A correlation was found between strong feelings of responsibility and likelihood of developing OCD or GAD in American university students
Credit: Emma Buchet and Associate Professor Yoshinori Sugiura/University of Hiroshima
A new study has found that people who reported intense feelings of responsibility were susceptible to developing Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) or Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) was published in the International Journal of Cognitive Therapy.
“People with OCD [are] tortured by repeatedly occurring negative thinking and they take some strategy to prevent it… GAD is a very pervasive type of anxiety. [Patients] worry about everything.” describes Associate Professor Yoshinori Sugiura of the University of Hiroshima.
Anxiety and OCD-like behaviors, such as checking if the door is locked, are common in the general population. However, it is the frequency and intensity of these behaviors or feelings that make the difference between a character trait and disorder.
“For example, you’re using two audio recorders instead of one,” says Sugiura when interviewed. “It’s just in case one fails … having two recorders will enhance your work but if you prepare [too] many recorders … that will interfere with your work.”
A problem Sugiura identifies in psychology is that each disorder that sufferers experience has several competing theories regarding their cause.
“There are too many theories and therapies for mental disorders for one expert to master them all.” elaborates Sugiura.
The goal of this research team (consisting of Sugiura and Associate Professor Brian Fisak (University of Central Florida)) was to find a common cause for these disorders and simplify the theories behind them.
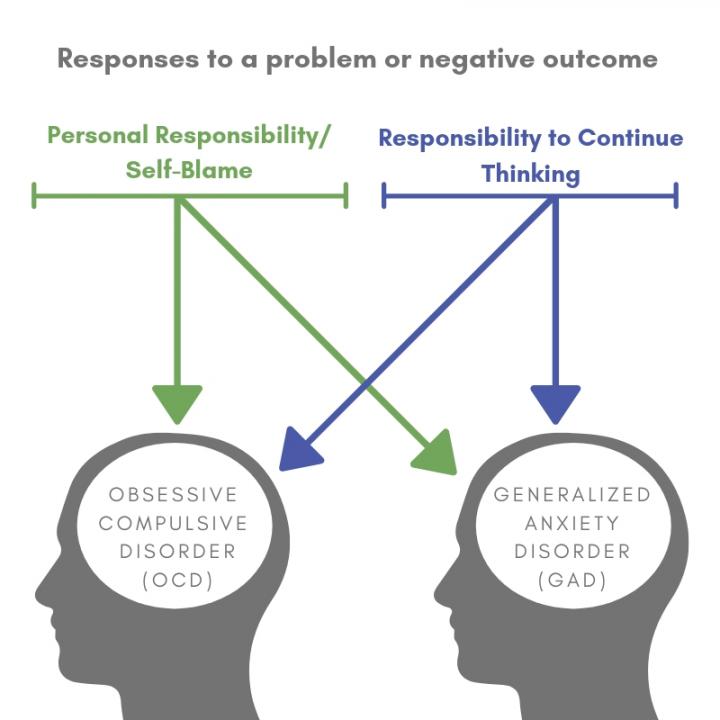
Sugiura and Fisak first defined and explored “inflated responsibility”. The team identified 3 types of inflated responsibility: 1) Responsibility to prevent or avoid danger and/or harm, 2) Sense of personal responsibility and blame for negative outcomes and 3) Responsibility to continue thinking about a problem. The research group combined tests used to study OCD and GAD as there had been no previous work that compared these tests in the same study.
To establish whether inflated responsibility was a predictor of OCD or GAD, Sugiura and Fisak sent an online questionnaire to American university students. Through this survey they found that respondents who scored higher in questions about responsibility were more likely to exhibit behaviors that resemble those of OCD or GAD patients. Personal Responsibility and Blame and the Responsibility to Continue Thinking, had the strongest link to the disorders.
The researchers would like to clarify that this preliminary study is not representative of the general population due to the small scale and skewed population (mostly female university students). However, the promising findings suggest that this format can be applied to a larger population and yield similar results.
Sugiura is currently looking into how to reduce responsibility and the preliminary outcomes are positive. When asked for any tips to reduce anxiety or obsessive behaviors he said:
“[A] very quick or easy way is to realize that responsibility is working behind your worry. I ask [patients] “Why are you worried so much?” so they will answer “I can’t help but worry” but they will not spontaneously think “Because I feel responsibility” … just realizing it will make some space between responsibility thinking and your behavior.”
###
Media Contact
Norifumi Miyokawa
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




