A stepwise transfer of energy through the different components of the nanostructure boosts its response to light, showing promise for solar cell applications
Credit: ACS Photonics
UPTON, NY–To absorb incoming sunlight, plants and certain kinds of bacteria rely on a light-harvesting protein complex containing molecules called chromophores. This complex funnels solar energy to the photosynthetic reaction center, where it is converted into chemical energy for metabolic processes.
Inspired by this found-in-nature architecture, scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and Stony Brook University (SBU) have assembled a nanohybrid structure that contains both biologically derived (biotic) and inorganic (abiotic) materials. They combined a light-harvesting protein from a cyanobacteria, semiconducting nanocrystals (quantum dots), and a two-dimensional (2-D) semiconducting transition metal only one atomic layer thick. Described in a paper published on April 29 in ACS Photonics–a journal of the American Chemical Society (ACS)–this nanostructure could be used to improve the efficiency with which solar cells harvest energy from the sun.
“Today’s best solar panels can convert nearly 23 percent of the sunlight they absorb into electricity, but on average, their efficiency ranges between 15 and 18 percent,” said corresponding author Mircea Cotlet, a materials scientist in the Soft and Bio Nanomaterials Group at Brookhaven Lab’s Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN)–a DOE Office of Science User Facility. “If this efficiency can be boosted, more electricity can be generated. The assembled biotic-abiotic nanohybrid shows enhanced harvesting of light and generation of electrical charge carriers compared to the 2-D semiconductor-only structure. These properties increase the nanohybrid’s response to light when the structure is incorporated into a field-effect transistor (FET), a kind of optoelectronic device.”
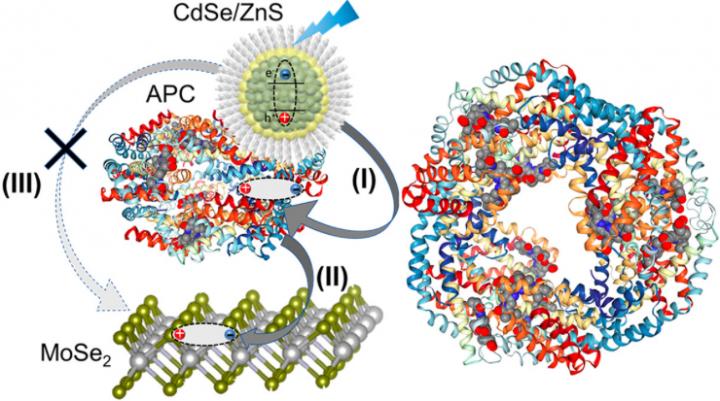
In designing the nanohybrid, the scientists chose atomically thin 2-D molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2) as the platform for bottom-up assembly. Molybdenum diselenide is a semiconductor, or a material whose electrical conductivity is in between that of a regular conductor (little resistance to the flow of electrical current) and insulator (high resistance). They combined MoSe2 with two strong light-harvesting nanomaterials: quantum dots (QDs) and the allophycocyanin (APC) protein from cyanobacteria.
The scientists chose the components based on their light-harvesting properties and engineered the components’ band gaps (minimum energy required to excite an electron to participate in conduction) such that a concerted stepwise energy transfer can be promoted through the nanohybrid in a directional manner. In the hybrid, energy flows from light-excited QDs to the APC protein and then to MoSe2. This energy transfer mimics natural light-harvesting systems where surface chromophores (in this case, QDs) absorb light and direct the harvested energy to intermediate chromophores (here, APC) and finally to the reaction center (here, MoSe2).
To combine the different components, the scientists applied electrostatic self-assembly, a technique based on the interactions between electrically charged particles (opposite charges attract; like charges repel). They then used a specialized optical microscope to probe the transfer of energy through the nanohybrids. These measurements revealed that the addition of the APC protein layer increases the energy transfer efficiency of the nanohybrid with single-layer MoSe2 by 30 percent. They also measured the photoresponse of the nanohybrid incorporated into a fabricated FET and found that it showed the highest responsivity relative to FETs containing only one of the components, producing more than double the amount of photocurrent in response to incoming light.
“More light is transferred to MoSe2 in the biotic-abiotic hybrid,” said first author and research associate Mingxing Li, who is working with Cotlet in the CFN Soft and Bio Nanomaterials Group. “Increased light transfer combined with the high charge carrier mobilities in MoSe2 means more carriers will be collected by the electrodes in a solar cell device. This combination is promising for boosting device efficiency.”
The scientists proposed that adding APC in between QDs and MoSe2 creates a “funnel-like” energy-transfer effect due to the way that APC preferentially orients itself relative to MoSe2.
“We believe this study represents one of the first demonstrations of a cascaded biotic-abiotic nanohybrid involving a 2-D transition-metal semiconductor,” said Li. “In a follow-on study, we will work with theoreticians to more deeply understand the mechanism underlying this enhanced energy transfer and identify its applications in energy harvesting and bioelectronics.”
###
Co-author Jia-Shiang Chen, an SBU graduate student, contributed to the research and acknowledges support from the DOE Office of Science Graduate Student Research program.
Brookhaven National Laboratory is supported by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit https:/
Follow @BrookhavenLab on Twitter or find us on Facebook.
Media Contact
Ariana Tantillo
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




