Credit: Morgan Beeby, [email protected]
In favorable conditions, many bacteria propel themselves to food sources and other sites of interest using whip-like molecular propellers known as flagella. However, according to new research published on March 19 in the open-access journal PLOS Biology, by Josie Ferreira and colleagues of Imperial College London, members of the bacterial class Gammaproteobacteria eject their flagella when nutrients are scarce.
These findings suggest a previously unknown mechanism for microbes to save energy in lean times. Earlier research has shown that bacteria switch from a mobile to stationary phase in the face of nutrient depletion, but it has been unclear how they deactivate their large, energy-intensive flagella.
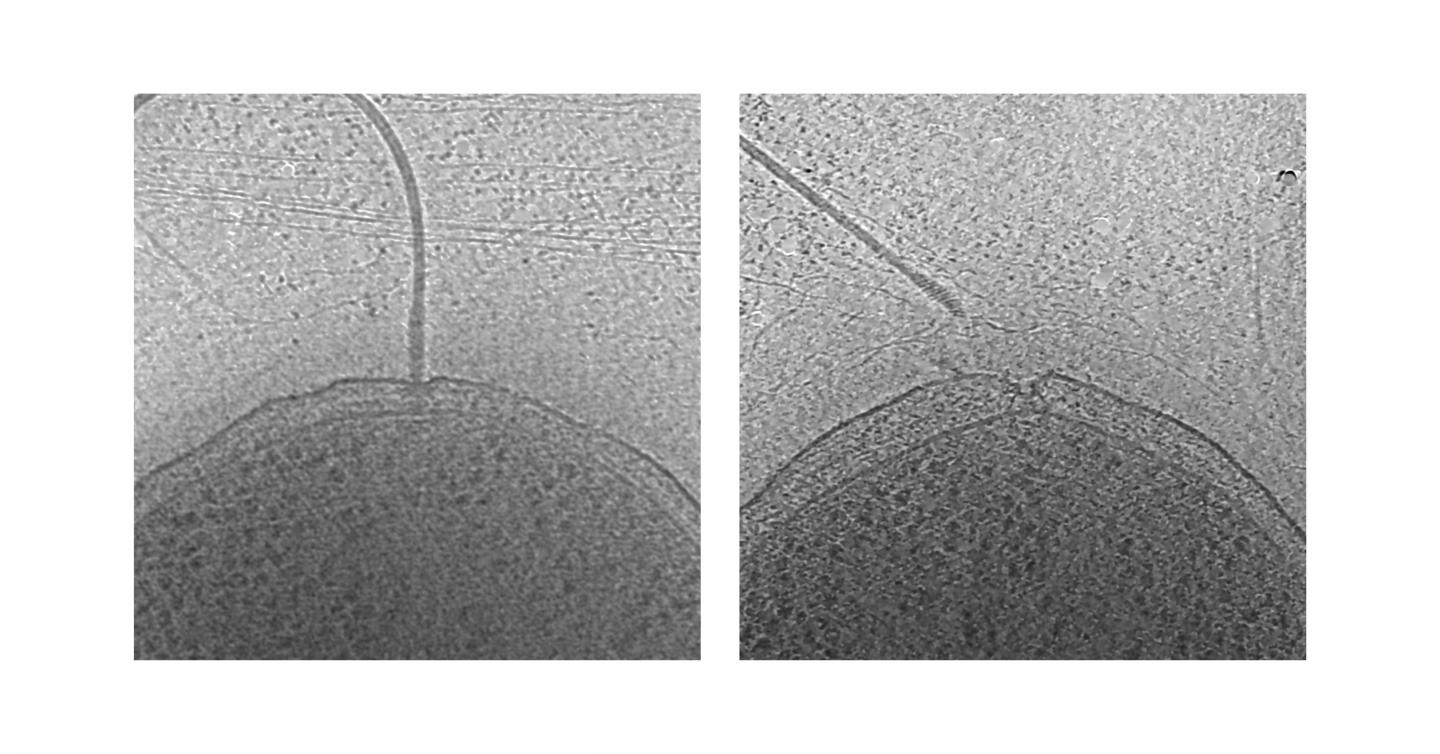
The authors of the new study used electron microscopy to get a 3-D look at Gammaproteobacteria that have one or more flagella clustered at one end of each cell. Focusing on two species, Plesiomonas shigelloides and Vibrio fischeri, they saw that microbes living in a nutrient-abundant environment had few partial flagella, but microbes in nutrient-depleted conditions had many more partial flagellar structures.
Further experiments confirmed that these partial structures were relics of flagella that had been ejected, and that a nutrient-depleted environment was indeed the trigger. So, like mountaineer Aron Ralston cutting off his own arm to avoid certain death in the film 127 Hours, bacteria cut off their own tails to avoid starvation.
Flagella are driven by tiny motors embedded in the cell membrane, so ejecting the flagella runs the risk of leaving empty motors with wide-open portals that would allow spillage of the insides of the cell into the environment. Intriguingly, the researchers found that an unidentified protein plugs up the relics of flagellar motors, and they hypothesize that this plug prevents leakage of cellular contents through the resulting hole in the cell membrane.
In the future, additional research could clarify the molecular details of the ejection process, including the identity of the plug protein.
###
Peer-reviewed / Experimental Study / Cells
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Biology: http://journals.
Citation: Ferreira JL, Gao FZ, Rossmann FM, Nans A, Brenzinger S, Hosseini R, et al. (2019) γ-proteobacteria eject their polar flagella under nutrient depletion, retaining flagellar motor relic structures. PLoS Biol 17(3): e3000165. https:/
Funding: This work was supported by a Medical Research Council grant MR/P019374/1 to MB, a Medical Research Council PhD Doctoral Training Partnership award grant number MR/K501281/1 to JLF, a Research fellowship of the German Research Foundation (DFG project number 385257318) to FMR, Grant TRR174 “Prokaryotic Cell Biology” from German Research Foundation (DFG) to KMT, Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO) BBOL.737.016.004 to AB, a German Academy of Sciences Leopoldina (Fellowship Programme LPDS 2017-01) to SB, and NIH (AM, grants R01-GM051350 and R35-GM118108) to PBR. PBR is also supported by the Francis Crick Institute, which receives its core funding from Cancer Research UK (FC001143), the UK Medical Research Council (FC001143), and the Wellcome Trust (FC001143). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Media Contact
Morgan Beeby
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




