Winter is coming to an end; the last nights of below zero temperatures are here. In the morning, one still spots the occasional icicle on a gutter or car bumper. When you look at these icicles carefully, you may notice that they show a characteristic pattern of ripples – always around one centimetre wide. What causes these ripples? Using an icicle machine of their own design, physicists and chemists from the University of Amsterdam investigated this question, and discovered that salt plays an important part in the formation process of the ripples.
Credit: UvA, Menno Demmenie
Winter is coming to an end; the last nights of below zero temperatures are here. In the morning, one still spots the occasional icicle on a gutter or car bumper. When you look at these icicles carefully, you may notice that they show a characteristic pattern of ripples – always around one centimetre wide. What causes these ripples? Using an icicle machine of their own design, physicists and chemists from the University of Amsterdam investigated this question, and discovered that salt plays an important part in the formation process of the ripples.
The research was carried out by PhD student Menno Demmenie and his colleagues of the Institute of Physics and the Van ’t Hoff Institute for Molecular Sciences at the University of Amsterdam. The results were published in the scientific journal Physical Review Applied last week.
Icicle machine
To carry out the research, Demmenie and his colleagues built an actual icicle machine. ‘In a large freezer with a window, we spent a few weeks becoming true icicle growth specialists’, Demmenie recalls. ‘The difficult question was how fast water must be added to make a nice icicle. If the water flows too quickly, one loses a relatively large amount of water, turning the floor of the freezer into a sheet of ice. On the other hand, if the flow of water is dialed down too much, the icicle tends to grow upward, like a stalagmite. Eventually we discovered that the optimal rate of growth occurs using an inflow of sixty millilitres per hour, at a temperature of -15 °C. This is comparable to a faucet dripping roughly once every three seconds.’
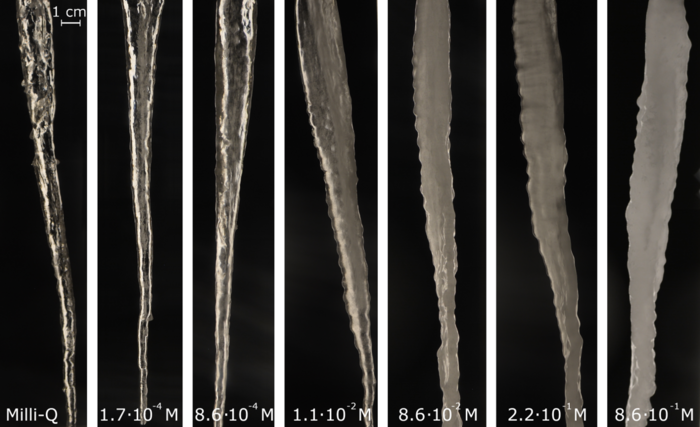
Once the correct inflow of water was found, the researchers could proceed. Using their machine they made many different icicles, under different circumstances and with different types of water. In the end, the crucial factor in the formation of icicle ripples turned out to be the concentration of salt in the water that was used. The image below shows icicles with different concentrations of salt, from an icicle made of extremely pure water (left) to icicles in relatively salty water (right). With the increase of the concentration of salt, the ripples on the icicles became more clearly visible.
The researchers used a clever trick to investigate the role that salt plays in the formation of icicles. When the water forming an icicle freezes, salt molecules get pushed out of the ice as ‘impurities’. As a result, most of the salt is found in a thin layer of liquid water on the outside of the icicle. The scientists added a colouring agent to the water they used, which underwent the same process as the salt molecules. This allowed them to nicely visualize where the liquid salty water was present.
Ripples explained
In this way, it was discovered that the flow of liquid water caused the ripples to appear. Using pure water, the layer of salty liquid water around the icicle was absent, and the formation process looked more like a dripping candle. When saltier water was used, the icicle was surrounded by a thin film of liquid, salty water, and the flow of that water created the regular ripples. The more salt the water contained, the stronger the process, causing thicker ripples to eventually form.
In nature, water always contains a small concentration of salt. This explains the beautiful structures we find on our gutters and car bumpers in the morning – rippled by a thin layer of slightly salty water that was at work throughout the night.
Journal
Physical Review Applied
DOI
10.1103/PhysRevApplied.19.024005
Article Title
Growth and Form of Rippled Icicles




