A single factor can reset the immune system of mice to a state likely similar to what it was 500 million years ago, when the first vertebrates emerged.
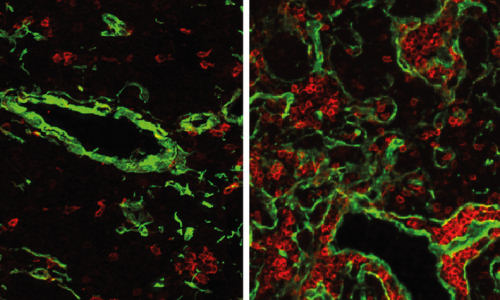
The normal mouse thymus (left) contains only a small fraction of B-cells (red). If the gene FOXN4 is activated, a fish-like thymus with many B-cells develops. This state is likely to have existed about 500 million years ago, at the time when the first vertebrates emerged.
Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics (MPI-IE) in Freiburg re-activated expression of an ancient gene, which is not normally expressed in the mammalian immune system, and found that the animals developed a fish-like thymus. To the researchers surprise, while the mammalian thymus is utilized exclusively for T cell maturation, the reset thymus produced not only T cells, but also served as a maturation site for B cells – a property normally seen only in the thymus of fish. Thus the model could provide an explanation of how the immune system had developed in the course of evolution. The study has been published in Cell Reports.
The adaptive immune response is unique to vertebrates. One of its core organs is the thymus, which exists in all vertebrate species. Epithelial cells in the thymus control the maturation of T-cells, which later fight degenerated or infected body cells. The gene FOXN1 is responsible for the development of such T-cells in the mammalian thymus. Scientists led by Thomas Boehm, director at the MPI-IE and head of the department for developmental immunology, activated the evolutionary ancestor of FOXN1, called FOXN4, in the thymic epithelial cells of mice. FOXN4 is present in all vertebrates, but appears to play only a role in the maturation of immune cells of jawed fish, such as cat sharks and zebra fish.
“The simultanuous expression of FOXN4 and FOXN1 in the mouse led to a thymus that showed properties as in fish,” said first author Jeremy Swann. Together with earlier results this suggests that the development and function of thymic tissue was originally intitiated by FOXN4. Due to an evolutionary gene duplication, which led to FOXN1, transiently both genes, and finally only FOXN1 were active in the thymus.
To the researchers surprise not only T-cells developed in the thymus of the mice, but also B-cells. Mature B-cells are responsible for antibody production. In mammals, they normally do not mature in the thymus, but in other organs, such as the bone marrow.
“Our studies suggest a plausible scenario for the transition of a bipotent lymphopoietic tissue to a lymphoid organ supporting primarily T cell development,” said Boehm. Since B- and T-cell progenitors can not yet be distinguished, it remains unclear whether the B-cell development is based on the migration of dedicated B-cell precursors to the thymus, or to maturation from a shared T/B progenitor in the thymus itself. Comparative studies often suggest that the origin of a particular evolutionary innovation must have occurred in an extinct species. „Here, the re-creation and functional analysis of presumed ancestral stages could provide essential insights into the course of such developments,” explained Boehm the study approach.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by Virginia Bioinformatics Institute.