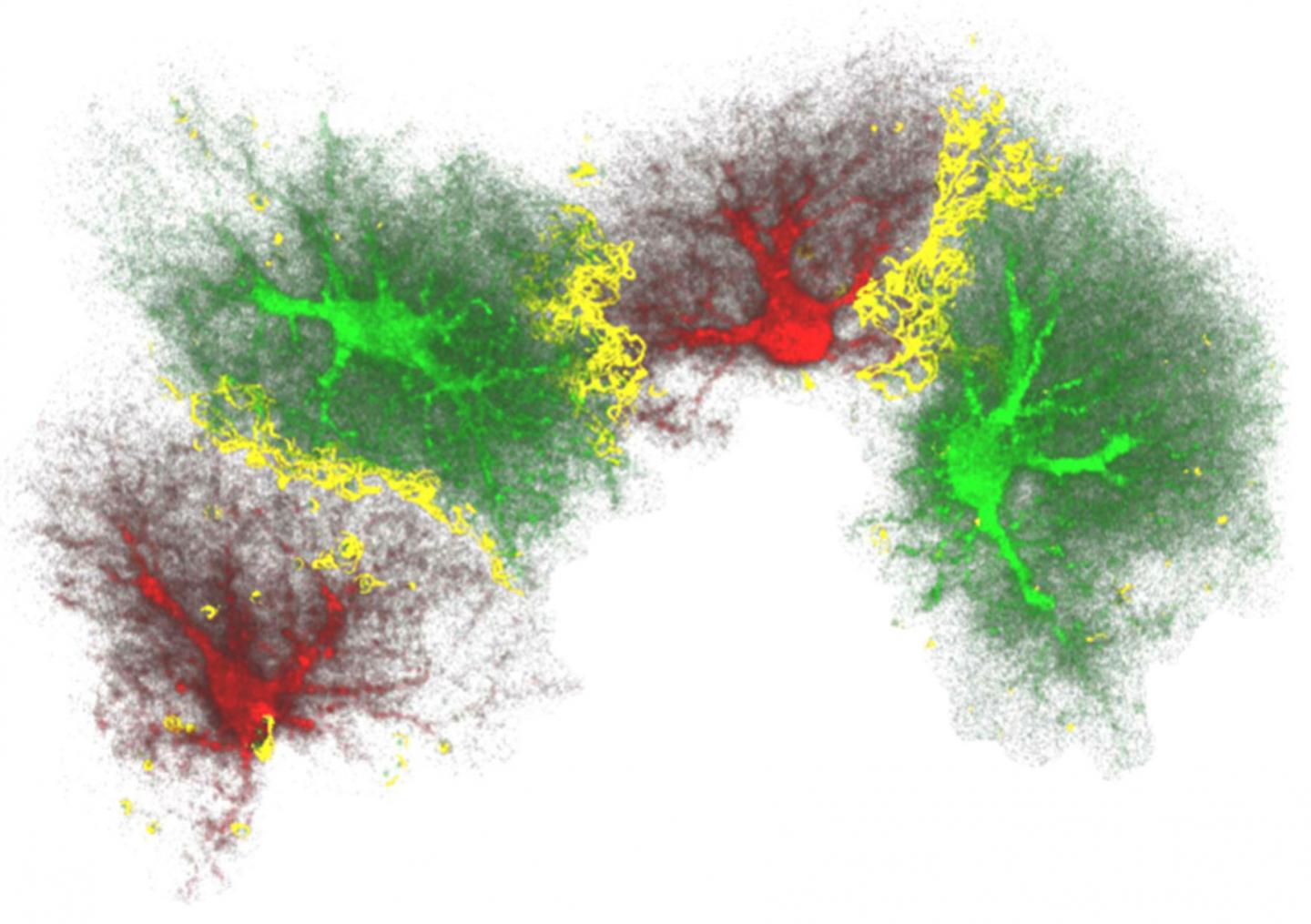
Credit: Milos Pekny and Marcela Pekna, Physiological Reviews, 2014.
Researchers at Sahlgrenska Academy at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, in collaboration with research groups in Finland, Canada, and Slovenia, have discovered a novel and unexpected function of nestin, the best known marker of neural stem cells.
In the developing brain, the 3 main cell types, specifically neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes, are generated from neural stem cells. In some parts of the brain, such as the hippocampus, the brain region involved in learning and memory, new neurons are being added to the existing neuronal circuitry even in the adulthood when severe restriction of neuronal differentiation occurs.
Using mice deficient in nestin, a protein that is a component of the part of the cytoskeleton known as intermediate filaments or nanofilaments, the research team led by Prof. Milos Pekny showed that nestin produced in astrocytes has an important role in inhibiting neuronal differentiation. They linked this regulatory function of nestin to the Notch signaling from astrocytes to neighboring neural stem cells. Thus, surprisingly, nestin does not control the generation of neurons by acting within neural stem cells, but indirectly by regulating the neurogenesis-inhibitory Notch signals that neural stem cells receive from astrocytes, important constituents of the neurogenic niche.
Generation and functional integration of new neurons in the adult mammalian hippocampus can lead to the reorganization of the neuronal circuitry, triggering 2 opposing effects: a better formation of new memories and a more pronounced loss of previously acquired memories. And indeed, adult mice lacking nestin have both increased number of newly born neurons in the hippocampus and impaired long-term memory.
Intermediate filament proteins, or nanofilament proteins as they are sometimes called, are important stress proteins that in many cell types act as crisis command centers in times of cellular stress and emerge as interesting targets in many diseases – says Milos Pekny. They are also linked to the control of cell differentiation and in the brain or spinal cord their regulation might be a new approach for improving brain plasticity and regeneration responses in situations such as stroke, neurotrauma or neurodegenerative diseases.
Our study adds to the list of important functions of astrocytes in the central nervous system, the cells that we increasingly view as the brain of the brain, a system that controls many processes in healthy and diseased brain – explains Ulrika Wilhelmsson.
###
Title: Nestin Regulates Neurogenesis in Mice through Notch Signaling from Astrocytes to Neural Stem Cells; https:/
Contact:
Ulrika Wilhelmsson +46 (0) 765 80 53 80; [email protected]
Milos Pekny +46 (0) 709 13 48 65; [email protected]
Images: The brain is largely divided between domains of astrocytes, cells profoundly affecting regeneration and functional recovery after stroke or neurotrauma (Milos Pekny and Marcela Pekna, Physiological Reviews, 2014). The picture shows astrocytes in red and green, the areas where individual astrocytes interconnect are yellow. A single human astrocyte can access as many as millions of neuronal synapses. Astrocytes emerge as a treatment target in stroke, neurotrauma or neurodegenerative diseases. Portrait images of Ulrika Wilhelmsson (selfie) and Milos Pekny (photo: Y. Pekny).
Media Contact
Milos Pekny
[email protected]
46-070-913-4865
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




