Credit: Washington State University
PULLMAN, Wash. – A Washington State University research team has improved an important catalytic reaction commonly used in the oil and gas industries. The innovation could lead to dramatic energy savings and reduced pollution.
They report on their work in the German journal Angewandte Chemie, which has designated the paper of particular interest and importance. The research is led by Jean-Sabin McEwen, assistant professor, and Su Ha, associate professor, of the Gene and Linda Voiland School of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering at WSU.
Efficiently converting methane
Methane gas is a byproduct in much of the oil and gas industry, where it may build up during operations and cause a safety concern.
Methane also is a primary ingredient in natural gas used to heat homes, and it can be converted into many useful products including electricity. But breaking the strong bond between its carbon and hydrogen takes a tremendous amount of energy.
"It's a very happy molecule," said McEwen. "It does not want to break apart."
To convert methane, the oil and gas industry most often uses a nickel-based catalyst. But it is often less expensive to simply burn the methane in giant flares on site; however, this adds greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, contributing to global warming, and wastes energy. In the U.S., for example, the amount of methane burned annually is as much as 25 percent of the country's natural gas consumption.
"Right now, we just waste all those gases," said Ha. "If we can efficiently and effectively convert methane from shale or gas fields to electric power or useful products, that would be very positive."
Nickel carbide an effective catalyst
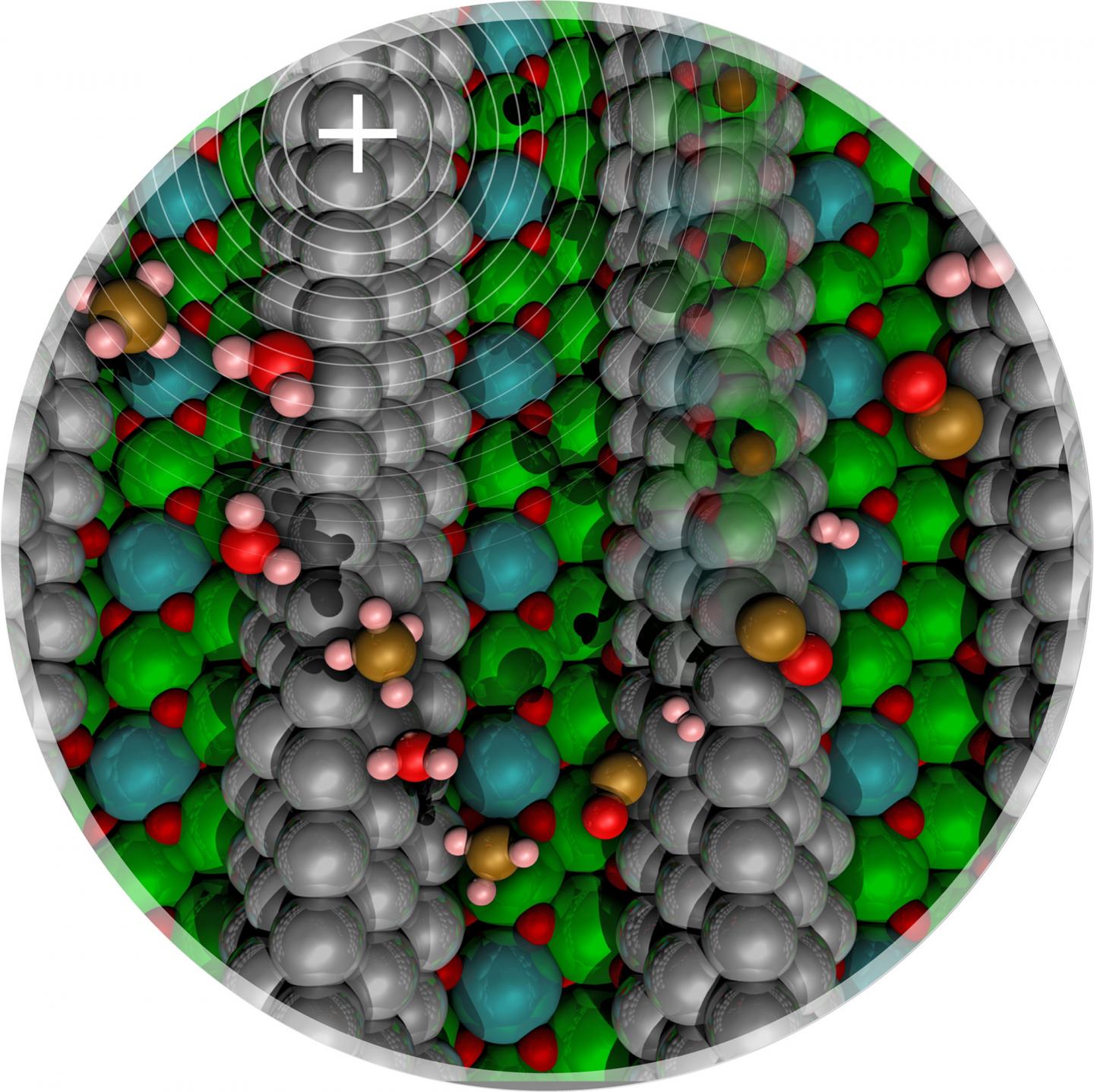
The researchers determined that they can dramatically reduce the energy needed to break the bond between carbon and hydrogen by adding a tiny bit of carbon within the nickel-based catalyst. This creates nickel carbide, which generates a positive electrical field. This novel catalyst weakens the methane molecule's hydrogen-carbon bond, allowing it to break at much lower temperatures.
The researchers found that while too much carbon in the catalyst kills the reaction, a very low concentration actually enhances it. They have built a numerical model of the reaction and are working to show the work experimentally.
"It's exciting to be conducting research in which experimentalists and computational researchers are working side by side to advance the field," said Ha. "This needs to be done more often in the sciences for the development of these breakthrough technologies."
###
Media Contact
Jean-Sabin McEwen
[email protected]
509-335-8580
@WSUNews
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag