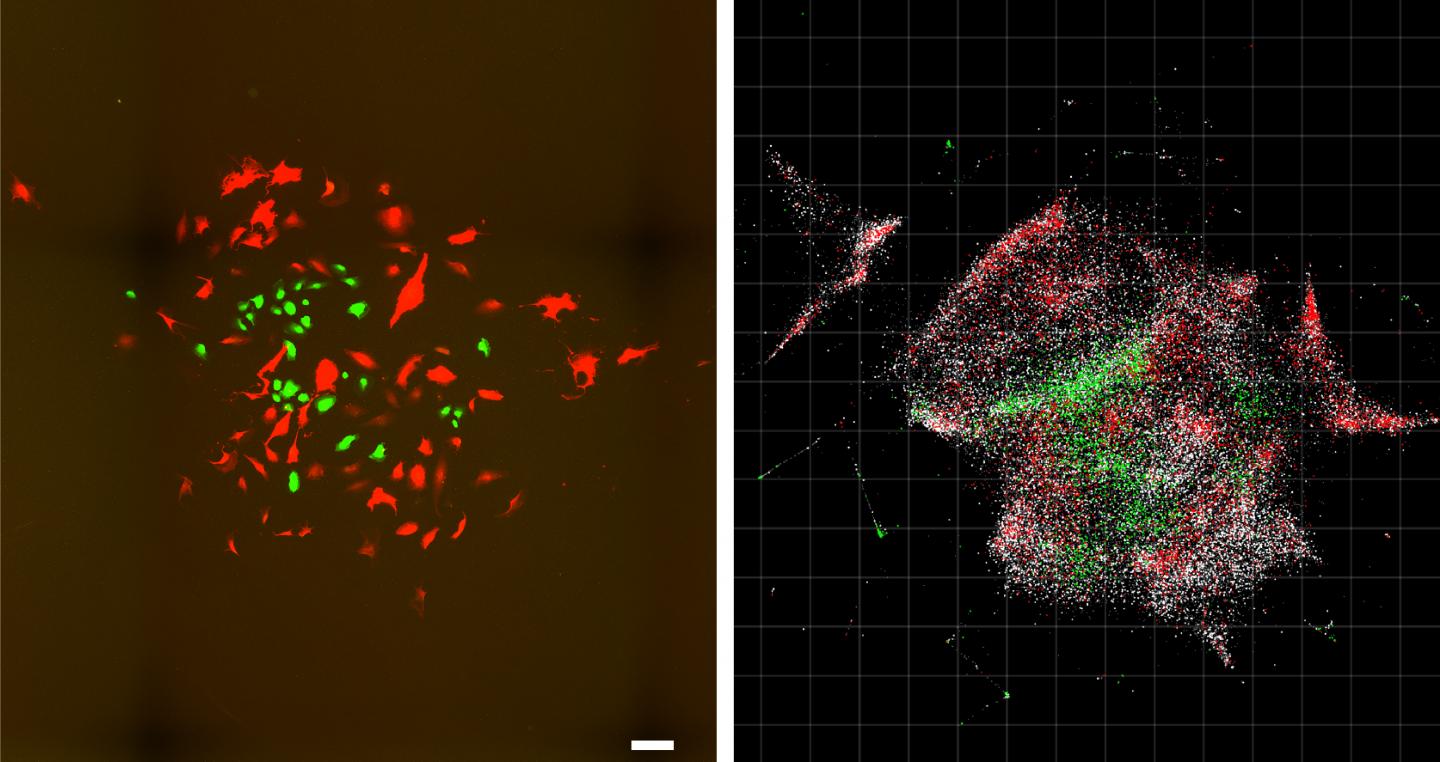
Credit: Weinstein et al./Cell
A team of researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard has developed a new technique for mapping cells. The approach, called DNA microscopy, shows how biomolecules such as DNA and RNA are organized in cells and tissues, revealing spatial and molecular information that is not easily accessible through other microscopy methods. DNA microscopy also does not require specialized equipment, enabling large numbers of samples to be processed simultaneously.
“DNA microscopy is an entirely new way of visualizing cells that captures both spatial and genetic information simultaneously from a single specimen,” says first author Joshua Weinstein, a postdoctoral associate at the Broad Institute. “It will allow us to see how genetically unique cells — those comprising the immune system, cancer, or the gut, for instance — interact with one another and give rise to complex multicellular life.”
The new technique is described in Cell. Aviv Regev, core institute member and director of the Klarman Cell Observatory at the Broad Institute and professor of biology at MIT, and Feng Zhang, core institute member of the Broad Institute, investigator at the McGovern Institute for Brain Research at MIT, and the James and Patricia Poitras Professor of Neuroscience at MIT, are co-authors. Regev and Zhang are also Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigators.
The evolution of biological imaging
In recent decades, researchers have developed tools to collect molecular information from tissue samples, data that cannot be captured by either light or electron microscopes. However, attempts to couple this molecular information with spatial data — to see how it is naturally arranged in a sample — are often machinery-intensive, with limited scalability.
DNA microscopy takes a new approach to combining molecular information with spatial data, using DNA itself as a tool.
To visualize a tissue sample, researchers first add small synthetic DNA tags, which latch on to molecules of genetic material inside cells. The tags are then replicated, diffusing in “clouds” across cells and chemically reacting with each other, further combining and creating more unique DNA labels. The labeled biomolecules are collected, sequenced, and computationally decoded to reconstruct their relative positions and a physical image of the sample.
The interactions between these DNA tags enable researchers to calculate the locations of the different molecules — somewhat analogous to cell- phone towers triangulating the locations of different cell phones in their vicinity. Because the process only requires standard lab tools, it is efficient and scalable.
In this study, the authors demonstrate the ability to molecularly map the locations of individual human cancer cells in a sample by tagging RNA molecules. DNA microscopy could be used to map any group of molecules that will interact with the synthetic DNA tags, including cellular genomes, RNA, or proteins with DNA-labeled antibodies, according to the team.
“DNA microscopy gives us microscopic information without a microscope-defined coordinate system,” says Weinstein. “We’ve used DNA in a way that’s mathematically similar to photons in light microscopy. This allows us to visualize biology as cells see it and not as the human eye does. We’re excited to use this tool in expanding our understanding of genetic and molecular complexity.”
###
Paper cited
Weinstein J, et al. DNA microscopy: optics-free spatio-genetic imaging by a stand-alone chemical reaction. Cell. Online June 20, 2019. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.019
Funding for this study was provided by the Simons Foundation, Klarman Cell Observatory, NIH (R01HG009276, 1R01- HG009761, 1R01- MH110049, and 1DP1-HL141201), New York Stem Cell Foundation, Simons Foundation, Paul G. Allen Family Foundation, Vallee Foundation, the Poitras Center for Affective Disorders Research at MIT, the Hock E. Tan and K. Lisa Yang Center for Autism Research at MIT, J. and P. Poitras, and R. Metcalfe.
The authors have applied for a patent on this technology.
Media Contact
David Cameron
[email protected]



