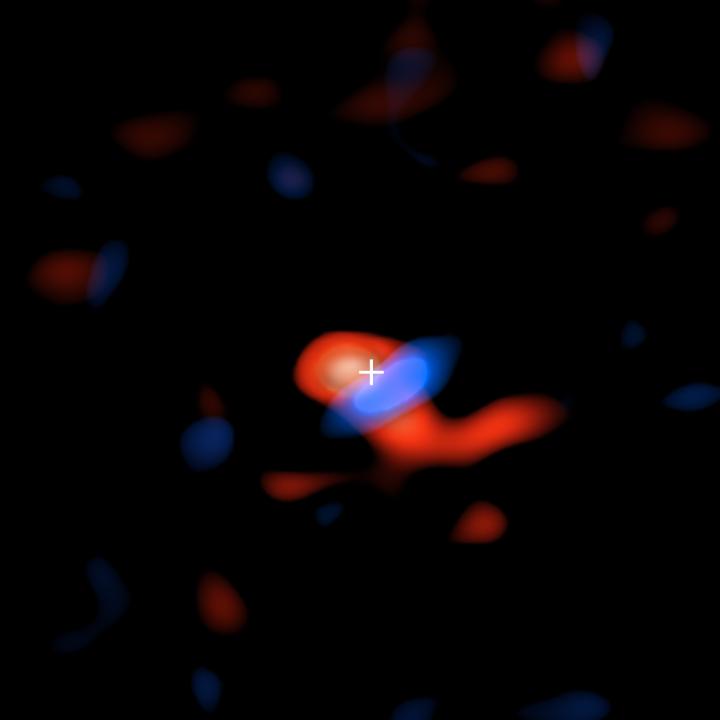
Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), E.M. Murchikova; NRAO/AUI/NSF, S. Dagnello
New ALMA observations reveal a never-before-seen disk of cool, interstellar gas wrapped around the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. This nebulous disk gives astronomers new insights into the workings of accretion: the siphoning of material onto the surface of a black hole. The results are published in the journal Nature.
Through decades of study, astronomers have developed a clearer picture of the chaotic and crowded neighborhood surrounding the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. Our galactic center is approximately 26,000 light-years from Earth and the supermassive black hole there, known as Sagittarius A* (A “star”), is 4 million times the mass of our Sun.
We now know that this region is brimming with roving stars, interstellar dust clouds, and a large reservoir of both phenomenally hot and comparatively colder gases. These gases are expected to orbit the black hole in a vast accretion disk that extends a few tenths of a light-year from the black hole’s event horizon.
Until now, however, astronomers have been able to image only the tenuous, hot portion of this flow of accreting gas, which forms a roughly spherical flow and showed no obvious rotation. Its temperature is estimated to be a blistering 10 million degrees Celsius (18 million degrees Fahrenheit), or about two-thirds the temperature found at the core of our Sun. At this temperature, the gas glows fiercely in X-ray light, allowing it to be studied by space-based X-ray telescopes, down to scale of about a tenth of a light-year from the black hole.
In addition to this hot, glowing gas, previous observations with millimeter-wavelength telescopes have detected a vast store of comparatively cooler hydrogen gas (about 10 thousand degrees Celsius, or 18,000 degrees Fahrenheit) within a few light-years of the black hole. The contribution of this cooler gas to the accretion flow onto the black hole was previously unknown.
Although our galactic center black hole is relatively quiet, the radiation around it is strong enough to cause hydrogen atoms to continually lose and recombine with their electrons. This recombination produces a distinctive millimeter-wavelength signal, which is capable of reaching Earth with very little losses along the way.
With its remarkable sensitivity and powerful ability to see fine details, the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) was able to detect this faint radio signal and produce the first-ever image of the cooler gas disk at only about a hundredth of a light-year away (or about 1000 times the distance from the Earth to the Sun) from the supermassive black hole. These observations enabled the astronomers both to map the location and trace the motion of this gas. The researchers estimate that the amount of hydrogen in this cool disk is about one tenth the mass of Jupiter, or one ten-thousandth of the mass of the Sun.
By mapping the shifts in wavelengths of this radio light due to the Doppler effect (light from objects moving toward the Earth is slightly shifted to the “bluer” portion of the spectrum while light from objects moving away is slightly shifted to the “redder” portion), the astronomers could clearly see that the gas is rotating around the black hole. This information will provide new insights into the ways that black holes devour matter and the complex interplay between a black hole and its galactic neighborhood.
“We were the first to image this elusive disk and study its rotation,” said Elena Murchikova, a member in astrophysics at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, and lead author on the paper. “We are also probing accretion onto the black hole. This is important because this is our closest supermassive black hole. Even so, we still have no good understanding of how its accretion works. We hope these new ALMA observations will help the black hole give up some of its secrets.”
###
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory is a facility of the National Science Foundation, operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc.
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international astronomy facility, is a partnership of the European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO), the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) and the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) of Japan in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. ALMA is funded by ESO on behalf of its Member States, by NSF in cooperation with the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) and the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) and by NINS in cooperation with the Academia Sinica (AS) in Taiwan and the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI).
ALMA construction and operations are led by ESO on behalf of its Member States; by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), managed by Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI), on behalf of North America; and by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) on behalf of East Asia. The Joint ALMA Observatory (JAO) provides the unified leadership and management of the construction, commissioning and operation of ALMA.
Media Contact
Charles Blue
[email protected]




