Credit: Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
LOS ANGELES – The use of acupuncture to treat pain dates back to the earliest recorded history in China. Despite centuries of acupuncture, it's still not clear why this method of applying and stimulating tiny needles at certain points on the body can relieve pain. Recent studies have raised additional questions, with some finding acupuncture reduced chronic pain while others showed that acupuncture has little, if any, impact on pain.
A new study from LA BioMed researchers offers some answers for why acupuncture may help and why clinical trials have produced mixed results. The researchers found the proper use of acupuncture (with the reinforcement method or coupled with heat, which is often used in acupuncture treatments) can lead to elevated levels of nitric oxide in the skin at the "acupoints" where the needles were inserted and manipulated. They noted that nitric oxide increases blood flow and encourages the release of analgesic or sensitizing substances, which causes the skin to feel warmer and contributes to the beneficial effects of the therapies.
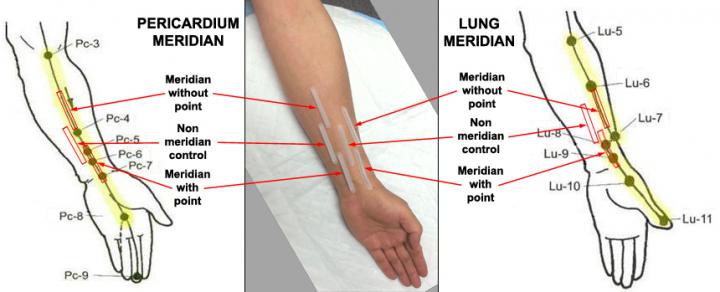
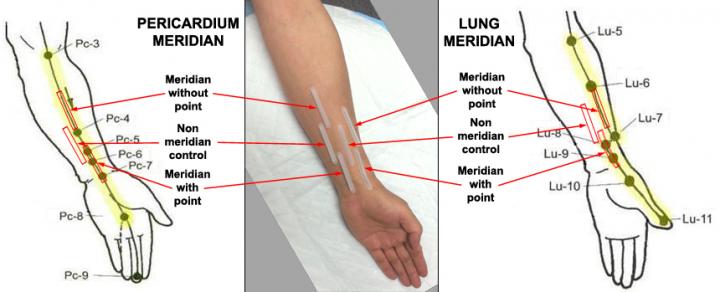
"Our lab has developed a painless, non-invasive biocapture device that can sample human biomolecules over specific skin regions," said Sheng-Xing Ma, MD, PhD, an LA BioMed lead researcher and corresponding author of the study published in Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, Volume 2017. "With this tool, we were able to obtain the first evidence that nitric oxide is released from the human skin surface at a higher level with the proper acupuncture methodology and the use of heat."
Dr. Ma said several acupuncture clinical trials by conventional researchers have produced negative results, finding little difference in pain relief between the use of acupuncture and "sham acupuncture," in which needles are manufactured and/or inserted unsystematically. He said these studies have puzzled the acupuncture community and led many to question whether the proper acupuncture methodologies were used.
For the latest study, the LA BioMed researchers used a low force and rate/reinforcement method of acupuncture. They gently inserted acupuncture needles into the skin of 25 men and women, aged 18-60 years, and delicately twisted the needles for two minutes or until they achieved a sensation of "de qi" (soreness, numbness, distension or pain). They then manipulated the needles using gentle amplitude and moderate speed for two minutes every five minutes for a total of 20 minutes.
They also applied electrical heat for 20 minutes and found elevated levels of nitric oxide at the acupoints. To further validate their findings, they conducted the test with high-frequency and force, which is known as a reduction method, and found nitric oxide levels over the areas of the skin region were reduced.
Dr. Ma said his team will continue to explore the differences in these two acupuncture techniques to determine the effectiveness of each in pain relief and better understand the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved.
"Based on traditional Chinese medicine, acupuncture reinforcement is attained by slowly twisting or rotating the needle with gentle force or by heat," Dr. Ma said. "Reduction is attained by rapidly twisting or rotating the needle with great force. Reinforcement results in local feeling of warmness, but reduction causes a local feeling of coldness."
###
In addition to Dr. Ma, LA BioMed researchers Paul C. Lee, Thomas L. Anderson, Xi-Yan Li and Isabelle Z. Jiang participated in the study. Funding was provided by National Institutes of Health Grant Nos. AT002478, AT004504 and AT004620 from the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine. See the study here: https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4694238
About LA BioMed
Founded in 1952, LA BioMed is one of the country's leading nonprofit independent biomedical research institutes. It has approximately 100 principal researchers conducting studies into improved treatments and therapies for cancer, inherited diseases, infectious diseases, illnesses caused by environmental factors and more. It educates young scientists and provides community services, including prenatal counseling and childhood nutrition programs. LA BioMed is academically affiliated with the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and located on the campus of Harbor-UCLA Medical Center. For more information, please visit http://www.labiomed.org
Media Contact
Laura Mecoy
[email protected]
310-546-5860
@labiomed52
http://www.LABioMed.org
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2017/469423
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag