Ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) is the world’s leading environmental health risk factor. At only 2.5 micrometers or smaller, these particles are small enough to be inhaled and cause respiratory problems, such as asthma and bronchitis, and cardiovascular issues, including heart attacks and high blood pressure. For children, PM2.5 can cause lifelong developmental issues, and for the general population, PM2.5 is associated with premature death.
Credit: Martin lab, Washington University in St. Louis
Ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) is the world’s leading environmental health risk factor. At only 2.5 micrometers or smaller, these particles are small enough to be inhaled and cause respiratory problems, such as asthma and bronchitis, and cardiovascular issues, including heart attacks and high blood pressure. For children, PM2.5 can cause lifelong developmental issues, and for the general population, PM2.5 is associated with premature death.
To ameliorate these wide-ranging negative impacts resulting from exposure to PM2.5, which is produced largely through traditional energy sources such as burning fossil fuels or wood, several countries have taken steps to reduce exposure to PM2.5. But how effective have these mitigation efforts been, and what region or regions are most responsible for driving global PM2.5 reduction?
Researchers working with Randall Martin, the Raymond R. Tucker Distinguished Professor in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, examined PM2.5 data from 1998-2019 to find out.
“The importance of PM2.5 as a leading risk factor for human health motivates assessment of its long-term changes,” Martin said. “We sought to analyze our satellite-derived PM2.5 estimates for insight into global and regional changes in PM2.5 exposure and its health effects.”
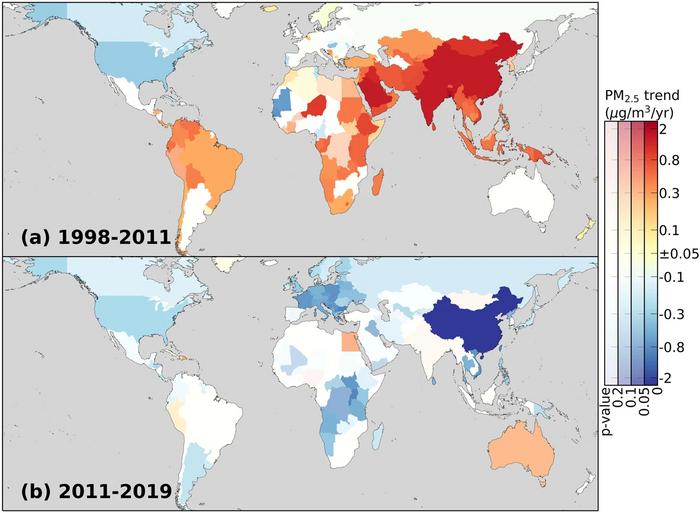
The team’s analysis, published Sept. 2 in Nature Communications, showed that global, population-weighted PM2.5 exposure, related to both pollution levels and population size, increased from 1998 to a peak in 2011, then decreased steadily from 2011 to 2019, largely driven by exposure reduction in China and slower growth in other regions.
“Before this work, there was a knowledge gap regarding quantitative local/regional contributions to global population exposure to PM2.5 and its changes,” said Chi Li, first author on the study and a staff scientist in Martin’s research group. “We developed a new regional decomposition approach that jointly considered pollution level and population size, and from that we depicted the first-ever time series of regional contributions to global PM2.5 air pollution.”
Li found that many regions exhibited decreasing exposure since 2011, including continuous reductions in North America and western Europe. He described recent emerging decreases in China as particularly striking.
“Rigorous air quality management in China, which has been most pronounced since 2013, turned out to be the biggest contributor to this global reversal,” Li said. “More than 90% of the reduction of global mean exposure from 2011 to 2019 is from China, according to our regional attribution. This result was astonishing when it was derived, but it could be explained well by the rapid reduction of PM2.5 concentrations due to China’s mitigation efforts, which benefit nearly one-fifth of the global population.”
Benefits from PM2.5 exposure reduction include 1.1 million fewer premature deaths in China alone between 2011 and 2019, as well as improved health more generally. Future interventions to reduce PM2.5 exposure will have even greater impacts for an aging and growing global population, Li said.
“By combining PM2.5 data with health data and exposure-response models, we also revealed that, despite the recent sustained reduction of global PM2.5 pollution, population aging and growth are now the main challenges in alleviating PM2.5 health impacts,” Li said. “Reducing the same amount of PM2.5 now will have stronger health benefits than it would have 20 years ago, a globally prevalent phenomenon highlighted in our study.”
The team calculated that in 2019, there were still millions of premature deaths worldwide that could be attributed to PM2.5, highlighting the urgent need for continued reduction to PM2.5 exposure. Careful monitoring, especially in regions that are currently poorly monitored but highly populated, including South Asia and the Middle East, will be critical to ongoing improvements in air quality and to evaluate the effectiveness of mitigation efforts, Martin said.
“There is need to continue to sustain and develop global monitoring capabilities for PM2.5 both from satellite, but also from ground-based measurements,” Martin said. “The successes in PM2.5 reductions serve to demonstrate the benefits of PM2.5 mitigation efforts, and to motivate further mitigation.”
Li C, van Donkelaar V, Hammer MS, McDuffie EE, Burnett RT, Spadaro JV, Chatterjee D, Cohen AJ, Apte JS, Southerland VA, Anenberg SC, Brauer M, Martin RV. Reversal of trends in global fine particulate matter air pollution. Nature Communications, Sept. 2, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41086-z
This work was supported by NASA (80NSSC21K0508, 80NSSC22K0200, and 80NSSC21K0511). All data and codes used for analyses and visualizations in this work are available at 10.5281/zenodo.7618789 along with detailed supporting documentation.
Originally published on the McKelvey School of Engineering website.
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-023-41086-z
Article Title
Reversal of trends in global fine particulate matter air pollution
Article Publication Date
2-Sep-2023




