Credit: QI Lei
The gut microbiome has been shown to have diverse impacts on human and animal physiology and health.
Now, a research group led by Prof. John R. Speakman from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has revealed the important role of gut microbiota in thermoregulation – the way animals respond to cold exposure.
During cold exposure it is well established that animals sustain their body temperature by activating heat production from a specialized tissue known as Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT) and promoting “browning” of white adipose tissue.
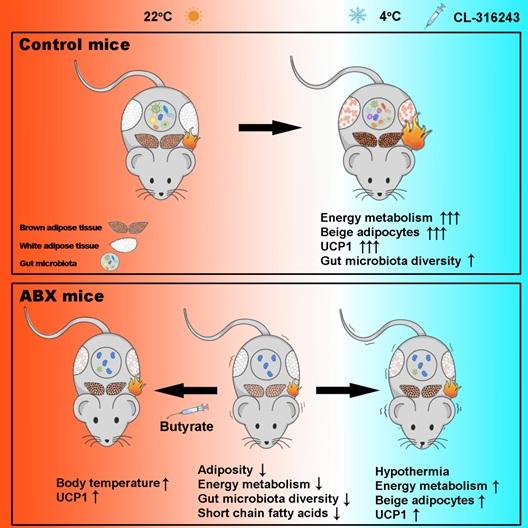
To evaluate the function of gut microbiota in the activation of BAT, researchers used different antibiotic recipes to eradicate gut microbiota. They subsequently found that animals lacking gut microbiota had impaired thermoregulation.
The results were also confirmed in germ-free mice. Specifically, the researchers found that removal of the gut microbiota blunted the increase in the expression of uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) in BAT and reduced white adipose tissue browning.
This effect could be because, in the absence of an intact microbiome, the animal is unable to digest sufficient quantities of food to meet elevated energy demands in the cold, and the impact on BAT is a secondary effect.
However, the team also showed that gavage of the bacterial metabolite butyrate increased the thermogenic capacity of ABX-treated mice, reversing the deficit. This suggests that microbiota plays an important signaling role in the process that stimulates cold-induced thermogenesis.
This research adds to the expanding areas of physiology and health that are impacted by the gut microbiome. Although the work was conducted in mice, and extensions to humans must be made cautiously, it may have several health implications.
In particular, elderly people have many problems raising an adequate thermoregulation response to the cold, which makes them susceptible to hypothermia. It will be interesting to discover if known changes in the human microbiome with age contribute to this effect, and if modulating the age-related changes in the microbiome will afford elderly people more protection.
This study was published in Cell Reports on March 5, and was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Natural Science Foundation of China.
###
Media Contact
QI Lei
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




